Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has given approval to the first fully indigenously developed Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine. This vaccine has been developed by Serum Institute of India, Pune.

Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has given approval to the first fully indigenously developed Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine. This vaccine has been developed by Serum Institute of India, Pune.
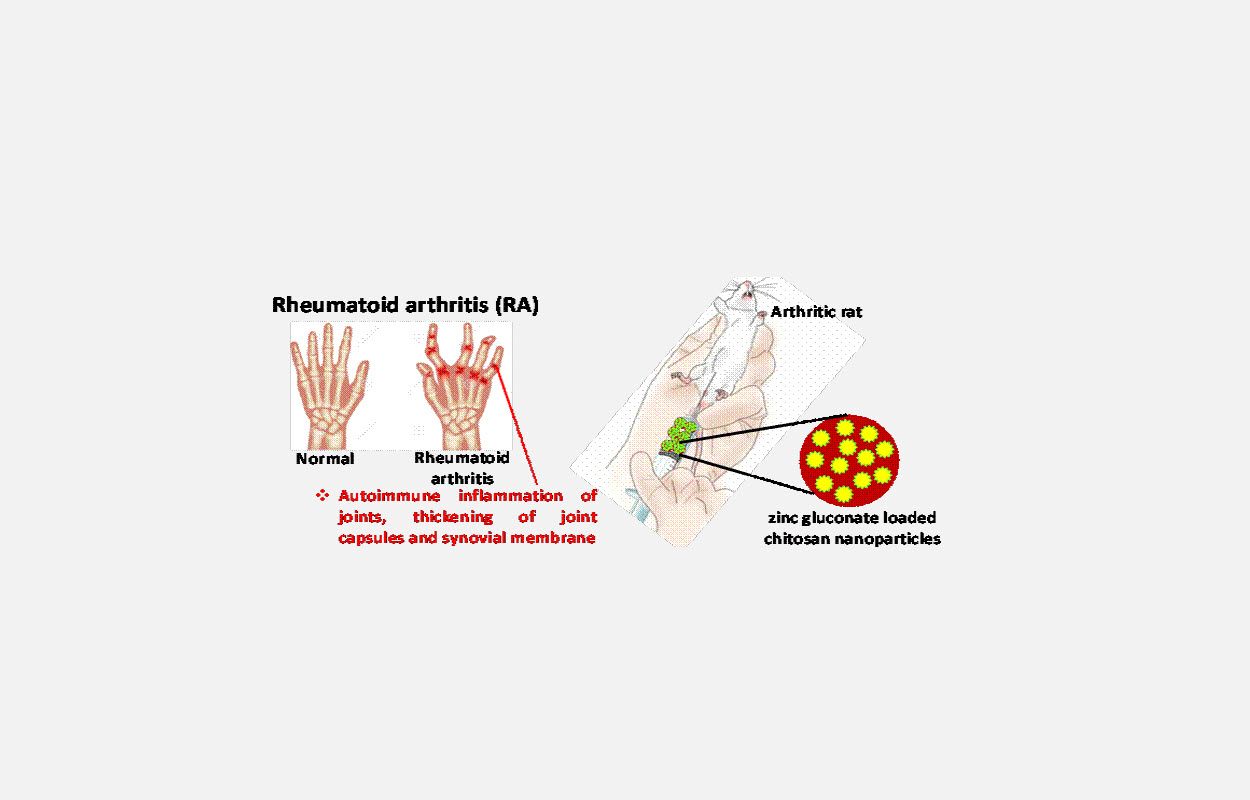
Scientists from the Institute of Nano Science & Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology Government of India, have formulated nanoparticles with chitosan and loaded these nanoparticles with zinc gluconate for reducing the severity of rheumatoid arthritis.
TLeishmaniasis is a neglected tropical disease affecting almost 100 countries including India. It is caused by a parasite called Leishmania, which is transmitted through the bite of sand flies.
A novel formulation of the prostate cancer drug abiraterone acetate - currently marketed as Zytiga - will dramatically improve the quality of life for people suffering from prostate cancer, as pre-clinical trials by the University of South Australia show the new formulation improves the drug's effectiveness by 40 per cent.
Caption : A novel formulation of the prostate cancer drug abiraterone acetate - currently marketed as Zytiga - will dramatically improve the quality of life for people suffering from prostate cancer. Credit : Hayley Schultz/UniSA

New research indicates that taking vitamin D supplements may help prevent a potentially serious side effect of a revolutionary form of anti-cancer therapy. The findings are published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society (ACS).

The Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI), Lucknow, has received permission from Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) for carrying out Phase III clinical trials to test the efficacy, safety and tolerability of the antiviral drug Umifenovir. The Phase III activities will be carried out at King George's Medical University (KGMU), Dr Ram Manohar Lohia Institute of Medical Sciences (RMLIMS) and ERA's Lucknow Medical College and Hospital, Lucknow.
In the darkest parts of the world where light fails to block out the unfathomable bounty of the stars, look up. There are still fewer specks illuminating the universe than there are bacteria in the world, hidden from sight, a whole universe inside just one human gut.

New modelling research, published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases journal, suggests the coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that causes COVID-19 may spread more easily among people living together and family members than severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) or Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). The estimates are the first of their kind to quantify symptomless transmission.
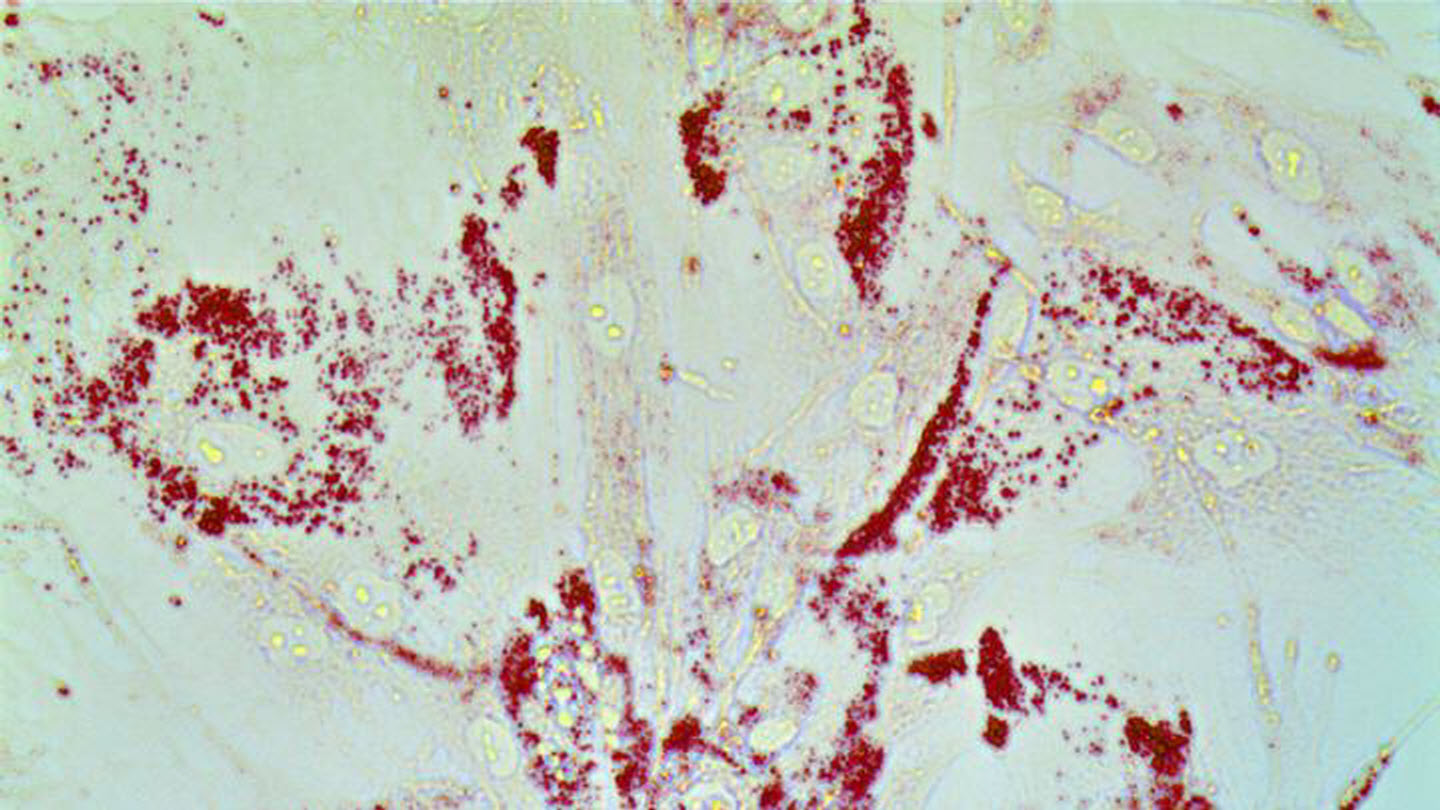
Caption : Cancer cells gobble up lipids. Prostate cells are stained with Oil-Red O to detect lipid droplets. Our work shows that redistribution of lipids from prostate cancer microenvironment triggers inflammation and drives prostate cancer metastasis. Credit : Nick (Jin-Yih) Low
Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center researchers from the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular Radiation Sciences identified a lipid-regulating protein that conveys what the researchers describe as "superpowers" onto prostate cancer cells, causing them to aggressively spread.