 CHAURASIYA AMRITA*, ARORA RIMJHIM, RATHORE KS, CHUNDAWAT AVS
CHAURASIYA AMRITA*, ARORA RIMJHIM, RATHORE KS, CHUNDAWAT AVS
Faculty of Pharmacy, BN University, Udaipur- Raj.313001
rimjhim.arora30@gmail.com*
ABSTRACT
Six Sigma is a highly disciplined activity that focuses on growing and giving near perfect product and services. Six Sigma focuses what is important to customer. It reduces defects in process variation so that virtually all the products or services provided meet customer expectations. Six Sigma has been used by some of the world’s most successful companies leading to savings of billions of dollars, increases in speed and capacity in their processes and achieving new, stronger customer relationships. The pharmaceutical industry is noticing diminishing promotes due to the competition from generic brands and errors within the manufacturing process. To improve this, many companies are attempting to increase efficiency within the manufacturing and operational processes by reducing waste and errors. By applying six sigma and lean manufacturing, many pharmaceutical companies are able to reduce waste and bring about effective change within the manufacturing process. The pharmaceutical industry rules and regulations are mainly alarmed with the quality, safety as well as efficacy of the products at the higher levels. This is the need to accomplish the best quality in the various processes in the pharmaceutical industry. The requirement of the business strategy such as six sigma arises in this condition.
INTRODUCTION
Six sigma is a process which is a combination of 4Ms that is man, machine, materials and methods for producingproducts or services which meets customer’s expectation these are evaluated by statistical methods and must have inherent statistical variability.This process yield nearly ideal products and services. It is a philosophy of quality and the way of surpassing accomplishment by determining where you are and where you could be. At six sigma level, there are 3.4 defects occurred per million opportunities (Acharya SK, 2015).
In statistics six Sigma is a way of measuring a process or a product in terms of defects and provides a way to pivot on growing and giving nearly perfect products and services. Six Sigma simply means a measure of quality. Six Sigma is a data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects in any process from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service (Sharma OP, Rathore GS, 2011).
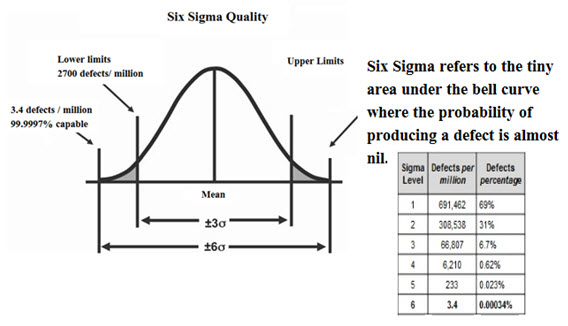
Fig.1: Six Sigma
Six sigma find strategies to decrease internal costs and cycle times by imparting high quality services, through innovative design and efficient response to the unexpected increase in demand for certain products. Six Sigma was developed based on preceding Quality Management concepts such as Total Quality Improvement, Quality Control and Zero Defects.The methodology measures a process in terms of defects, uses statistical tools to identify the vital factors that affect most for improving the quality of the process and tries to eliminate defects.
Definition
Six sigma is both a methodology for process improvement and a statistical concept that seeks to define the variation in any inherent process (Craig JS, 2018 July8).
Key Concepts of Six Sigma
At its core, Six Sigma revolves around a few key concepts.
1. Critical to Quality: what is important for the customer needs to be identified (Jernelid M, Roan S, 2009)
2. Defect: Failing to deliver what the customer wants (Tutorial Point, 2020).
3. Process Capability: The processes need to be able to deliver what the customer wants.[5]
4. Variation: What the customer sees and feels (Jernelid M, Roan S, 2009).
5. Stable Operations: Ensuring consistent, predictable processes to improve what the customer sees and feels (Jernelid M, Roan S, 2009).
6. Design for Six Sigma: The design must meet all the customer requirements and the capability of the process (Tutorial Point, 2020).
Our Customers Feel the Variance, Not the Mean. So Six Sigma focuses first on reducing process variation and then on improving the process capability.
Goals of six sigma :
• To enhancing customer satisfaction
• To enhance competitiveness.
• To change organizational culture.
• To enhance quality of product and services.
• Decreasing defects.
• Controlling variation and improving predictability.
• Lessen costs – without unintended consequences.
