- Aerosol filling methods
- EVALUTION TEST OF AEROSOLS
Aerosol filling methods :-
Cold filling process :- High speed of filling usually used for non-aqueous products. Propellant is refrigerated (-20 to -40?) & added to container as cold liquid. Product conc. Cooled to 0 to 10? & then added to container. Moisture elimination is problematic and may cause corrosion. Dis –advantage :- High propellant vapor losses , high costs for refrigeration and humidity control equipment and possible induction of non reversible physical changes in the formulation. Advantages :- Is greater accuracy of the total drug content in the inhaler.
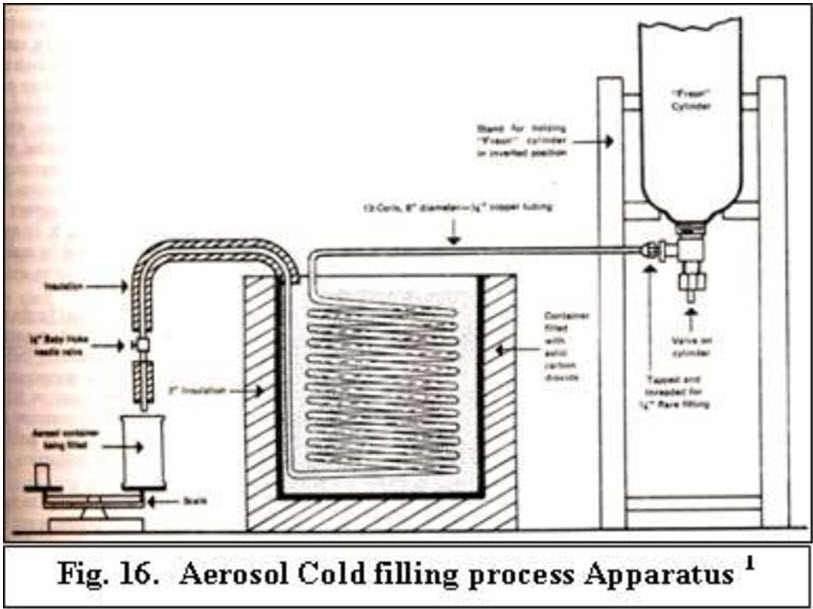
Pressure filling process :- Carried out at room temperature (30-40 ?). First product conc. is added. Through valve opening propellant is added by pressuring propellant at temp. of filling area. Headspace air may be compressed. So headspace purging is necessary.
Under cup filling :- It is advanced pressure filling. Propellant is added to an open aerosols container by evacuation of air and focusing propellant under the aerosols valve cup just prior to sealing the valve. Container is filled with drug concentrate and sealed with same unit operation.
EVALUTION TEST OF AEROSOLS
A.FLAMMABILITY AND COMBUSTIBILITY:-
1.FLASH POINT
2.FLAME PROJECTION
B. PHYSICOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS:-
1. VAPOUR PRESSURE
2. DENSITY
3. MOISTURE CONTENT
4.IDENTIFICATION OF PROPELLANTS
C. PERFORMANCE:-
1. AERSOL VALVE DISCHARGE RATE
2. SPRAY PATTERN
3. DOSAGE WITH METERED VALVES
4. NET CONTENTS
5. FOAM STABILITY
6. PARTICLE SIZE DETERMINATION
D.BIOLOGICAL TESTING :-
1.THERAPEUTICAL ACTIVITY
2.TOXICITY STUDIES:-
1. Flash point: Apparatus : Open Cup Tag Apparatus Test liquids temp. is allowed to increase slowly & temp. at which vapors Ignite is called as Flash Point.
2. Flame Projection: Product is sprayed for 4 sec onto flame & exact length is measured with ruler
B. Physicochemical characteristics:
|
Property |
Method |
|---|---|
|
1. Vapor Pressure |
Can Puncturing Device |
|
2. Density |
Hydrometer, Pycnometer. |
|
3. Moisture |
Karl Fisher Method, Gas Chromatography |
|
4. Identification |
Gas Chromatography, IR Spectroscopy. |
C. Performance:
1.Aerosol valve discharge rate : Aerosol product of known weight is discharged for specific time. By reweighing the container, the change in the wt. per time dispensed is the Discharge rate in gm/sec
2. Spray pattern : The method is based on the impingement of spray on piece of paper that has treated with Dye-Talc mixture.
3. Dosage with metered valves : Reproducibility of dosage determined by: »Assay »Accurate weighing of filled container followed by dispensing several dosage. containers again reweighed & diff. in wt. divided by no. of dosage dispensed gives average dose.
4. Net Contents : Tared cans placed on filling lines are reweighed & then difference in wt. is equal to net content. In Destructive method : opening the container & removing as much of product possible.
5. Foam stability : Various Methods : » Visual Evaluation, Time for given mass to penetrate the foam, Time for given rod to fall which is inserted into the foam, Rotational Viscometer.
6. Partical Size Determination : Methods :
» Cascade Impactor,
» Light Scattering Decay
a). Cascade Impactor : Principle : Stream of particle projected through a series of nozzle & glass slides at high velocity, larger particle are impacted on low velocity stage , & smaller on higher velocity stage. b). Light Scattering Decay : Principal : As aerosol settles under turbulent condition, the changes in the light of a Tyndall beam is measured.
D. Biological testing :
1. Therapeutic Activity : » For Inhalation Aerosols : is depends on the particle size. » For Topical Aerosols : is applied to test areas & adsorption of therapeutic ingredient is determined.
2. Toxicity : » For Inhalation Aerosols : exposing test animals to vapor sprayed from Aerosol container. » For Topical Aerosols : Irritation & Chilling effects are determined