- ADVANTAGE
- DIS ADVANTAGE
- Parenteral Routes
- Classification of parenteral products
• The term derived from Greek word ‘Para’ means outside & ‘enter one’ means intestine.
• Parenteral are sterile solutions or suspension of drug in aqueous or oily vehicle.
• Parenteral drugs are administered directly into the veins, muscles or under the skin or more specialized tissues such as spinal cord.
ADVANTAGE :-
1. Avoidance of first pass metabolism.
2. Faster absorption and rapid site on action.
3. The successful administration of the drug sensitive to the digestive system.
4. An immediate physiological response is usually provided by an intravenous injection of an aqueous solution.
DIS ADVANTAGE :-
1. The necessity of aseptic technique in production ,compounding and administration.
2. The requirement of trained personnel for administration.
3. The real or psychological pain associated with the injection.
4. Its higher cost as compared to oral dosage forms.
Ideal requirements of sterile dosage :-
1. All product must be sterile.
2. All products must be free from pyrogenic contamination.
3. Injectable solution must be free from visible particulate matter.
4. It is isotonic nature.
5. It is chemical purity.
Parenteral routes :-
the term parenteral literally means to avoid the gut & refers to any route of administration outside of or besides the alimentary tract.
1. Intravenous
2. Intramuscular
3. Subcutaneous
4. Intra dermal
5. Intra arterial
6. Intracardiac
7. Intrathecal
8. Intracisternal
9. peridural
10. intraarticular
11. intracerebral
Classification of parenteral products :-
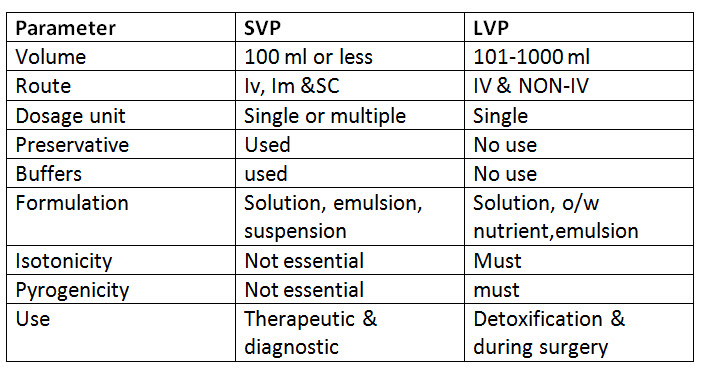
1. small volume parenterals (SVP) :- An injection that is packed in containers labeled as containing 100 ml or less.
2. Large volume parenterals (LVP) :- :- An injection that is packed in containers labeled as containing 101 ml or more.
FORMULATION OF PARENTERALS :-
1. Aqueous vehicle :-
• Water for injection (WFI) USP :- High purified water used as a vehicle for injective preparation which will be subsequently sterilized. USP requirements include not more than 10 ppm of total solids & pH of 5.0-7.0. WFI may be prepared by either distillation or reverse osmosis. Stored in chemically resistant.
• Bacteriostatic water for injection :- this type of water used for making parenteral solutions prepared under aspetic conditions & not terminally sterilized. Need to meet USP sterility test. It can contain an added bacteriostatic agents when in containers of 30 ml or less.
• Sterile water for injection :- SWFI’s containing one or more suitable bacteriostatic agents. Multiple-dose containers not exceeding 30 ml. they are permitted to contain higher levels of solid than WFIs because of possible leaching. Used for washing wounds surgical incisions or body tissues.
• Water miscible vehicle :- the number of solvent that are miscible with water has been used as a portion of vehicle. Primarily to affect solubility of drugs and to reduced hydrolysis. Example :- ethyl alcohol, liquid propelene glycol, glycerine, ethyl alcohol used in the case of cardiac.
2. Non – Aqueous vehicles :- fixed oil (vegitable origin, liquid & rancid resistance, unsaturated free fatty acid content )
• Peanut oil
• Corn oil
• Sesame oil
• Soybean oil
• Isopropyl myristate
3. Other additives :-
• Anti bacterial agents :- these are added in multiple dose containers. To prevent micro organism growth. Limited conc. of agent are used. To prevent micro organism growth. Example benzethonium chloride & benzalkonium chloride 0.01 % , phenol & cresol – 0.05 % chlorobutanol 0.05 %
• Buffers :- they are used to maintain pH. They are used in cocn. Of 0.1 to 5%. Example is acetic acid, adipic acid, benzoic acid, citric acid
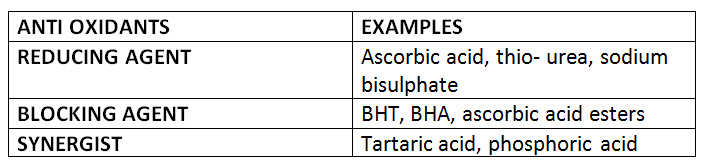
• Anti oxidants :-
• Chelating agents :- forms complexes & inactive metal those are responsible for oxidative degradation of drug. Ex. EDTA, Di sodium edentate
• Tonicity adjusters :- Nacl , mannitol
• Stabilizer :- glycerin, niacinamide
• Emulsifying agents :- lecithin
• Suspensing agents :-gelatin, pectin, methyl cellulose









