About Authors:
Tyagi Nitin*, Singh Vikram Jeet, Mishra Santosh Kumar
CARPS, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shobhit University,
Meerut, U.P.(250110), India.
*nitintyagi27@yahoo.in
Abstract
These tablets were introduced in 1980s in the market and since their introduction in the market the fast dissolving tablets are gaining popularity regularly. Due to their rapid disintegration or dissolution in the oral cavity as they come into contact of saliva normally with in one minute, without the use of water these provides patient compliance particularly to the pediatric, geriatric ,bedridden patients and for patients who are very much busy in travelling and does not have easy access to water. The present article aims on the recent advancements in the fast dissolving tablets and provides a good information about the advantages,limitations, mechanism of action of superdisintegrants, the conventional and patented development techniques and about the evaluation parameters of the fast dissolving tablets.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1466
Introduction
Therapeutic agents are still be best administered by the oral route despite of tremendous achievements in the drug delivery systems1 and this has got a wide acceptance of upto 50-60% of total in comparison to other dosage forms of drug administration. Now a days tablets are most popular and widely used dosage form in comparison to other dosage forms due to its ease in self administration and compactness but one demerit of tablet dosage form is that the number of patients are having difficulty in swallowing. As in case of geriatric, paediatric and mentally ill patients who reports difficulty in swallowing in many cases for conventional tablets. This problem is reported in all age groups, mainly in elderly and dysphasic patients which rise in poor patient compliance also the drinking water is having a important role in the swallowing of the tablet dosage form. So to resolve these shortcomings research scholars have developed a new drug delivery system i.e., The mouth dissolving or disintegrating tablets (MDTs)2-3.
Fast dissolving tablets disintegrates rapidly in the oral cavity without the need of water and turns into solution or suspension form. These were introduced in 1980s4.These tablets are the solid dosage forms which contains medical substances that disintegrate rapidly in few seconds when comes into the contact of tongue and requires no water for swallowing. These are best for tablets that undergoes high first pass metabolism and thus improving the bioavailability without reducing dosing frequency for minimizing the side effects5.
The term used by the European pharmacopoeia for the tablets that readily disperses within 3 min in the mouth before swallowing is the orodispersible tablets.These are also known as porous tablets or rapid melts,however the United States pharmacopoeia approved these dosage forms as the ODTs. United States food and drug administration (FDA) defined the ODTs as “ a solid dosage form containing medicinal substance or active ingredient which disintegrates rapidly usually within a matter of seconds when placed upon the tongue”. The time taken for disintegration by the mouth dissolving tablets ranges from few seconds to about a minute6.
Ideal characteristics for the fast dissolving tablets7.
1. Must disintegrate or dissolve in mouth within few seconds as no water is needed for swallowing .
2. MDTs should be compatible with taste masking and provides pleasant mouth feel.
3. Leaves no or minimal residue in the oral cavity after administration.
4. Allows maximum drug loading.
5. Should be stable in altered environmental conditions.
Advantages of FDDDS 8,9,10.
1. Comfort of administration to patients such as elderly, stroke victims, bed-ridden, renal failure patients etc. who cannot swallow the tablets.
2. Includes rapid drug therapy interventionto promote good health.
3. Best for patients who rejects to swallow like the pediatrics, psychiatric and geriatric patients.
4. Good mouth feel changes the general view of medication as “ bitter pill” especially in the case of pediatric patients.
5. Patient’s compliance for bed-ridden patients and busy persons in case of water scarcity.
6. Conveniently administered and précised dosing when compared with liquid formulations.
7. Assistance of liquid medications in the form of solid preparations.
8. Fast absorption and increased bioavailability as a result of pregastric absorption of medicament.
9. Due to physical obstruction there is a risk of suffocation or chocking when orally administered but it is avoided in case of MDTs.
10. New business opportunity and cost effective.
Limitations of fats dissolving tablets11.
