
A recent study by scientists from University of Connecticut has revealed that the Ultra Violet (UV) light, in particular, is associated with decreased disease growth rate relative to other analyzed factors.

A recent study by scientists from University of Connecticut has revealed that the Ultra Violet (UV) light, in particular, is associated with decreased disease growth rate relative to other analyzed factors.
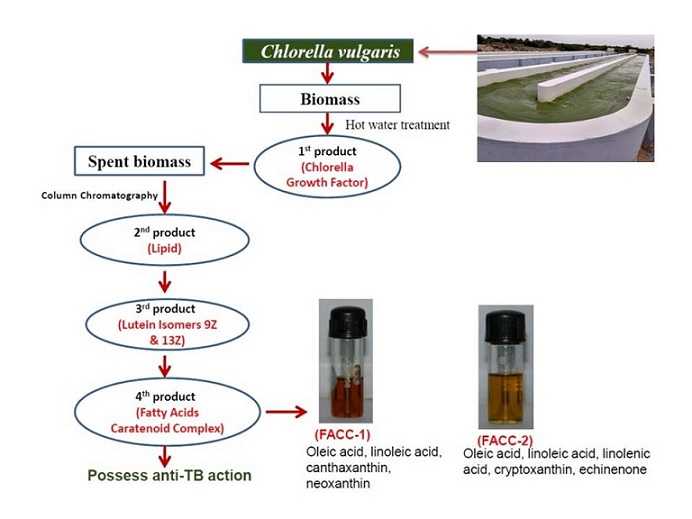
Marine Biotechnology Division of National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) has discovered a potential anti-TB agent to fight against tuberculosis (TB) by successfully isolating the biomolecules of pharmacological importance from a marine microalgae Chlorella vulgaris.
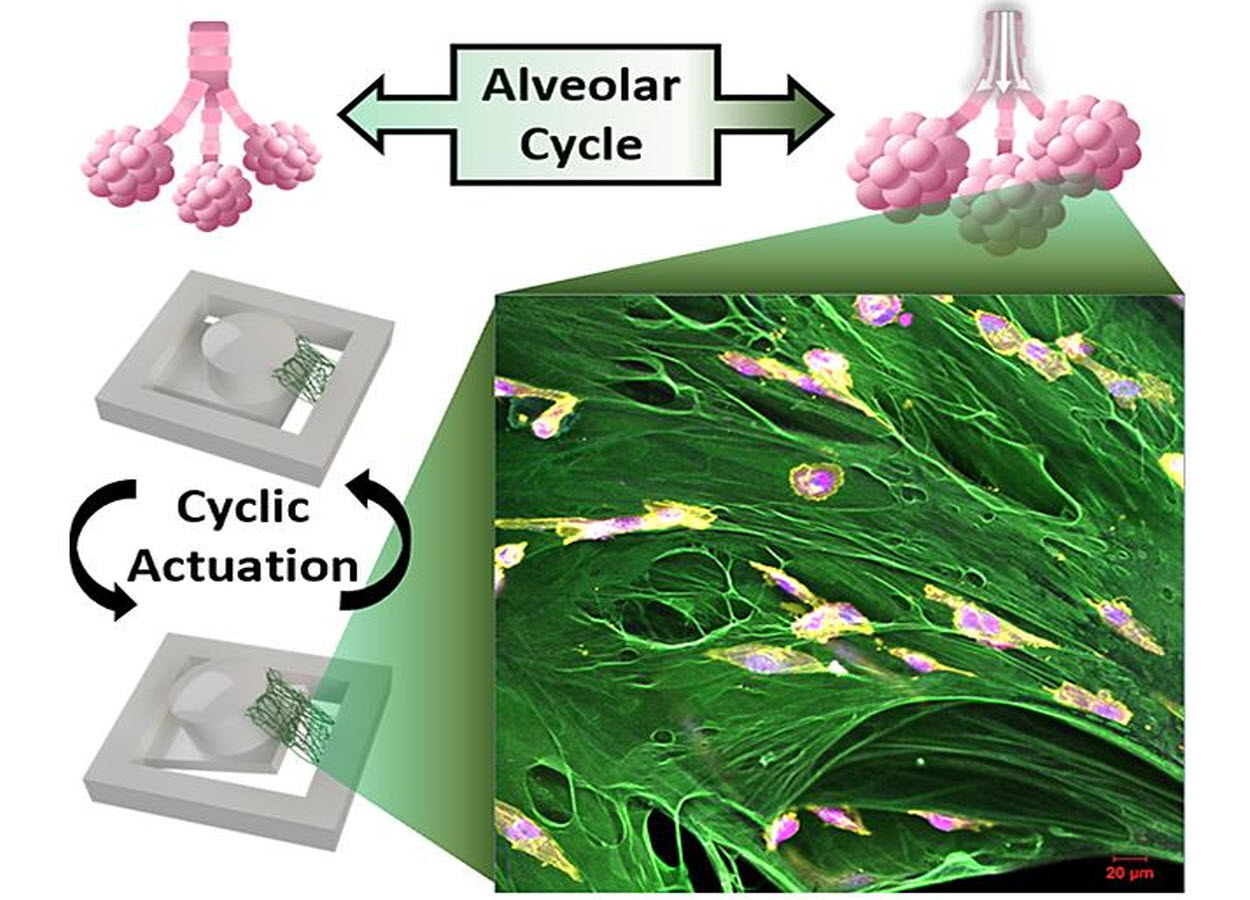
Caption : A Purdue University team has developed a novel testing platform to evaluate how breast cancer cells respond to the recurrent stretching that occurs in the lungs during breathing.
