 About Authors:
About Authors:
Nishtha mukherjee
Shri ram institute of technology
jabalpur (m.p.) 482002
Nishthamukherjee210@gmail.com
ABSTRACT: Eclipta alba offers a remarkable activities for curing of many diseases. It has wide range of chemical constituents. Clinical investigations have been done on pharmacological activities like hepatotoxicity, proliferative, diabetic, hypolipedemic etc. Eclipta alba leaves were collected and dried. Furthur aquous and ethanolic extract were prepared and evaluated for anti microbial, anxiolytic and muscle relaxant activity.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1584
INTRODUCTION
ECLIPTA ALBA: ECLIPTA ALBA (L.) is a small branched annual herbaceous plant with a long history of traditional medicines uses in many countries espicially in tropical and subtropical region. The herb has been known for its curative properties and has been utilised as antimytotoxic, analgesic, antibacterial, antihepatotoxic, antihyperglycemic, antioxidant, immunomodulatory properties and it is considered as a good rejuvenator too.
Eclipta alba (L.) is an annual herbaceous plant, commanly known as false daisy. It is an erect or prostate, much branched, roughly hairy, annual, rooting at the nodes, the leaves are opposite, sessile and lanceolate.Belonging to family Asteraceae.It is also known as Bhringaraj and Karisilakanni, which is found a comman weed throughout India ascending up to 6000ft. The genus name comes from the Greek word meaning “Deficient,” with reference to the absence of the bristles and awns on the fruits. The specific Eclipta alba means white which refers to the color of the flower. Main active principle consist of constituents like furanocoumaris, oleanane and taraxastane glycosides.

[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
1. Eclipta alba(L.) Hassk. (syn.Eclipta prostrata L.), commonly known as False Daisy , yerba de tago, and bhringraj, is a plant belonging to the family Asteraceae.
2. Root well developed, cylindrical, greyish. It is also named 'kehraj' in Assamese and karisalankanni in Tamil. Floral heads 6-8 mm in diameter, solitary, white, achene compressed and narrowly winged.
3. It grows commonly in moist places as a weed all over the world. It is widely distributed throughout India, China, Thialand and Brazil.
4. In ayurvedic medicine, the leaf extract is considered a powerful liver tonic, rejuvenative, and especially good for the hair.
5. A black dye obtained from Eclipta alba is used for dyeing hair and tattooing.
6. Eclipta alba also has traditional external uses, like athlete foot, eczema and dermatitis, on the scalp to address hair loss and the leaves have been used in the treatment of scorpion stings.
7. It is used as anti-venom against snakebite in China and Brazil (Mors, 1991). It is reported to improve hair growth and colour.
GEOGRAPHICAL SOURCE
Eclipta alba has been used in various parts of tropical and subtropical regions like south America,Asia ,Africa.There are three kinds of eclipta alba the white flowering, the yellow flowering and tha black fruiting,but all three grow throughout India by marshes, rivers, and lakes or on the foot hills of the himalayas.
Macroscopy: It is an erect or prostrate, much branched, roughly hairy, annual, rooting at the nodes, the leaves are opposite, sessile and lanceolate ,The specific Eclipta Alba means white which refers to the colour of the flowers.Flower heads have 6 to 8 mm in diameter,solitary, white, achene compressed and narrowly winged. Root well developed, cylindrical, greyish.

Plant is bitter, hot, sharp, dry in taste and is used in ayurveda & "siddha" for the treatment of Kapha and Vata imbalances. In India, the plant is known as bhangra, "bhringaraj" or bhringraja. Another plant Widelia calendulacea is also known by the same name, but Eclipta has white flowers so called white bhangra and Widelia has yellow flower so it is called yellow Bhangra.
PHYTOCHEMISTRY
Eclipta alba (L.) contains wide range of active principles which includes coumestans, alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, polyacetylenes, triterpenoids. The leaves contain stigmasterol, a-terthienylmethanol, wedelolactone, demethylwedelolactone and demethylwedelolactone-7-glucoside. The roots give hentriacontanol and heptacosanol. The roots contain polyacetylene substituted thiophenes.The aerial part is reported to contain a phytosterol, P-amyrin in the n-hexane extract and luteolin-7-glucoside, P-glucoside of phytosterol, a glucoside of a triterpenic acid and wedelolactone in polar solvent extract. The polypeptides isolated from the plant yield cystine, glutamic acid, phenyl alanine, tyrosine and methionine on hydrolysis. Nicotine and nicotinic acid are reported to occur in this plant.
