 About Authors:
About Authors:
Revathy subramani, Anand M., Muralidharan P.
Department of pharmacology,
C.L. Baid metha college of pharmacy,
Thoraipakkam, Chennai 600097,
India
Abstract
Obsessive Compulsive Disorders (OCDs) involve habitual, repetitive behaviors that can be bizarre, disruptive and eventually disabling and it is characterized by intrusive thoughts. Aim of this study is to investigate the methanolic extracts of convolvulus pluricaulis (MECP) action on OCD with animal models by using invivo pharmacological evaluations such as Marble burying behavior, Hole board test, Rota-rod test using mice. These tests are well-accepted paradigm to screen anti-compulsive activity and it also reflects an anxiety-like responses. In this study we used seven groups of mice all the three tests were made on the seven groups. First group serves as control. Second and third groups were treated with 15 mg/Kg and 30 mg/Kg of fluoxetine which is a standard drug and also it is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRIs). Then fourth and fifth groups were treated with 2.5 mg/Kg and 5 mg/Kg of diazepam which is an anxiolytic-sedative drug useful in the symptomatic relief of anxiety and tension states it serves as a negative control. Sixth and seventh groups were treated with 200 mg/Kg and 400 mg/Kg MECP the results show that the MECP can modulate serotonin or dopaminergic levels, which is the major pathway of OCD pathophysiology. Involvement of the serotonergic or dopaminergic receptors for its effect on OCD has been planned based on this study.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1215
Introduction
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is an anxiety disorder and is characterized by the presence of obsessions and compulsions [1]. Obsessions are recurrent and persistent thoughts, impulses or images that are unwanted, and cause extreme distress [2]. An action based on an obsessive thought is called a compulsion Compulsions range from mild checking behavior to severe life threatening cases [3]. OCD was considered a rare disorder, affecting only 0.5% peoples; currently it is believed to affect 2–3% of the total population and 1% children. OCD is one of the 10 leading causes of disability [4], reports WHO. Over 12 million Indians have it in one form or other [5]. Twenty five percentages of American adults experience intense anxiety disorder sometime in their lives. In United States it affects more than 20 million peoples [6]. The plant Convolvulus pluricaulis belongs to family of Convolvulacea. It has branched cylindrical roots. The stem is Slender, cylindrical, about 1–2 mm in thickness [7]. The chemical constituents present in this plant are Microphyllic acid, maltose, Kamepferol, N-hexaconsanol, N-octacosanol, N-triacontanol Shankhpushpine, Ceryl alcohol. It contain Foreign matter 2%, total ash 17%, Acid insoluble ash 8%, Alcohol soluble extractive 6%, water soluble extractive 10%[8]. It is bitter in taste a prime ingredient in following Ayurvedic formulations Abhrak bhasma, agastva haritki and Brahma rasvan used as a mental booster, brain tonic, insomnia, memory loss, anti stress effects [9] and for mental and physical fatigue [10]. Its anti-depressive like effect in mice is comparable with fluoxetine [21]. Studies on this plant showed maximum memory-enhancing activity [11] and Anti-convulsive activity [12].
Materials and methods
Collection of plant material
convolvulus pluricaulis choisy of family Convolvulacea was purchased from Abhirami Botanicals, Tuticorn, Tamilnadu, authenticated by Dr. Chelladurai and a voucher of the specimen is deposited in (Agricultural university, Coiambatore)
Preparation of methanolic extract of C. pluricaulis [13]
A defined quantity of whole plant of C. pluricaulis choisy was weighed and extacted using methanol as solvent in soxhlet apparatus at the temperature of 60 °C. The percentage yield was calculated against 2 kg of powder used. It was 50% (1000 g).
Acute oral toxicity study
Acute oral toxicity studies were made with this extract using OECD 423 guidelines. This method uses defined doses (5, 50, 500, 2000 mg/kg body weight) and the results allow a substance to be ranked and classified according to the Gobally Harmonized System (GHS) for to classify the chemical which cause acute toxicity. The onset and signs of toxicity were noted using 3 female mice observed for 3 days with dose (200 mg/Kg) and the experiment was repeated and no considerable changes was occurred [20].
Preliminary phytochemical analysis [14]
Preliminary phytochemical analyses were done and MECP showed positive results for the following chemicals. Alkaloids, carbohydrates, proteins, sterols, flavonoids, glycosides, gums and mucilages.
Experimental Animals
Colony inbred strains of Swiss albino mice (female) weighing 22–25 g at the age of 5–6 weeks, obtained from C.L. Baid Metha college of pharmacy was used for the pharmacological studies. The animals were kept under standard conditions maintained at 23–25 °C, 12 h light/dark cycle and standard pellet diet (Hindustan lever, Bangalore) provided conditions for a week prior to the experimentation and randomly divided into four groups of each six animals. Principles of animals handling were strictly adhered to and the handling of animals was made under the supervision of animal ethics committee of the institute. The experimental protocol was approved by Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) of Control and supervision of Experiments and Animals (CPCSEA). With reference number NOIAEC/x111/06/CLBMCP/2008-2009 dated: 16.6.2008.