• To develop organizational competencies.
• To improve organizational performance.
• Reducing process cycle times and time-to market.
• Boosting end-to-end process management and measurement. (Sharma OP, Rathore GS, 2011and Kare PT, 2014)
• Less equipment and human are needed (Nnanna I, 2019).
Features of Six Sigma
1. It eliminate waste and inefficiency, thus increases customer satisfaction by delivering what the customer is expecting.
2. Six Sigma is strictly structured methodology, which is very specific for the particular participants.
3. Six Sigma is statistical data driven methodology which requires accurate or error-less data to perfectly analyse the process.
4. Six Sigma put results on financial statements.
5. Six Sigma is a business-driven, multi-dimensional structured approach for:
• Upgrading Processes
• Decreasing Defects
• Diminishing process variability
• Diminishing costs
• Extending customer satisfaction
• Widening profits (Jernelid M, Roan S, 2009 and Kare, PT, 2014).
DMAIC
Six Sigma Methodologies totally revolves around one main cycle called DMAIC

D = Define
The Define Phase is the first phase, in this phase, the leaders of the project begin to understand the needs of the customers or simply what new business objective or customer demand. (Manish Rathi, 2020 and Krishnan RB, 2013)
M = Measurement
This is the crucial step.The team focuses on data collection initially they have two focuses: determining the start point or baseline of the process and looking for clues to understand the root cause of the process (Krishnan RB, 2013).
A = Analyse
In this step the team has to analyse what is causing the problem and where there will be the opportunity to improve the process or service quality or cost or product. In this step team spend their time on discovering root causes of problem and constructing the solution as per the results (Manish Rathi, 2020).
I = Improvement
In this step the team has to accumulate data to check if there is measurable improvement or not if yes then the team will follow these process as a core process than pilot process and then finally refine the baseline ultimately it leads to refine the service quality or product quality which finally meets the customer satisfaction (Manish Rathi, 2020).
C = Control
This is the step in which team has to control the process and sustain the changes and improvement they made in the process or service (Manish Rathi, 2020).
Lean Methodology
Lean is a systematic approach to reduce or eliminate activities that don’t add value to the process that is waste. It has five principles:
1. Precisely specify value by specific product
2. Identify the value stream for each product,
3. Make value flow without interruptions
4. Let the customer pull value from the producer
5. Pursue perfection
The first requirement in making a successful transition to leanis to have a clear vision of what the company will become (Tohidi H, Liravias KK, 2012 and Henderson, BA, Larco LJ, 2003).
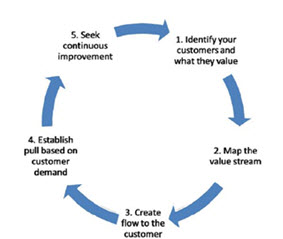
Fig. 2: Five principles of lean methodology
Lean six sigma (educba.com, 2020)
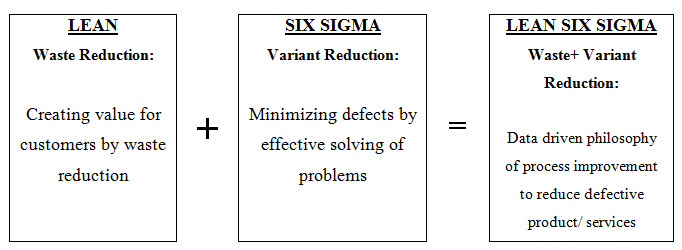
Fig. 3: Lean methodology with six sigma process
As the name indicates, ‘Lean Six Sigma’ is merger of ‘Lean’ and ‘Six Sigma’ processes. Thus, Lean Six Sigma (LSS) is a combined process to make the business effective itsanctions improvement in quality and efficiency. Lean is all about speed and efficient management of the business by reducing the waste of resources. While, Six Sigma, is a methodology that minimizing errors of the processes and quality improvement.