1. These are hygroscopic in nature so must be kept in dry conditions.
2. MDTs requires special packing so that properly stabilized and have safety of stable product.
3. In many cases MDTs possesses mouth feel.
Main ingredients used in preparation of MDT are superdisintegrants12.
In the design and development of Mouth dissolving tablets the basic approach is the use of disintegrants which plays a important role in the disintegration and dissolution of MDTs. Super disintegrants provides fast
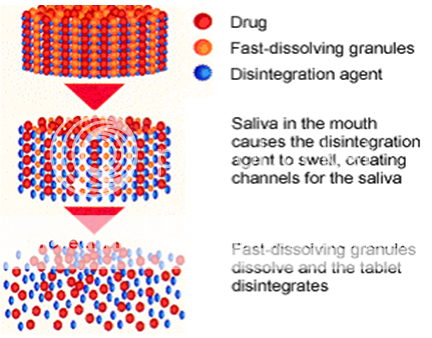
Fig. 1: The mechanism of action of Superdisintegrants .
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
disintegration because of the associative effect of water absorption and swelling by MDTs. That raises the wettability and dispersibility of the system, thereby increasing the disintegration and dissolution. The time of disintegration of MDTs is inversely proportional to the amount or concentration of the superdisintegrants. The various examples of the superdisintegrants are Microcrystalline cellulose, Pregelatinised starch, Ac?di?sol(crosscarmellose sodium), Crospovidone, Sodium starch glycolate etc.
Mechanism of action of superdisintegrants3,13.
1. By porosity and capillary action (wicking).
2. By swelling.
3. Because of heat of wetting.
4. Due to release of gases.
5. By enzymatic action.
6. Due to disintegrating particle/particle repulsive forces.
7. Due to deformation.
1. By porosity and capillary action- It is also known as wicking. Disintegration by wicking is always the first step. The tablet in the suitable aqueous medium allows the penetration of the medium into it. Which replaces the air adsorbed on the tablet particles and softens the intermolecular bond due to which the tablet breaks down into fine particles.
2. By swelling- This is the well accepted mechanism of action for disintegration of tablet. The tablet which are having the high porosity displays poor disintegration as it lacks the sufficient swelling force. The required swelling force is exerted in the tablets which are having low porosity. It is important to know that if the packing fraction is very high, the medium is unable to penetrate in the tablet and due to this the tablet disintegration again slows down.
3. Because of heat of wetting- The disintegrants which are having exothermic properties gets wetted and the localized stress is generated as a result of capillary air expansion that helps in tablet disintegration.
4. Due to release of gases- After wetting the carbon dioxide is released within tablets as the interaction occurs between bicarbonate and carbonate with citric acid or tartaric acid. The disintegration of tablet is due to the generation of pressure.
5. By enzymatic action- The enzymes present in the human body also acts as disintegrants. They destroys the binding property of the binder and facilitates the disintegration of the mouth dissolving tablet.
6. Due to disintegrating particle/particle repulsive forces- In case of non swellable disintegrants Guyot-Herman has proposed this particle repulsion theory which is based on the assumption that non swellable disintegrants also causes the tablet disintegration. The electric repulsive forces between the particles are the disintegration mechanism and water is needed for it.
7. Due to deformation- when we compress the tablet the disintegrant particles are deformed and these get into their original structure when they come in the contact of the suitable aqueous medium.
Methods of preparation of fast dissolving tablets.
A. Conventional Techniques 14,15,16,17,18
1. Molding: In this technique, molded tablets are formulated by employing the ingredients which are water soluble as of which the mouth dissolving tablets dissolve rapidly and completely. The powder blend is prepared by moistening with a hydro-alcoholic solvent and is then molded into tablets with pressure which is lower than the one used in compression of conventional tablet. The hydro-alcoholic solvent is then removed from the mouth- dissolving tablet by air-drying.The tablets which are prepared by moulding technique are less compact than compressed tablets. These tablets possess porous structure that enhances dissolution.
