Types of Vibrations in IR
Simple diatomic molecules have only one bond, which may stretch. In polyatomic molecules, each atom having a three degrees of freedom in three directions which are perpendicular to each other. Thus, a molecule of n atoms has 3n degrees of freedom.
For a linear molecule, two degrees of freedom describe rotation and three degrees describe translation, so the remaining 3n -5 are number of fundamental vibrations. While for a non-linear molecule, three degrees of freedom describe rotation and three degrees describe translation, so the remaining 3n -6 are number of fundamental vibrations.
More complex molecules have more then one bonds and different types of vibrations may occur. Vibrations fall into the two main categories of stretching and bending.
- Stretching vibrations
In this type of vibrations, the bond length is increased or decreased at regular intervals. There are two types of stretching vibrations. Symmetrical stretching and asymmetrical training.
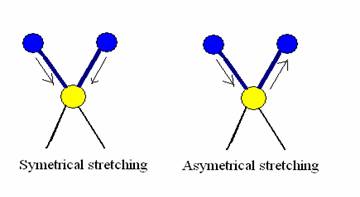
a) Symmetrical stretching- In this type of stretching, bond length increase or decrease symmetrically.
b) Asymmetrical stretching- In this type of stretching, length of one bond increases and the other one decreases.
- Bending vibrations
In this type of vibrations, a change in bond angle occurs between bonds with a common atom, or there is a movement of a group of atoms with respect to the remainder of the molecule without movement of the atoms in the group with respect to one another.
The bending vibrations are also called as deformation vibrations. Deformation vibrations are of two types.
a) In-plane Bending vibrations
b) Out of plane Bending vibrations
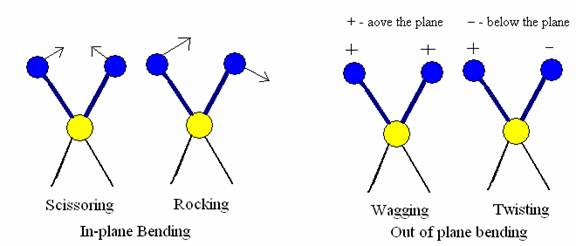
a) In plane bending- In these types of vibrations, there is a change in bond angle. This type of bending takes place within the same plane. In plane bending are of two types.
i. Scissoring in which bond angle decreases
ii. Rocking in which the bond angle is maintained but both bonds moves within the same plane.
b) Out of plane bending- This type of bending takes plane outside of the plan of molecule.
i. Wagging in which both atoms move to one side of the plane
Twisting in which one atom is above the plane and the other is below the plane.