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
Experimental design
On the 1st day of experiment the animals were divided randomly in to seven groups of five animals each. And the drugs were given 30 min before the mice were subjected to the studies.
Group I: Normal control, Vehicle (1% saline)
Group II: Fluoxetine (15 mg/Kg i.p.)
Group III: Fluoxetine (30 mg/Kg i.p.)
Group IV: Diazepam (2.5mg/Kg i.p.)
Group V: Diazepam (5mg/Kg i.p. )
Group VI: MECP (200mg/kg i.p. )
Group VII: MECP (400 mg/Kg. i.p.)
Marble Burying Behavior test [15][16]
The marble-burying test is the most sensitive to the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) class of psychotherapeutics, which is currently used as a drug of choice for OCD hence this test is considered as model for compulsive behavior.
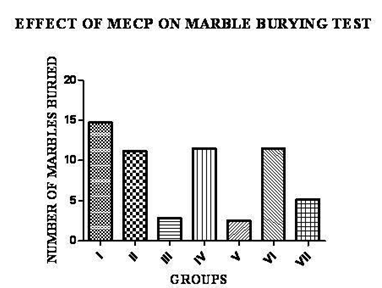
Mice were placed individually in a small mouse-size Plexiglas cage containing bedding that was 5 cm in depth, along with 25 small marbles arranged in six evenly spaced rows of four, with one marble in the middle test was conducted for 30 min and only those that buried at least 12 marbles were used for further testing. And respective drug were given to all the mice in the seven groups and the test was conducted and the values are given in table 1. Marbles were considered to be buried if they were at least one-half covered with bedding.
Rota-Rod [17]
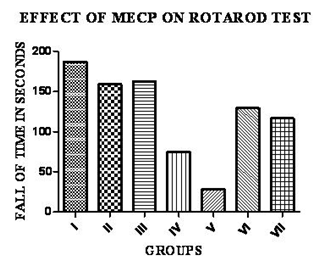
Motor coordination was measured using Rota rod test Mice were placed on a rotating rod with a non-skid surface, and the latency until the mice fell. It was measured for up to 2 min. Rotating speed was 5 rpm and values are shown in table 1.
Hole Board Test [18]
The test is used to determine the motor activity and behavior of animals. Mice were placed in hole-board, which is 40x40 cm with 16 holes and diameter of 3 cm each. The board is also marked with lines of equally distributing the holes of 16 squares. The board is elevated so that the mice poking its nose into the hole do not see the bottom. Nose poking is through to indicate curiosity and is measured by visual observation and the number of line crossing indicates the locomotor activity. This test was conducted for 5 min and the values are shown in table 1.
Table 1. These values show the action of MECP.
|
S.NO. |
Groups |
Number of marbles Buried |
Fall of Time in seconds |
Total beam break in 10 min |
|
1 |
I(control) |
14.71±1.222 |
187.0±5.972 |
406.3±11.01 |
|
2 |
II(Fluoxetine 15 mg/Kg) |
11.17±0.4014a,* |
159.0±4.494a,* |
496.3±8.139a,* |
|
3 |
III(Fluoxetine 30 mg/Kg) |
2.833±0.4014a,** |
162.7±2.333a,** |
531.8±7.842a,** |
|
4 |
IV( Diazepam 2.5mg/Kg) |
11.50±0.5000 |
74.67±3.639 |
303.2±21.75 |
|
5 |
V(Diazepam 5mg/Kg) |
2.500±0.4282 |
28.33±3.667 |
143.0±20.23 |
|
6 |
VI(MECP 200mg/kg) |
11.50±0.5500b,* |
129.3±4.695b,** |
501.3±29.55b,* |
|
7 |
VII(MECP400mg/Kg) |
5.167±0.7491b,** |
116.8±1.701b,* |
489.0±29.43b,* |
The values are expressed as Mean±SEM of 5 animals
Comparison were made between:
a-Group I with Group II,III,IV & V
b-Group IV & V with VI & VII
*P<0.05, **P<0.01
Results and discussions
Effect of MECP on marbles burying
The MECP treated groups show significant tendency to inhibit the marble burying behavior with low dose and high dose. Comparison was made between all the groups. Statistical comparisons were made by one way ANOVA followed by Dunnets multiple comparison Test Graph pad prism software, Inc. Version 4.03. 1992-2005. Shown in Fig. 1. Results show that MECP 200mg/Kg and 400mg/Kg orally showed a significant increase in the number of marbles buried to that of the standard as well as so significant changes are exhibited in the location of the animal as compared to that of the standard.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Effect of MECP on Rota Rod
There is a decrease in the fall of time in negative control group when compared with standard group (P < 0.01) of two groups. The group treated with 200 mg/Kg MECP group 400 mg/Kg treated showed the significance of (p < 0.01) respectively. The values are expressed in graph using above said software shown in Fig. 2. Results show that there is a decrease in the fall of time in negative control (diazepam) when compared with the groups treated with 200 mg/Kg and 400 mg/Kg of MECP.
