Openings in MNF-OSD at Amneal Pharmaceuticals | B.Pharm, BSc


Xu Yu, MD, Ragon Institute group leader, recently published a study entitled “Distinct viral reservoirs in individuals with spontaneous control of HIV-1,” in Nature. Yu’s lab, in collaboration with Ragon group geaders Mathias Lichterfeld, MD, PhD and Mary Carrington, PhD, and Ragon Director, Bruce Walker, MD, found rare sequences of HIV DNA by analyzing billions of cells from 64 elite controllers (people living with HIV who suppress the virus naturally without the need for medication), and 41 individuals on antiretroviral drugs (ART). Unlike ART-treated individuals, elite controllers’ viral reservoirs appear to be incapable of being reactivated. This likely helps the elite controllers maintain spontaneous, drug-free control of HIV and may represent a distinguishing feature for a functional cure of HIV infection.
HIV affects more than 35 million people worldwide and can be effectively controlled, but not cured, with a daily regimen of ART. Upon infection, retroviruses like HIV place copies of their viral genetic material into cells’ genomes, creating viral reservoirs, sanctuaries where HIV persists despite ART, throughout the body. When a complete copy of the virus, or intact viral genome, is incorporated into a cell’s genome, it can be used to create new copies of HIV. For people living with HIV, this means that if they stop taking ART, the intact viral genomes previously integrated into the cells’ genomes start making new copies of the virus, leading to rapid viral rebound and disease progression. The HIV viral reservoir has remained a major obstacle to an HIV cure.
Elite controllers’ immune systems use a T-cell mediated immune response to control the virus without medication, to the point that the virus is completely undetectable by standard assays. Understanding the interplay between their immune system and HIV may hold the key to helping the immune systems of people living with HIV to suppress the virus without daily treatment, achieving what is known as a functional cure
Yu’s group studied the viral reservoir in elite controllers, using next-generation sequencing techniques to precisely map the locations of intact HIV genomes in the human genome. They found that in elite controllers, HIV was often found in locations of the genome that researchers call gene deserts. In these inactive parts of the human genome, human DNA is never turned on, and HIV cannot be effectively expressed but remains in a “blocked and locked” state. This means that HIV is locked in the cell’s genome, and the viral genome is blocked from being used to create more viruses and is therefore incapable of causing disease.
“This positioning of viral genomes in elite controllers,” Yu, says, “is highly atypical, as in the vast majority of people living with HIV-1, HIV is located in the active human genes where viruses can be readily produced.”
When the authors collected cells from elite controllers and infected them with HIV in the lab, they found the virus integrated into active sites in the cell genomes, not in the inactive gene deserts. This suggests that the elite controllers’ unique viral reservoirs may be a result of their HIV-suppressing T cell response eliminating intact viral genomes from active sites.
If researchers are able to identify which viral reservoirs can make new copies of the virus after treatment stops, it may help them to target a treatment against the active, or rebound-competent, reservoirs. This study suggests that if researchers can activate the kind of T cell immunity that is present in elite controllers, they may be able to eliminate rebound-competent viral reservoirs in people living with HIV, achieving a functional cure. The remaining viral DNA, located in non-active parts of the human genome, could be allowed to exist without causing disease.
“NHLBI is interested in understanding how the immune systems of some people living with HIV naturally control their infection without medication,” said Keith Hoots, M.D., director of the Division of Blood Diseases and Resources at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, and a veteran HIV researcher himself. “What happens with these individuals, whom we call elite controllers, may shed light on an HIV-1 cure and also help us understand how a person with HIV might control virus and avoid HIV-associated comorbidities.”
Yu’s group had one more finding: one of their elite controller participants had no intact HIV found in over 1.5 billion cells analyzed. This raises the possibility that a “sterilizing cure” of HIV, in which the participant’s immune system has removed all intact HIV genomes from the body, may be achieved naturally in extremely rare instances.
This project was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Drug Abuse, the National Institutes of Health, the Mark and Lisa Schwartz Family Foundation, the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and the Foundation for AIDS Research (amfAR).