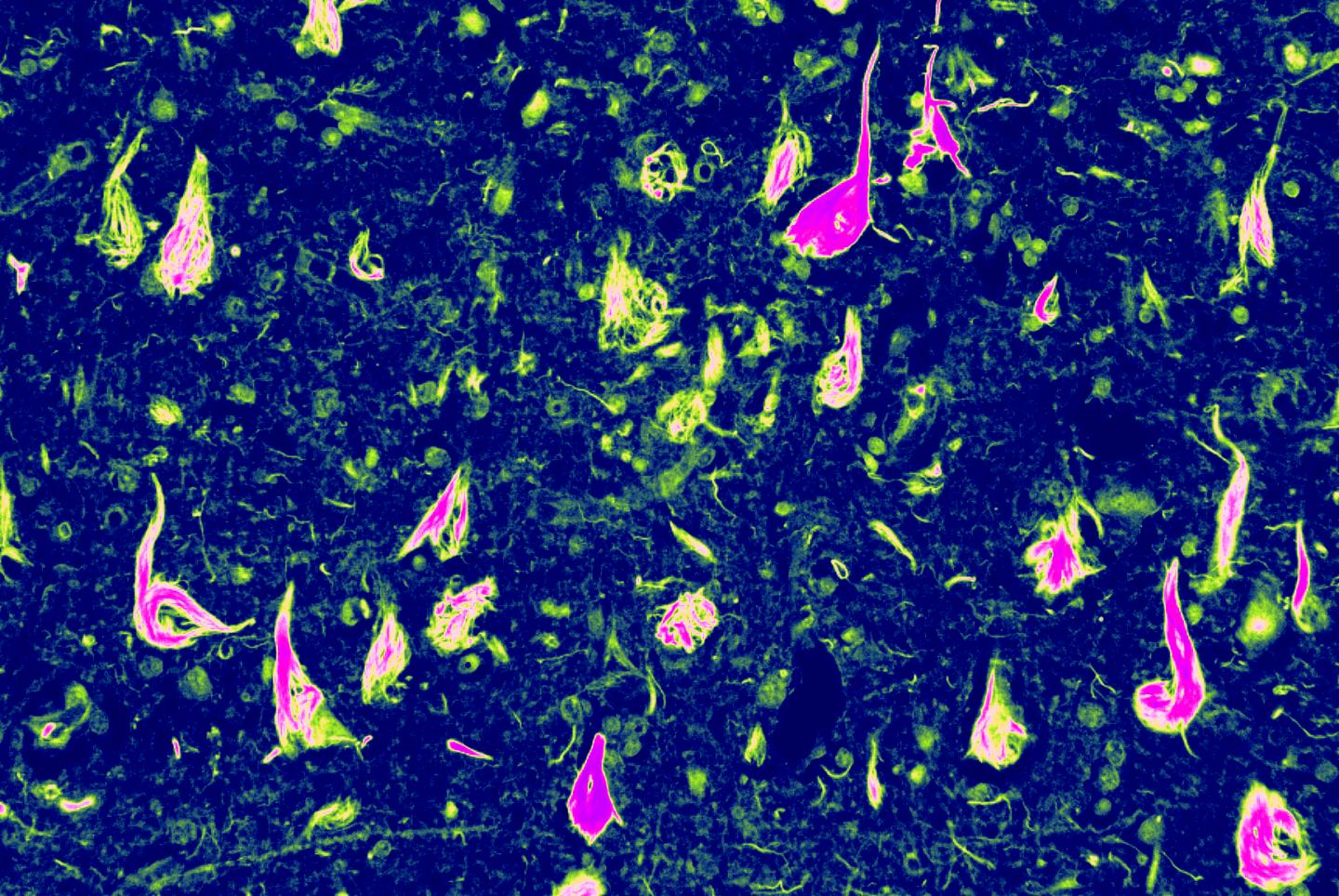
Caption: Abnormal neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) -- a buildup of tau protein in parts of the brain -- helped Edward Lee, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and other Penn Medicine scientists uncover this new form of dementia.