2. Direct Compression:The tablets prepared by the conventional compression technique are less friable, but also disintegrate slowly. The compression technique, with or without wet granulation, is most convenient and cheap procedure to formulate tablets with good structural integrity.
3. Sublimation: For generating porous matrix, volatile ingredients which shows high volatility are used and then subjected to a process of sublimation. The inert solid ingredients that shows high volatility for e.g., ammonium carbonate, ammonium bicarbonate, benzoic acid, camphor are then compressed with other excipients into a tablet. The volatile ingredients were then removed by the process of sublimation that leaves porous matrix behind.
4. Melt granulation: This is a technique that involve the effective agglomeration of pharmaceutical powders by using the binders which may be a solid, a molten liquid or may also be a solid which melts within the formulation process. For facilitating the process, high shear mixers are used, where temperature of the product is elevated above the melting point of binder .
5. Lyophilization or Freeze-Drying: In this process water is sublimed from the product after it is frozen. This method forms anamorphous porous structure which dissolves rapidly.The active ingredient is dispersed or dissolved in an aqueous solution of a carrier/polymer. The mixture is transfered in the walls of the pre-formed blister packs. The trays carrying the blister packs are passed from liquid nitrogen freezing tunnel for freezing the active ingredient dispersion or solution. Afterwards frozen blister packs were put into the refrigerated cabinets to further proceed the freeze-drying. After completing the freeze drying process we apply the aluminum foil backing on blister-sealing machine. This method has an advantage of improved absorption and increased bioavailability.
B. Patented techniques19,20,21,22,23
1. Zydis Technology: The tablet in this process is formulated by freeze-drying or lyophilizing the active ingredient in a matrix usually consisting of gelatin. The formulated product is very fragile and light in weight and these must be dispensed in a special blister pack. The formulated product is designed so that it can dissolve on the tongue in nearly 2 to 3 seconds. The main advantage of the Zydis product is increased in bioavailability as compared to traditional tablets. As its dispersion and dissolution occurs in saliva when it is still in oral cavity, there will be a adequate amount of pre-gastric absorption from this Zydis formulation. The pre-gastric absorption in the oral cavity avoids the first-pass metabolism and this is an advantage for the drugs that undergoes a greater extent of hepatic metabolism. The main disadvantages to the Zydis technology are that, these formulations are very light in weight and are also fragile,be given a special attention while packaging and storage. Also, these formulations have got poor stability at elevated temperature and humid conditions. The Zydis formulations readily absorbs water, and are very much sensitive to degradation when the humidity is greater than 65%.
2. Orasolv technology: It was the Cima's first fast disintegrating /dissolving dosage form. The active medicament in Orasolv technology is taste masked. The disintegration of the Orodispersible tablets in the oral cavity is achieved due to the performance of an effervescent agent, that is activated by saliva. The effervescent agent is in amount of about 20-25% to the total weight of the Orodispersible tablet. The broadly utilized effervescent disintegration pair normally contains an acid source (citric, malic, tartaric, fumeric, succinics and adipic) and the carbonate source (sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, potassium carbonate, potassium bicarbonate and magnesium carbonate). These microspheres are firmly compressed to retain the integrity of the coating.The main disadvantage of these formulations is its mechanical strength. Due to this reason, Cima designs a unique packaging and handling system for OraSolv. Also the formulation requires a well controlled environment which is having a low relative humidity and protects the final Orodispersible tablets with moisture impermeable blisters.
3. Flashtab-technology: This technique is patented by Ethypharm France. The Flashtab- technology includes wet or dry granulation of excipients and then followed by compression into tablets. There are two types of excipients used in this technology.
Swelling agents consists of starch, modified starch, carboxymethylcellulose, carboxy methylated starch, microcrystalline cellulose, etc and the disintegrating agents consists of carboxy methylcellulose or reticulated polyvinylpyrrolidine.The Flashtab tablets have got satisfactory physical resistance and the disintegration time is inside 1 min.