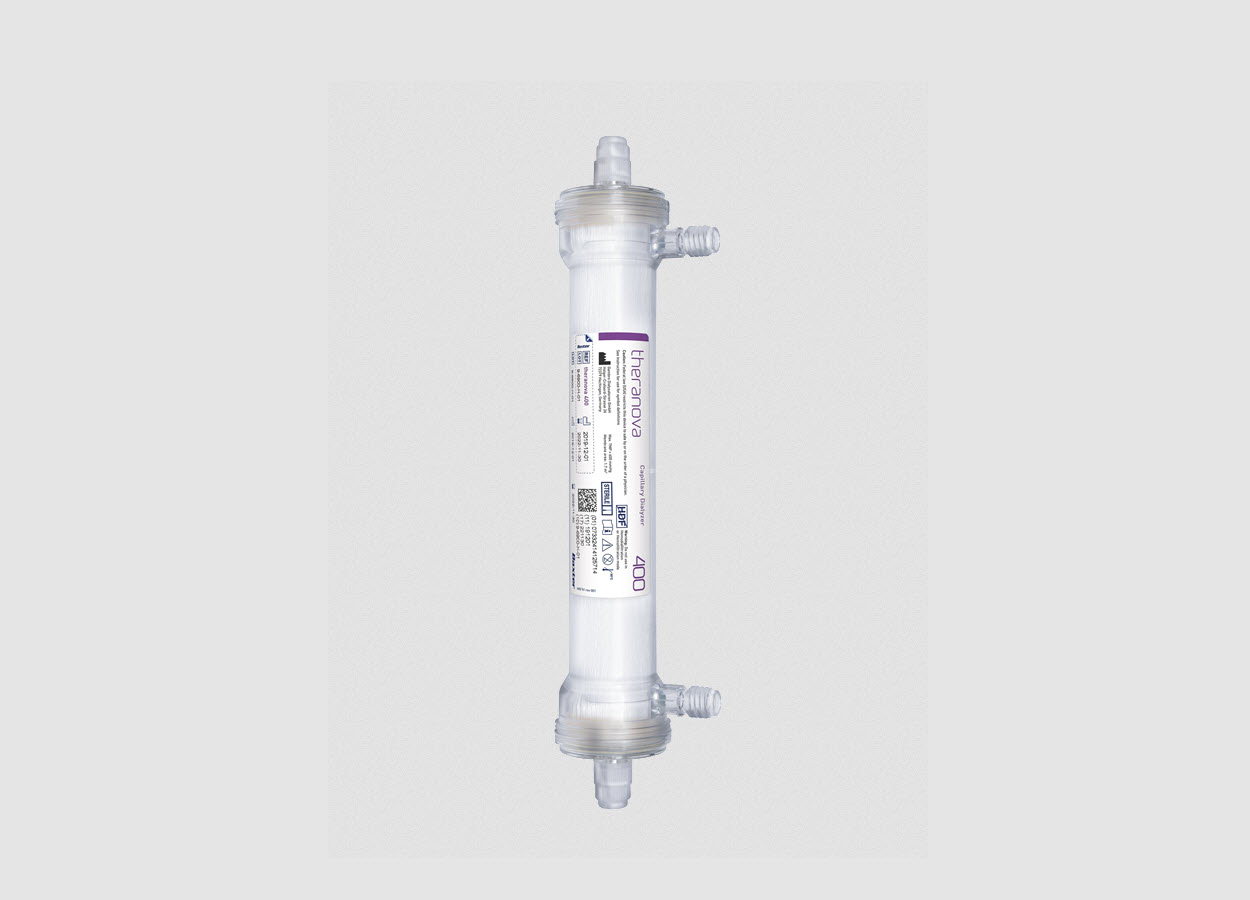
Baxter International Inc a global innovator in renal care, announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted the De Novo application for Theranova, the company’s novel dialysis membrane. Theranova was designed to deliver expanded hemodialysis (HDx) therapy, which filters a wider range of molecules from the blood than traditional hemodialysis (HD) filters, like high-flux membranes, by targeting effective removal of conventional (500 Da to 25 kDa) and large middle molecules (25 kDa to 45 kDa). These middle molecules may be associated with inflammation and cardiovascular disease in patients with kidney failure.
By granting a De Novo application, the FDA is establishing a new class of dialyzer technology with unique performance standards. The FDA utilizes the De Novo pathway for low and moderate risk medical devices that have no existing predicate in the United States; such designations are rare in the dialysis space. In fact, less than 1% of devices granted marketing authorization under De Novo have been for the care of patients with kidney failure since the pathway’s inception in 1997.
HDx is performed the same way as conventional HD, with only a change of the dialyzer membrane required. Once in the machine, the Theranova dialyzer’s innovative Medium Cut-Off® membrane combines high permeability and selectivity for uremic toxins (up to 45 kDa), while retaining essential proteins and maintaining albumin levels during treatment2,3. This unique cut-off and high retention onset profile expands clearance, allowing for filtration closer to that of the natural kidney.
"U.S. patients on HD deserve more options than are currently available to them, and we are taking extraordinary steps to support their access to Theranova," said Gavin Campbell, general manager of Baxter's U.S. Renal Care business. "Patients are currently treated with HDx enabled by Theranova in more than 40 countries worldwide, and we are doing everything we can in the U.S. to ensure healthcare providers can also realize the full value of this therapy for their patients on HD."