The fight against Typhoid fever is all set to get a major fillip with a team of scientists led by Dr. Amit Kumar from Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)-Indore, finding new ways to tackle Salmonella enterica, the pathogenic bacterium that causes the fever.
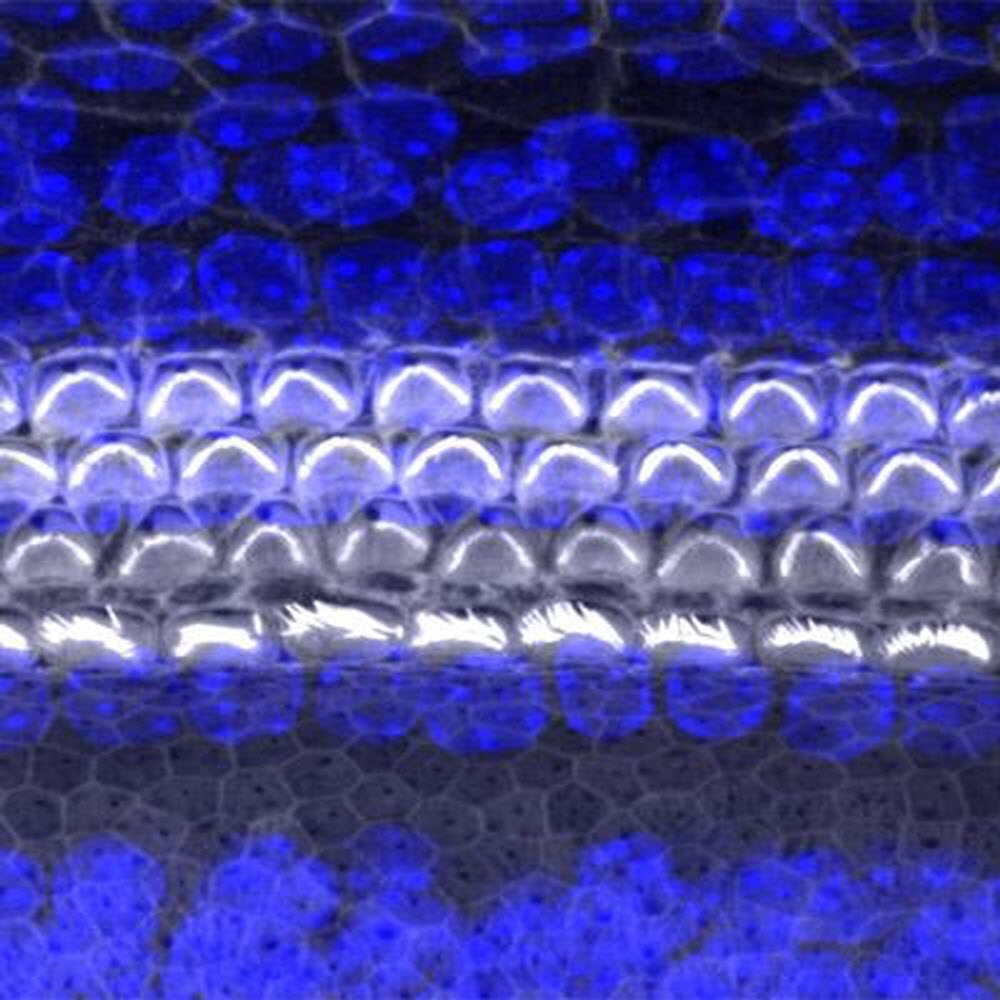
Caption : A surface view of the organ of hearing (cochlea) from a mouse, using confocal microscopy. The sensory cells are named hair cells