Parts containing chemical constituents:
|
Sl.No. |
Parts |
Chemical constituents |
|
1 |
Leaves |
Wedelolactone[1.6%], Desmethylwedelolactone,Desmethyl-wedelolactone-7-glucoside, stigmasterol |
|
2 |
Roots |
Hentriacontanol, Heptacosanol& Stigmasterol, Ecliptal, Eclalbatin. |
|
3 |
Aerial parts |
P-amyrin & Luteolin-7-O-glucoside, Apigenin, Cinnaroside, Sulphur compounds, Eclalbasaponins I-VI |
|
4 |
Stems |
Wedelolactone |
|
5 |
Seeds |
Sterols, Ecliptalbine (alkaloid) |
|
6 |
Whole plant |
Resin, Ecliptine, Reducing sugar, Nicotine, Stigmasterol, Triterpene saponin, Eclalbatin, Ursolic acid, Oleanolic acid |
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES:
Crude extract:
The crude extract has been found to have wound healing properties. It been reported to counteract CCl4-induced inhibition of the hepatic microsomal drug metabolizing enzymes. The loss of hepatic lysosomal acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase by CCl4 was significantly restored by Eclipta alba. The study shows that hepatoprotective activity of Eclipta alba is by regulating the levels of hepatic microsomal drug metabolizing enzymes. The fresh plant is used as self medication by AIDS patients in southern Thailand and showed potential as a therapeutic agent against Giardia intestinalis infections. The leaf extract showed hypolipedemic activity in atherogenic diet induced hyperlipedemic rats. It has antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. 3% extract of Eclipta alba is used in pilex formulation with other ingredients. It has been reported to decrease bleeding time. Leaf extract has been used in edema. It is used in the treatment of paronychia.
Pharmacological activities of the chemical constituents:
|
Sl.No |
Chemical constituents |
Pharmacological activites
|
|
1 |
Wedelolactone |
Antihepatotoxic Antibacterial, Trypsin Inhibitor, Antivenom |
|
2 |
Eclalbosaponins |
Hair revitalizing, Antiproleferative, Antigiardial |
|
3 |
Demethylwedelolactone |
Antihepatotoxic, Antihaemorrhage, Antivenom, Dye (cosmetic) |
|
4 |
Dasyscyphin C |
Antiviral,Anticancer |
|
5 |
Eclalbatin |
Antioxidant |
|
6 |
Ecliptalbine, verazine |
Lipid lowering, Analgesic |
Other pharmacological activities:
It has been reported that the importance of free carboxylic acid at C-28 position in echinocystic acid derivatives from the methanolic extract Eclipta prostrata showed antifibrotic activity. Ethanolic and ethyl acetate fractions of Eclipta prostrata were tested for its antibacterial activities against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Shigella dysenteriae, Salmonella typhi, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus. Eclipta prostrata is combined with a non-plant material which is used to bath children suffering from malnutrition for 9 days and used as self medication by AIDS patients in southern Thailand. 16 parts of Eclipta prostrata (bhringaraj), 1 part of Triphala formula {Emblica officinalis (amalaki), Terminalia chebula, (haritaki), Terminalia belerica (bibhitaki)}, 1 part of Caltropis gigantean (arka) and 1 part of Smilax officinalis (sariva) mixed with 80 parts of sesame oil and boiled to make a medicated oil which is reported to be used in skin diseases.
Combination therapy:
Eclipta alba (whole plant), Mimosa pudica (whole plant), Vitex negundo (whole plant), and Solanum nigrum (aerial parts) possessed styptic and anti-inflammatory properties and help in regeneration of the vascular endothelium36. Combination of Herbs like Anethum sowa (Shatapushpa), Piper longum (Pippali mool), Valeriana wallichii (Tagar), Cassia fistula (Aragvadh), Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) and Triphala (A herbal combination of three fruits) with Eclipta alba (Bhringaraj) pacify the aggravated Vata dosha and combination with Elaeocarpus ganitrus (Rudraksha), Herpestris monniera (Brahmi) showed a tranquilizer effect
LITERATURE REVIE
1.David Banji et.al reported the Impact of aqueous extract of Eclipta alba on material aggression in rats
2.Anal K Jha, Kamlesh Prasad, et.al studied the biosynthesis of silver nano particles using eclipta leaves.