4. Wowtab®: This was developed by Yamanouchi Pharma Technologies, USA. This technique consumes saccharides as they have the properties of quick dissolution in water or saliva and attains the adequate tablet hardness after compression.The low moldable sugars for example mannitol, glucose, lactose, erythritol and sucrose shows quick dissolution with low compressibility and high moldable sugars for example maltose, maltitol , trehalose and sorbitol shows appropriate hardness upon compaction.This technique formulates tablets by granulating a low moldable sugar together with a high moldable sugar. These tablets posses the properties of fast dinintegration along with appropriate hardness. These tablets have got disintegration time in between 1 to 40 sec.
5. Durasolv® Technology:Durasolv technology is the patented technology of CIMA labs. The fast dissolving tablets formulated by thistechnique contains the drug, fillers and a lubricant. The fast dissolving tablets are formulated byutilizing the conventional tableting machine and posses good rigidity. The conventional packaging system like blisters can also be utilized in the packaging of tablets prepared by Durasolv technology. This Durasolv technology is appropriate for the formulations that utilizes less amount of active ingredients.
Evaluation tests for fast disintegrating tablets24,25,26,27,28,29,30
1. General appearance- The mouth dissolving tablets are randomly chosen from the various batches formulated after that organoleptic characteristics like shape, color, taste, odor were examined.
2. Hardness- The hardness of the tablet is defined as the force required to break a tablet The Monsanto hardness tester is used for determining the hardness of the tablet.
3. Tablet friability- The friability is measured in the Roche Friabilator . Twenty tablets are weighed as W0 and subjected in a drum for a fixed number of 100 revolutions and weighed again as W. Then the percentage friability is calculated as loss in weight and must not be more than 1 % and is given by the equation.
% Friability = [(WO – W)/WO ] x 100
4. Wetting time- Twice folded tissue paper was put into a Petri dish with the internal diameter of 9cm. After that the 10ml of water comprising of Eosin, which is a water soluble dye , was transfered into the petridish. Then the mouth dissolving tablet was put on the tissue paper and then the time was noted which was taken by the water to thrust out on the uppermost portion of the mouth dissolving tablet and is refered as the wetting time.
5. In vitro disintegration time- The disintegration time for the fast dissolving tablets is done by using tablet disintegration test apparatus. Firstly the phosphate buffer pH 6.8 is maintained at atemperature of 37°±2°C and then the six tablets are placed individually in each tube and there discs are placed on the top. The time taken for the whole fast dissolving tablet to disintegrate fully is noted.
6. In vitro dissolution studies- In vitro dissolution studies for the fast dissolving tablets is carried out by using USP Type II apparatus (USP XXIII Dissolution Test Apparatus) with a speed of 50 rmp for the paddle and containing 900 ml of phosphate buffer pH 6.8 in the flask which is maintained at 37±0.5ºC. After the specific time period the 5 ml aliquot is withdrawn from the flask, filtered and assayed spectrophotometrically by using Shimadzu 1700 spectrophotometer and also the same volume of fresh medium, that must be pre-warmed at 370C is put into the dissolution flask every time so that the constant volume of the buffer is maintained till the completion of the test.
7. Stability study (Temperature dependent)- These tablets are stored and packed within appropriate packaging and are subjected to the subsequent environment for a time as permitted by the ICH guidelines for the accelerated studies.
· 40 ± 1 °C
· 50 ± 1 °C
· 37 ± 1 °C and RH 75% ± 5%
Then the tablets are taken out after a span of 15 days and again evaluated. After that calculation are done according to first order equation for finding out the kinetics of degradation then the plotting of the data is done for accelerated stability in accordance with the Arrhenius equation for determining the shelf life at the temperature of 250 C.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Marketed preparations of fast dissolving tablets31.
