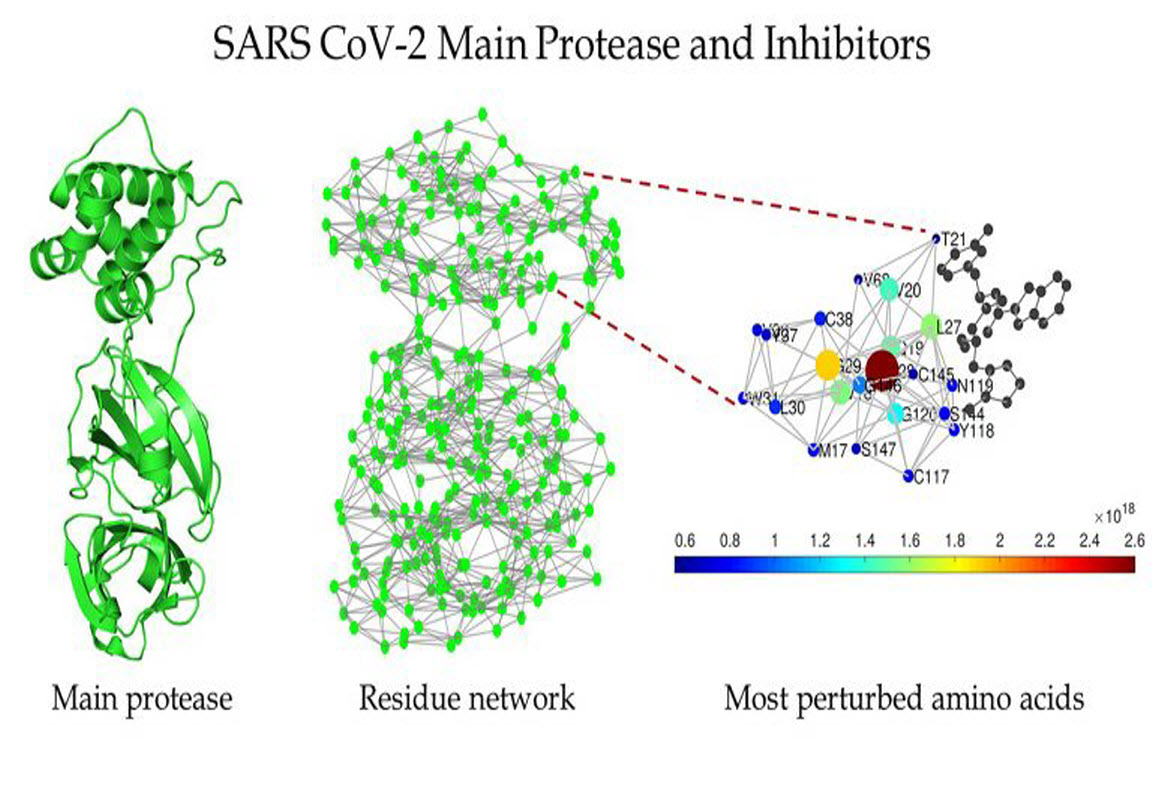
Schematic of the main protease of SARS CoV-2 (left), the protein residue network of the main protease of SARS CoV-2 (center), and a zoomed-in view of the region around the binding site as detected by Estrada (right). CREDIT: Ernesto Estrada
As the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 continues to spread around the world, many researchers are studying epidemiological models to predict its propagation.