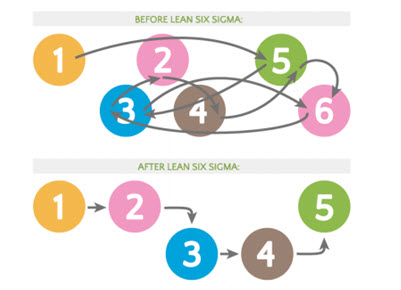
Fig. 4 : Lean six sigma process; before and after (Goleansixsigma.com, 2020)
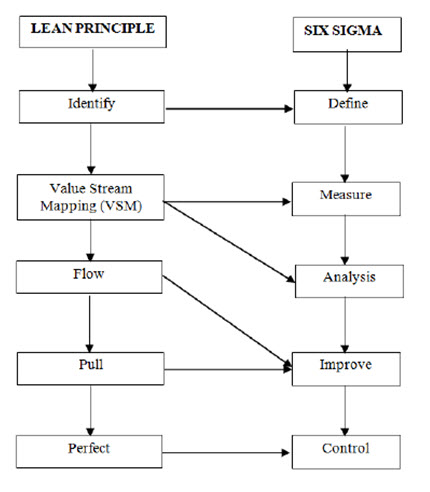
Fig. 5. The relationship of Lean Principles and Six Sigma Model (Nnanna I, 2019 and Elbermawy MF, 2014)
Link between lean and pharma environment:
Lean’s has twogoals : to reduce or abolish waste and to create value while cGMP has goal to ensure that controls are in place to deliver a safe and effective medicinal product. In the pharma environment to improve the operational efficiency effective lean management concepts should be identified because in many a time cGMP and lean management concepts overlap.
Pharma companies are concern about the product quality as compare to cost and productivity. There is a definite role of quality control and quality assurance in implementing lean principles. Only if quality control and quality assurance are strictly adopted, the management goals such as name of the company, sales and profits could be achieved because of quality products with less cost (Jaiganesh V, Sudhahar JC, 2013).
Example of DMAIC in pharmaceutical industry (Acharya SK, 2015)
A tablet is a pharmaceutical solid dosage form which contains amixture of active and inactive substances which are natural or synthetic in a powdered form, pressed or compacted from a powder into a solid dose.
D = Define
Define phase defines what can be the problems. Such as what is metal in tablet? How is metal enters in tablets? What is the toxicity level of metal? Etc. so that we can be aware of problem before the process starts.
M = Measurement
In this phase we try to measure the process. Such as theoretical weight of tablet. Raw material testing.Processes to find metals in tablets such as assays etc.
A = Analyse
In this phase we try to understand the root cause of the problem. Such as why metal enters in tablet? Why weight variation can occur etc.
I = Improvement
In this phase we apply the decisions which are taken after the analysis phase so that no problem will be there in process.
C = Control
In this process we have to go for process capability index at the start of every process.
For example samplings of tablets should be done in definite interval.
Six sigma and the pharmaceutical industry :
The following key strategies are suggested to launch a Six Sigma effort within the pharmaceutical industry:
• By the use of Six Sigma with a commitment from top down leadership conventional ways of conducting clinical trials can be changed by promoting implementation of needed integration initiatives
• Focus on the integration of technology and workflow improvement in meeting challenges and extend new ventures not possible using conventional isolated implementation of technology or home grown process improvement methodologies.
• Provide tested research approaches for the quantitative evaluation of clinical development and process improvement strategies, the integration of which highly correlates with strong financial performance (Kare PT, 2014).
• Six sigma in pharmaceutical manufacturing industry :
The six sigma quality improvement theory allows continuous improvement in business. This process is so composite, businesses will require a flexible systems that will allow information to pass across the entire business. Lean six sigma allows information to flow and keeps management in a row with this information.
Within the pharmaceutical industry, minimizing data and interpreting it quickly are very important aspects of lean six sigma. Having data as quickly as possible will also make it much easier to respond to and evaluate FDA inquiries.
In pharmaceutical industry once a process has validated and then a compliant is made, thencompany are naturally restrained to changes. Various drug manufacturers have had no real economic incentive implemented which would have them change their processes.
In order to have profitable change within the pharmaceutical industry many companies are turning towards lean six sigma concept.With its implementation, the pharmaceutical industry will be able to effect positive change. They will be able to reduce and eliminate waste, improve customer service and change the market entirely (Kabir A, 2013).
