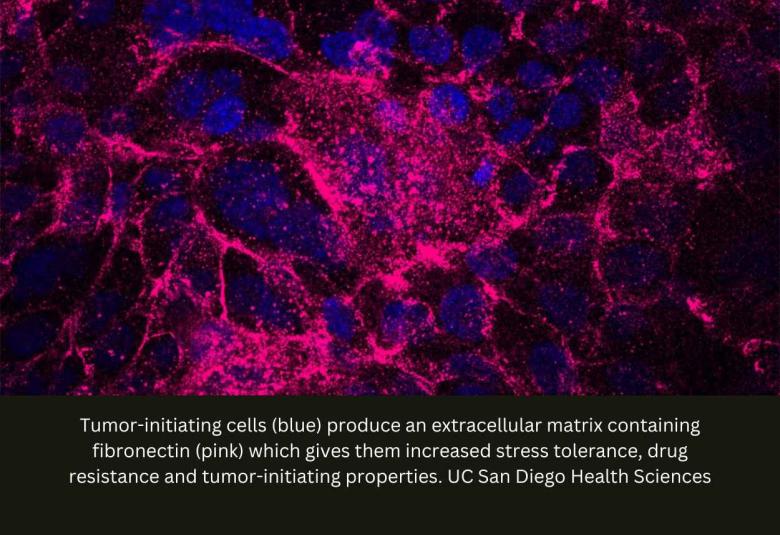
Stress-Tolerant Cells Drive Tumor Initiation in Pancreatic Cancer
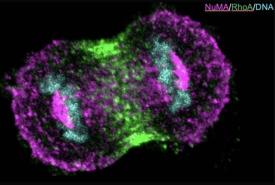
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have discovered a molecular pathway critical to the initiation of pancreatic tumors. The mechanism could also contribute to the disease’s high resistance to chemotherapy and its propensity for metastasis.