To date, over 90 independent and Baxter-led or sponsored studies have been conducted on HDx therapy enabled by Theranova. The studies evaluated a range of clinical and quality-of-life measures, including the ability to clear conventional and large middle molecules, albumin retention, chronic inflammation and other side effects of standard HD therapy.
"Individually, the side effects from standard HD, which patients typically undertake three days a week, four hours per day, may seem manageable. However, the chronic effects of treatment accumulate and over time, cause some patients to give up on therapy," explained Mary Gellens, M.D., nephrologist and senior medical director at Baxter. "HDx therapy enabled by Theranova is a promising alternative to what is currently available because it delivers a filtration profile that is closer to the natural kidney."
Due to the novel nature of Theranova, Baxter conducted a randomized controlled clinical study in the United States that evaluated the safety and efficacy of HDx therapy enabled by Theranova. During the study, as reported during the 2019 American Society of Nephrology Kidney Week, 172 hemodialysis patients received therapy with either a medium cut-off dialyzer (Theranova 400) or a high-flux dialyzer (ELISIO-17H) over 24 weeks of treatment, with a primary efficacy endpoint measuring the reduction ratio of lambda (λ) free light chains at 24 weeks of treatment, while maintaining pre-dialysis serum albumin levels. Data from the study, which was just published in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN), found that expanded hemodialysis therapy with the Theranova 400 dialyzer provides superior removal of large middle molecules, as exemplified by λ free light chains, as compared to a similarly sized high flux dialyzer while maintaining serum albumin levels7. Large middle molecules are a diverse group of uremic toxins that are believed to contribute to the high cardiovascular disease burden in end stage kidney disease8. Dialysis technologies available to date offer limited clearance of these molecules8. The ability to efficiently remove these large middle molecules provides dialysis patients with a new alternative therapy.

Zydus Cadila has received final approval from the USFDA to market Cisatracurium Besylate Injection USP (US RLD: Nimbex ®) in the strength of 20 mg (base)/10 mL (2 mg/mL) Multiple-Dose Vial.
Since the outset of our discovery of impurities called nitrosamines in some types of drugs more than two years ago, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has undertaken a thorough investigation in an effort to protect patients. While nitrosamines are common in water and foods, nitrosamine impurities may increase the risk of cancer if people are exposed to them above acceptable levels and over long periods of time. For this reason, the discovery of unexpected nitrosamine impurities in some drug products is a serious concern, and the FDA has been working, in collaboration with regulatory counterparts around the world, to find and remove drugs with unacceptable nitrosamine impurities from the U.S. drug supply. As we do so, we’re also taking proactive efforts to help ensure that in the future, drugs can be free from unsafe levels of these impurities from the start of production.
Ensuring that drugs are safe, effective and high-quality is a critical part of FDA’s mission. In our continued efforts to be transparent and provide guidance to manufacturers on how to detect and prevent unacceptable levels of nitrosamine impurities, today we’re publishing our guidance Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs for immediate implementation. This guidance recommends steps, including a comprehensive risk assessment strategy and other actions that manufacturers can take to reduce or prevent the presence of nitrosamine impurities in their drugs.
There are many reasons why these impurities might appear in some drugs, and consequently many approaches to screening for and preventing the appearance of nitrosamines to help ensure drug quality and safety. The source of these impurities can be related to the drug’s manufacturing process, the materials used in manufacturing, the drugs’ chemical structure, or even the conditions in which drugs are stored or packaged. Under FDA’s oversight, manufacturers are responsible for mitigating these impurities.
The most common nitrosamine impurity, N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), is found at low levels in water and foods, including cured and grilled meats, dairy products and vegetables. The FDA and the international scientific community do not expect NDMA to cause harm when ingested at low levels. However, given the risk that genotoxic substances such as NDMA may increase the risk of cancer if people are exposed to them above certain levels and over long periods of time, manufacturers have recalled drugs with NDMA levels higher than the FDA’s recommended acceptable intake levels. Patients taking medications with potential nitrosamine impurities should not stop taking their medications and should talk with their health care professional about concerns and other treatment options.
We believe that the guidance we’ve issued today will assist manufacturers in preventing unacceptable levels of nitrosamines in drugs. Protecting patients is the FDA’s highest priority, and we will continue to work with manufacturers and our international regulatory partners to investigate and definitively resolve this problem.
The FDA, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, protects the public health by assuring the safety, effectiveness, and security of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products for human use, and medical devices. The agency also is responsible for the safety and security of our nation’s food supply, cosmetics, dietary supplements, products that give off electronic radiation, and for regulating tobacco products.