Table No. 1 Top ODT products ranked by sales
|
Product |
Company name |
Technology |
|
Zyprexa |
Eli Lilly |
Zydis–Cardinal Health |
|
Claritin Reditab |
Schering Plough |
Zydis–Cardinal Health |
|
Zoming ZMT |
Astra Zeneca |
Orasolv-Cima(Cephalon) |
|
Maxalt MLT |
Merck |
Zydis–Cardinal Health |
|
Zofran ODT |
GSK |
Zydis–Cardinal Health |
|
Prevacid Solutab |
TAP |
Unknown |
|
Risperdal |
Janssen |
Quicksolv-Janssen |
Table No. 2 Fast-Dissolve Generics
|
Product |
Technology Provider |
|
Mirtazapine |
Teva |
|
Mirtazapine |
Barr |
|
Mirtazapine |
Actavis |
|
Mirtazapine |
Aurobindo |
|
Clonazepam |
Kali |
|
Tramadol |
Biovail |
|
Citalopram |
Biovail |
|
Tramadol |
Ethypharm |
1.10 Drugs to be promising candidate for fast dissolving tablet32,33.
Table No. 3 Example of some drug candidates best for FDT
|
S.No |
Class of API |
Examples |
|
1 |
Analgesics and Anti-inflammatory Agents |
Diflunisal, Fenbufen, Flurbiprofen, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Ketoprofen, Meclofenamic Acid, Mefenamic Acid, Nabumetone, Naproxen, Piroxicam,Sulindac. |
|
2 |
Anti-Gout Agents |
Allopurinol, Probenecid, Sulphinpyrazone. |
|
3 |
Anti-Hypertensive Agents |
Amlodipine, Carvedilol, Benidipine, Darodipine, Dilitazem, Felodipine, Indoramin, Isradipine, Nifedipine, Nimodipine,Prazosin, Reserpine, Terazosin. |
|
4 |
Gastro-Intestinal Agents |
Cimetidine, Cisapride, Domperidone, Famotidine, Loperamide, Nizatidine, Omeprazole, Ondansetron, Ranitidine. |
|
5 |
Nutritional Agents |
Betacarotene, Vitamin A, Vitamin B 2 , Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K. |
|
6 |
Anti-migraines |
Almotriptan, dihydroergotamine mesylate, eletriptan, frovatriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan and zolmitriptan. |
|
7 |
Statins |
Atorvastatin, cerivastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin and simvastatin. |
|
8 |
Anti-Thyroid Agents |
Carbimazole, Propylthiouracil. |
|
9 |
Anti-Gout Agents |
Allopurinol, Probenecid, Sulphinpyrazone. |
|
10 |
Anti-Neoplastic Agents and Immunosuppressants |
Aminoglutethimide, Chlorambucil, Cyclosporin, Etoposide, Lomustine, Melphalan, Mercaptopurine, Methotrexate,Procarbazine, Tamoxifen Citrate, Testolactone. |
|
11 |
Anti-Epileptics |
Beclamide, Carbamazepine, Clonazepam, Ethotoin, Methoin, Methsuximide, Methylphenobarbitone, Oxcarbazepine, Phenobarbitone,Phenytoin, Valproic Acid. |
|
12 |
Anti-Fungal Agents |
Amphotericin, Econazole Nitrate, Fluconazole, Griseofulvin, Itraconazole, Ketoconazole, Miconazole, Natamycin, Nystatin, Sulconazole Nitrate. |
|
13 |
Cardiac Inotropic Agents |
Amrinone, Digitoxin, Digoxin, Enoximone, Lanatoside C, Medigoxin. |
|
14 |
Anti-Parkinsonian Agents |
Bromocriptine Mesylate, Lysuride Maleate. |
|
15 |
Diuretics |
Acetazolarnide, Amiloride, Bendrofluazide, Bumetanide, Chlorothiazide, Chlorthalidone, Ethacrynic Acid, Frusemide, Metolazone, Spironolactone, Triamterene |
Conclusion
The presence of fast dissolving tablets in the market has solved lots of problems specially associated with the pediatric, elderly patient, bedridden and psychotic patients. As of wide acceptance of FDTs by the patients we may also see many more classes of drug to be formulated in FDTs. But we might also suffer with the problem of cost , so cost reduction is the big task to deal with.
