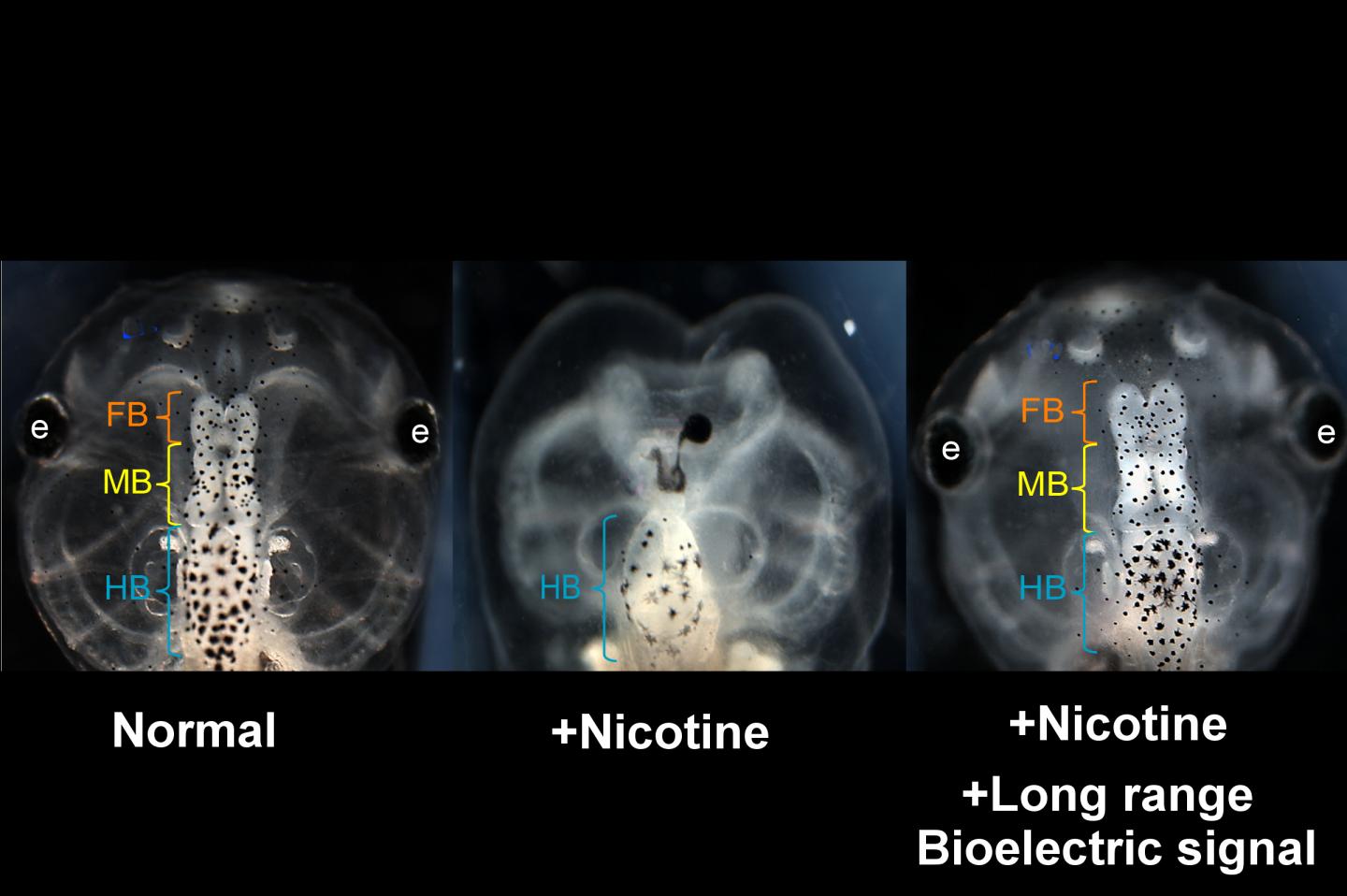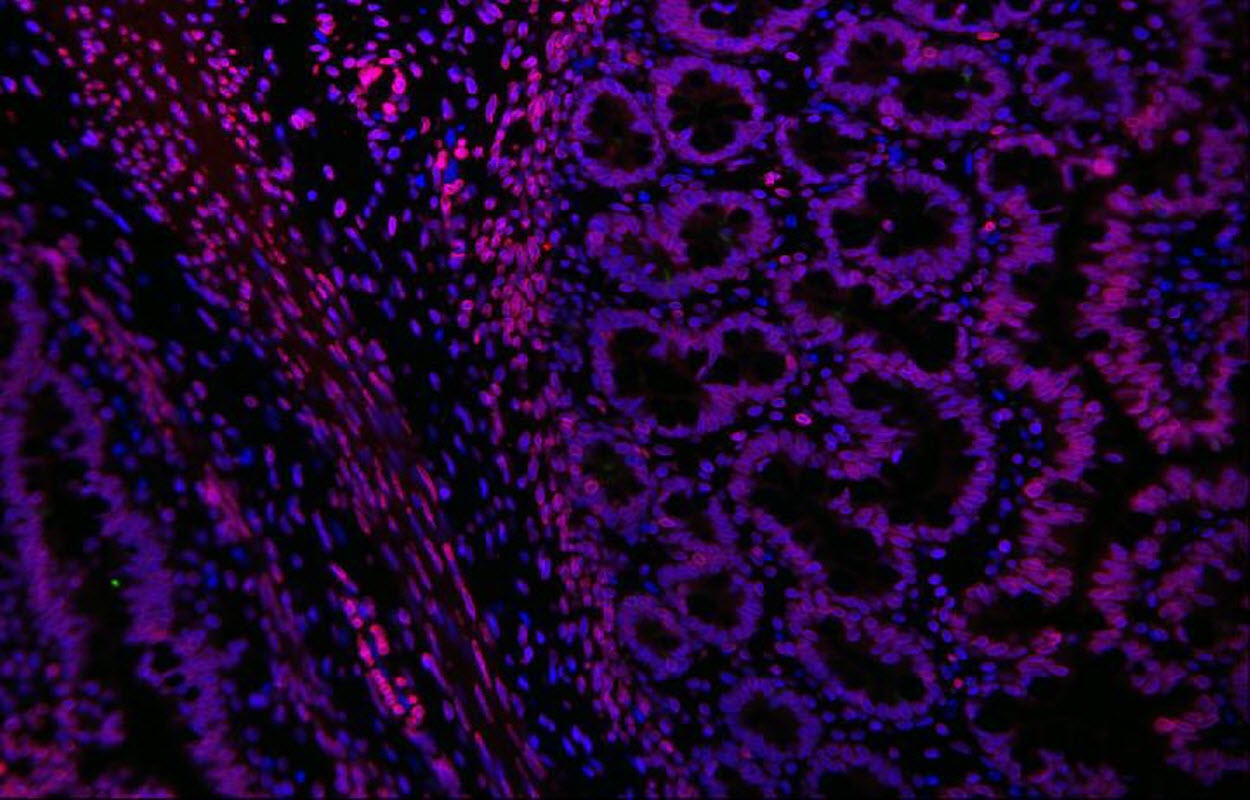
Caption : Human intestine, engineered in the laboratory of Tracy Grikscheit, MD.
Babies with Hirschsprung's disease are born with an incomplete or absent gut nervous system. Children's Hospital Los Angeles investigator Tracy Grikscheit, MD, runs a laboratory that investigates the therapeutic potential of tissue engineering - the induced growth of healthy tissue using stem cells. In a new study, Dr. Grikscheit successfully grew a fully functional gut nervous system - or ENS - in a pre-clinical model. While not yet available clinically, the finding brings surgeons like Dr. Grikscheit one step closer to helping babies in need.