because of their apical projections (stereocilia) which move from stimulation by sound. Credit : University of Maryland School of Medicine
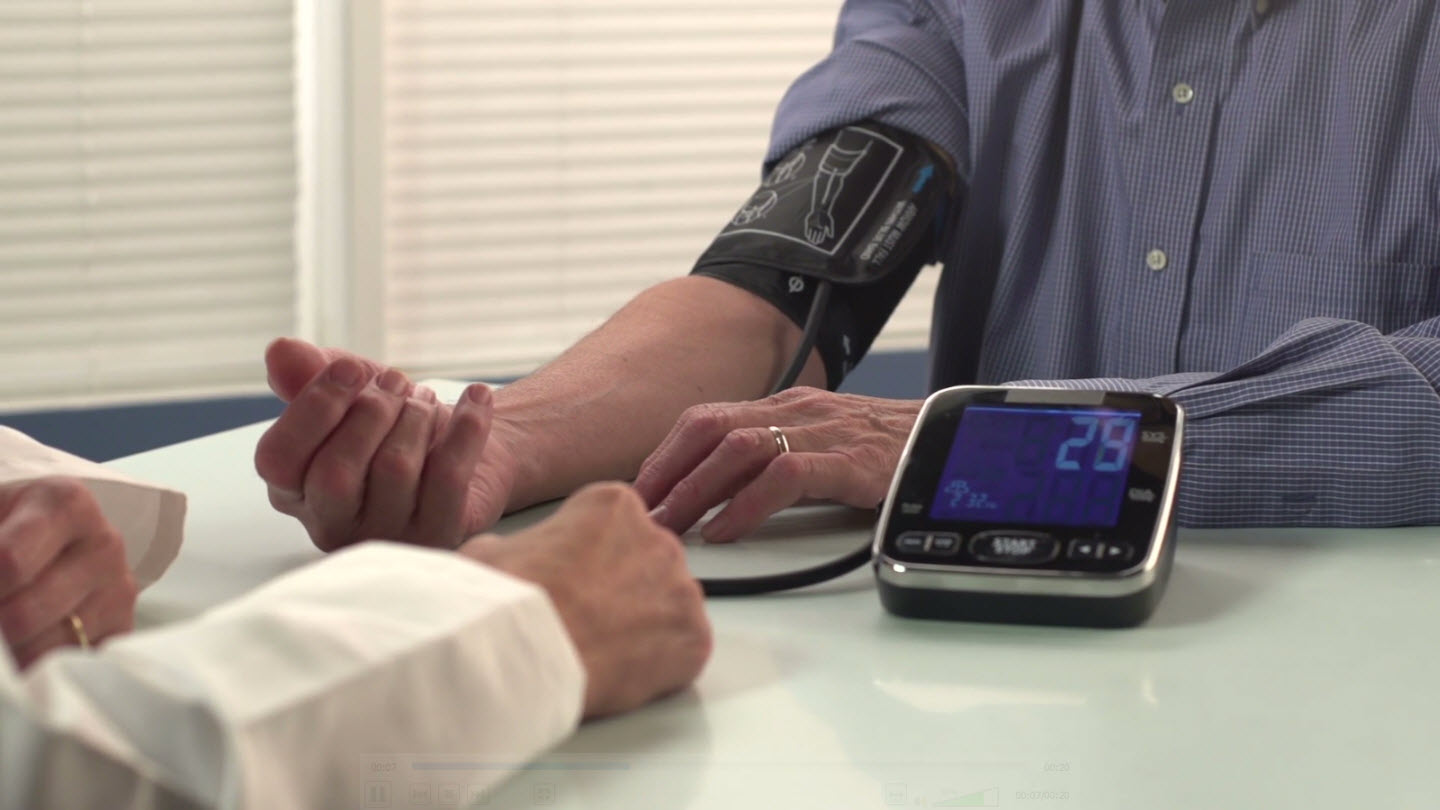

New findings from a large European study of patients in 18 countries, including the UK, show that while many patients are able to reduce their risk through taking statins, those at the highest risk of cardiovascular events may benefit from combinations of lipid-lowering therapies.