Bibliography
1. Panwar, P.B., Mansuk, A.G., Ramteke, K.H., Sharma, Y.P., Patil, S.N., 2011. Mouth Dissolving Tablet: A Review. IntJ.Herbal.Drug.Res. 1(2), 22-29.
2. Bhowmik , D., Chiranjib, B., Krishnakanth., Pankaj., Chandira, R.M., 2009. Fast Dissolving Tablet: An Overview. J.Chem.Pharm.Res. 1(1), 163-177.
3. Gajare, G.G., Bakliwal, S.R., Rane, B. R., Gujrathi, N.A., Pawar, S.P., 2011. Mouth Dissolving Tablets: A Review. Int. J.Pharm.Res.Dev. 3(6), 280-296.
4. Deshmukh, K.R., Patel, V., Verma, S., Pandey, A.k., Dewangan, P., 2011. A Review on Mouth Dissolving Tablets Techniques. Int.J.Res.Ayur.Pharm. 2(1), 66-74.
5. Kakade, S.M., Mannur, V.S., Ramani, K.B., Dhada, A.A., Naval, C.V., Bhagwat, A., 2010. Formulation and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Tablets of Losartan Potassium by Direct Compression Techniques. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 1(3), 290-295.
6. Bharawaj, S., Jain, V., Sharma, S., Jat, R.C., Jain, S., 2010. Orally Disintegrating Tablets: A Review. Drug Invention Today. 2(1), 81-88.
7. Nagar, P., Singh, K., Chauhan, I., Verama, M., Yasir, M., Khan, A., Sharma, R., Gupta, N., 2011. Orally disintegrating tablets : formulation, preparation techniques and evaluation. J.Applied.Pharm.Sci. 1(4), 35-45.
8. Konapure, S.A., Prafulla, S., Chaudhari., Osawal, R.J., Kshirsagar, S.S., Antre, R.V., Chorage, T.V., 2011. Mouth Dissolving Tablets An Innovative Technology. Int.J.Applied.Bio.Pharm.Tech. 2(1), 496-503.
9. Desale, K.Y., Bankar, V.H., Gaikwad, P.D., Pawar, S.P., 2011. Review On: Fast Dissolving/Disintegrating Tablets. Int.J.Pharm.Sci.Rev.Res. 11(1), 152-158.
10. Shukla, D., Chakraborty, S., Singh, S., Mishra, B., 2009. Mouth Dissolving Tablets I: An Overview of Formulation Technology. Sci.Pharm. 77, 309-326.
11. Patidar, A., Mishra, P., Main, P., Harsoliya, M.S., Agrawal, S., 2011. A Review On-Recent Advancement in the Development of Rapid Disintegrating Tablet. Int.J.Life.Sci.Pharm.Res. 1(1), 7-16.
12. Kaur, T., Gill, B., Kumar, S., Gupta, G.D., 2011. Mouth Dissolving Tablets: A Novel Approach to Drug Delivery. Int.J.Curr.Pharm.Res. 3(1), 1-7.
13. Nandy, B.C., Mazumder, B., Pathak, K., Saxena, N., Jain, S., Sharma, S., Amishaben, R., Shrivastava, A., Saxena, P., 2011. An Overview On Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System. Asian.J.Pharm.Sci.Res. 1(2), 1-30.
14. Ashish, P., Harsoliya, M.S., Pathan, J.K., Shruti, S., 2011. A Review- Formulation of Mouth Dissolving tablet. Int.J.Pharm.Clinical.Sci. 1(1), 1-8.
15. Soni, J.V., Patel, N.R., Bharadia, P.D., Pandya, V.M., Modi, D.M., 2011. Different Methods and Evaluation Parameters of Fast Disintigrating Tablets. IJPI’s.J.Pharm.Cosmetology. 1(4), 61-75.
16. pharmatutor.org/articles/a-review-on-fast-dissolving-tablet technology? page =0,1.