Effect of MECP on hole board Test
There is no significant decrease in the locomotor activity, which is considered favorable during the treatment of OCD with conventional drugs. Results were shown in Fig. 3.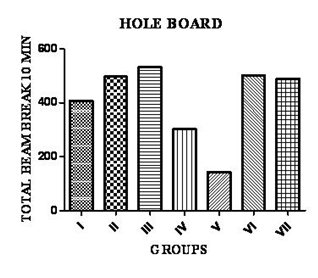
Conclusion
It may be concluded that anti obsessive compulsive disorder of the MECP might be due to decrease in serotonin or dopaminergic levels.
This study confirms that the MECP inhibits marble burying activity without any significant decrease on the locomotor activity which is a favorable criterion in the treatment of OCD. Hence we can hypothesize from this study that receptor ligand binding assay in order to study the involvement of the serotonergic or dopaminergic receptors for its effect on OCD.
References
[1] Goodman wk, price Lh, Rasmussen SA. The yale-brown obsessive compulsive scale. Development use and reliability Arch Gen psychiatry 1989; 46(11):1006-11
[2] Bartz J, Hollander E. Is obsessive-compulsive disorder an anxiety disorder. Neuropsychopharmacol Biol psychiatry 2006; 30: 338-352
[3] Denys D, Van Nieuwerburch F, Deforce D, Wester B. Detail studies on OCD 2006; 446-450.
[4] American psychiatric Association work group on obsessive compulsive disorder Functional imaging studies on ocd. Am J psychiatry 2007; 164:1-56.
[5] Health mental disorder OCD. Indian today 2008; 3:64-67.
[6] American psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental Disorder. 4th Edition, Test Revision (DSM-IV-TR). Washington, DC: American psychiatric Association 2000; 221-132.
[7]Karandikar, G.K, S. satakopan. Shankhpushpi - A pharmacognostic study. Indian j pharm 1959; 21: 200-203
[8]Shukla S.P. Chemical & pharmacological studies on the indigenous drug, Sankhapuspi (Convolvulus Pluricaulis). J. Res. Ind. Med., Yoga & Homoeo 1979; 14: 133-134
[9] Barar FS, Sharma VN. Preliminary pharmacological studies on Convolvulus pluricaulics chois – an Indian indigenous herb. Indian J Physiol Pharmacaol 2007; 8: 56-62
[10] Convolvulus pluricaulics Wickepedia the free encyclopedia.
[11] Dhingra and Valecha. Shankhpushpi. An effective antidepressant, Some pharmacological actions of Convolvulus pluricaulics choosy. pharmacology online 2007; 1: 262-278.
[12] Mudgal, V & K.N. Udupa. Anti-convulsive action of shankhpusphi. J. Res. Ind. Med. Yoga & Homoeo. 1977; 12: 127-129
[13] Rakhit S and N.K. Basu. Investigation on convolvulus pluricaulis chois. Part I. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 1958; 20: 239-240
[14] Barar Fs, Sharma VN. Preliminary pharmacological studies on convolvulus pluricaulis chois – an Indian indigenous herb. Indian j physiol pharmacol 2007; 8: 56-62.
[15] Njunge K, Handley SL Evaluation of marble-burying behavior as a model of anxiety pharmacol. biochem. behave. 1991; 38:63-67
[16] Njunge k,SSRI class psychotherapeutics is the choice of OCD U.S. Department of health and human science 1991; 156-162
[17] Egashri VW Motor coordination was measured by Rota rod. Experimental pharmacology 2004; 87-89.
[18] Dunham NW, Miya Ts. A note on simple apparatus for detecting neurological effect deficit in rats and mice. J. Am. Pharmacol 1957; 46:208-209
[19]Virbala C.S., & P.V. Bole. Further Pharmacognostic studies on the drug Shankhapushpi. J. Univ. Bombay. 1960; 29 B: 154-165.
[20]Sharma, V.N., Barar F.S.K., Khanna N.K., Mahawar M.M. Some Pharmacological actions on Convolvulus pluricaulis Chois. An Indian indigenous herb. Indian J. Med. Res. 1965; 53:871-876.
[21] Basu, N.K. and Dandiya P.C. Chemical investigation of convolvulus pluricaulis chois. J.Amer. Pharm. Asso. Sci. Ed., 1948; 37: 27-28
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









