Tau protein can be focal point for future drug therapies in Alzheimers
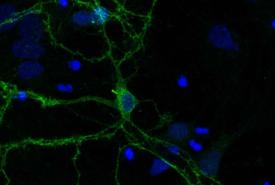
Novel discovery has revealed how the tau protein, a critical element in the formation of Alzheimers disease, is also involved in normal learning processes in the healthy brain, potentially providing a focal point for future drug therapies.
Employing a sensitive method named proximity labelling, the team aimed to identify all proteins that tau comes in contact with within brain cells, labelling and identifying the whole collection of interacting proteins as they went.