17. Nayak, A.K., Kaushik, M., 2011. Current developments in orally disintegrating tablet technology. J.Pharm.Educ.Res. 2(1), 21-34.
18. Kumar, V.D., Sharma, I., Sharma, V., 2011. A comprehensive review on fast dissolving tablet technology. J.Applied.Pharm.Sci. 1(5), 50-58.
19. Sharma, C., Dangi, V., Gupta, A., Ahamad, D., Ahmad, A., 2010. Orally disintegrating tablets: A Review. Int.J.Pharmacy.Life.Sci. 1(5), 250-256.
20. Velmurugan, S., Vinushitha, S., 2010. Oral Disintegrating Tablets: An Overview. Int.J.Chem.Pharm.Sci. 1(2), 1-12.
21. asiapharmaceutics.info/article.asp?issn=0973 8398;year= 2008;volume = 2; issue = 1;spage=2;epage=11;aulast= Bandari.
22. Mundada, A.S., Badgujar, B.P., 2011. The technologies used for developing orally dis integrating tablets: A review. Acta.Pharm. 61, 117-139.
23. Dhakane, K., Rajebahadur, M., Gorde, P., Salve, P., 2011. Fast Dissolving Tablet: A Future Prospective. J.Pharmacy.Res. 4(11), 4176-4180.
24. Nayak, R.K., Narayana Swamy, V.B., Senthil, A., Hardikkumar, T., Kumar, D.M., Mahalaxmi, R., 2011. Formulation and Evaluation of fast dissolving tablets of Lornoxicam. Pharmacologyonline. 2, 278-290.
25. Patel, B., Patel, D., Parmar, R., Patel, C., Serasiya, T., Sanja, S.D., 2009. Develpoment and In Vitro Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Tablets of Glipizide. Int.J.Pharmacy.Pharm.Sci. 1(1), 145-150.
26. Deshmukh, G., Ruikar, D., Seth, A.K., Patel, J., Ghelani, T., Kumar, S., Yadav, Y.C., Rajyaguru, K., Rathi, A., 2011. Formulation and Development of Lamotrigine Fast Disintegrating tablet. Pharma.Sci.Monitor.An.Int.J.Pharm.Sci. 2(3), 7-15.
27. Sharma, A., Jain, A., Purohit, A., Jatav, R., Sheorey, R.V., 2011. Formulation and evaluation of aceclofenac fast dissolving tablets. Int.J.Pharmacy.Life.Sci. 2(4), 681-686.
28. Ghenge, G., Pande, S.D., Ahmad, A., Jejurkar, L., Birari, T., 2011. Development and Characterisation of Fast Disintegrating Tablet of Amlodipine besylate using Mucilage of Plantago ovata as a Natural Superdisintegrant. Int.J.PharmTech.Res. 3(2), 938-945.
29. Mohsin, A.A., Nimbalakr, N.E., Sanaullah, S., Aejaz, A., 2010. Formulation and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Tablets of Amitriptyline Hydrochloride by Direct Compression Technique. Int.Journal.Pharmacy.Pharm.Sci. 2(1), 204-210.
30. Shaikh, S., Khirsagar, R.V., Quazi, A., 2010. Fast Disintegrating Tablets: An Overview of Formulation and Technology. Int.J.Pharmacy.Pharm.Sci. 2(3), 9-15.
31. ondrugdelivery.com/publications/Oral_Drug_Delivery_07.pdf.
32. Bhowmik, D., Chiranjib., Jaiswal, J., Dubey, V., Chandira, M., 2009. Fast dissolving tablet: A review on revolution of novel drug delivery system and new market opportunities. Sch.Res.Lib. 1(2), 262-276.
33. Nehal Siddiqui, M.D., Garg, G., Sharma, P.K., 2011. A Short Review on “A Novel Approach in Oral Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System and Their Patents”. Adv.Bio.Res. 5 (6), 291-303.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