Key characteristics and success criteria:
George, Rowlands and Kastler define four key factors which form the basis for Lean Six Sigma:
(1) Satisfy customer demand by delivering speed and quality
(2) Improve processes by increasing flow while reducing variation and defects
(3) Take decisions based on data and facts, and
(4) Use human resources to increase cross functional teamwork (Reijins TJF, 2010)
Conclusion
Lean is anapproach to reduce or eliminate activities that don't add value to the processthat is waste and additionalactivities such astime loss, transportationand replacement of inappropriate material,over- production of the product. On the other hand six sigma is both a methodology for process improvement and a statistical concept that tries to define the variation in any inherent process.This review showedhow the combination of leanmanufacturing principles and six sigma tools and techniqueschanged both process and quality level of the productproduced in the industry. The combination of the twoconcepts is called lean-six-sigma which is a powerful tool that caninfluence processes and customer’s satisfaction. Lean six sigma is a methodology for continuous improvement. In pharmaceuticals lean manufacturing evaluate all of the operation of a processesand review and reduce the additionalactivities.It also predict errors and remove them.Combination of these two methods is ahard and strong barrier against the dispersion thatincludes plant layout and concern on special stages.
REFERENCES:
• Acharya SK, Laha A, Acharya PK, Tripathy S (2014 November - April 2015); Applications of Six-Sigma in Pharmaceutical Industries.International Journal of Research in Mechanical Engineering and Technology; 5(1), 22-28.
• Craig JS (2018 July8); Council for Six Sigma Certification, Six sigma A Complete step by step guide.
• educba.com; Career Lean Six Sigma Available from: https://www.educba.com/career-lean-six-sigma/ As on 12 January 2020.
• Elbermawy MF, Manhawy AA and Ibrahim HEA (2014); Implementation of Lean six sigma For Improving Supply Chain processes in a Pharmaceutical Industry. International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research; 5(8), 519-529.
• Goleansixsigma.com; The Basics of Lean Six Sigma; Available from:http://www.goleansixsigma.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/The-Basics-of-Lean-Six-Sigma-www.GoLeanSixSigma.com. Accessed on 12 January 2020.
• Henderson, BA, Larco LJ (2003); Lean Transformation: How to change your business into a lean enterprise. Virginia: Oaklea Press.
• Jaiganesh V, Sudhahar JC (2013 February); Sketching Out the Hidden Lean Management Principles in the Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications; 3(2), 1-12.
• Jernelid M, Roan S (2009); Six Sigma Strategies Applied To the Pharmaceutical Industry - How Customer Benefits, MBA Thesis; Submitted to Blekinge Institute of Technology.
• Kabir A [November 15, 2013]; Pharmamirror.com; Six sigma in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Industry Available from: https://www.pharmamirror.com/pharmaceutical-articles/six-sigma-in-pharmaceutical-manufacturing-industry/
• Kare PT, Bhor NJ, Bhusare SE, Chaudhary RA (2014); Six Sigma: An Emerging Approach in Pharma Industry. International Journal of Pure and Applied Bioscience; 2 (5)132-138.
• Krishnan RB, Prasath KA (2013); Six Sigma Concept and DMAIC Implementation International Journal of Business Management and Research; 3(2)111-114.
• Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certificate, 2020; https://www.stcloudstate.edu/continuingstudies/ceo/project-management/lean-six.aspx. Accessed on April 10, 2020.
• Manish Rathi, Novelvista [Last updated 09/01/2020]; Overview of Six Sigma - Top 5 Principles, Features, Benefits Available from: https://www.novelvista.com/blogs/quality-management/top-5-sixsigma-certification-benefits.
• Nnanna I, Olanrewaju F, Uzorh AC (2019); Lean Six Sigma Methodology and Its Application in the Manufacturing Industry – A Review. American Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering; 4(3), 40-44.
• Reijins TJF (2009/2010); The Advantages and Limitation of Lean Six Sigma in Process (Re) Design. Bachelor’s Thesis Organization and Strategy – Lean Management. Submitted to Tilburg University in Premaster Logistics and Operations Management.
• Sharma OP, Rathore GS (2011); Six Sigma in Pharmaceutical industry and Regulatory A?airs: A Review; Journal of Natura Conscientia; 2(1), 273-293.
• Tohidi H, Liravias KK (2012); Six Sigma Methodology and its Relationship with Lean Manufacturing System. Advances in Environmental Biology; 6(2), 895-906.
• Tutorial Point (2020); Six Sigma – Introduction Available from: www. Tutorials point. Com. Six Sigma Process Improvement Approach.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT admin@pharmatutor.org
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