3.R.K.Roy,Mayank thakur et.al revealed the hair growth promoting activity of Eclipta alba in male albino rats.
4.Otilia J.F. Lobo David Banji et al evaluated the antiaggressive activity of Eclipta Alba in experimental animals.
5.Saroj Bapna, et.al.revealed Anti malerial activity of Eclipta alb AGAINST PLASMODIUM BERGHEI.
6.Vasavi Rangineni et.alreveiled diuretic,hypotensive and hypocholesterolemic effects of Eclipta Alba in mild hypertensive subjects :a pilot study.
7.V.D.Thakur and S.A.Mengi reveiled the Neuropharmacological profile of eclipta alba (linn.) Hassk.
MATERIAL AND METHOD:
COLLECTION OF BHRINGRAJ PLANT.The proper source of the crude drug was identified and the bhringraj plants were collected from Jabalpur division of M.P. State.during JULY2011.
HARVESTING:. the bhringraj plants were collected and washed properly and other plants like grass etc. Were removed from it.
DRYING: Drying consists of removal of excess moisture content of crude drug,so as to improve its quality and make it resistant to microbial contamination.Hence the collected plants were dried for sufficient amount of time under shade to prevent loss of volatile constituents.
PREPARATION OF EXTRACT: The mature leaves were cleaned, dried under shade and were ground into a coarse powder. 50 gram of the powdered plant was successively extracted with ethanol and water by hot soxhlet method. The extraction was carried out for 4 hours for each solvent. The ethanolic as well as aquous extract were concentrated to get the dry residue.The dried residue were weighed.The extracts were condensed using rotary vaccum evaporator followed by vaccum evaporator and stored in a desiccators.EXTRACTIVE VALUE
|
EXTRACT |
WEIGHT OF HERB |
EXTRACTIVE VALUE |
|
Ethanolic extract |
50gm |
6.328% |
|
Aquous extract |
50gm |
4.677% |
4.3.2 PRELIMNARY PHYTOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATION:
Identification Of The Plant Constituents By Phytochemical Tests: Ethanolic extract is subjected to various preliminary phytochemical analysis to test for the presence or absence of various phytoconstituents by the following tests.
1. Test for alkaloids: To the extract dilute hydrochloric acid will be added and filtered. The filtrate will be treated with various alkaloid reagents.
a) Mayer’s test: The filtrate will be treated with Mayer’s reagent: appearance of cream colour indicates the presence of alkaloids.
b) Dragendroff’s test: The filtrate will be treated with Dragendroffs reagent: appearance of reddish brown precipitate indicates the presence of alkaloids.
c) Hager’s test: The filtrate when treated with Hager’s reagent, appearance of yellow colour precipitate indicates the presence of alkaloids.
2) Test for carbohydrates and reducing sugar: The small quantities of the filtrate will be dissolved in 4ml of distilled water and filtered. The filtrate will be subjected to
a) Molisch’s test: A small portion of the filtrate will be treated with Molisch’s reagent and sulphuric acid. Formation of a violet ring indicates the presence of carbohydrates.
b) Fehling’s test: The extract will be treated with Fehling’s reagent A and B. The appearance of reddish brown colour precipitate indicates the presence of reducing sugar.
c) Benedict’s test: The extract will be treated with Benedict’s reagent; appearance of reddish orange colour precipitate indicates the presence of reducing sugar.
d) Barfoed’s test: The extract will be treated with barfoed’s reagent and heated. Appearance of reddish orange colour precipitate indicates the presence of non reducing sugars.
3) Test for proteins:
a) Biuret test: The extract will be treated with copper sulphate solution, followed by addition of sodium hydroxide solution; appearance of violet colour indicates the presence of proteins.
b) Millon’s test: The extract will be treated with Millon’s reagent; appearance of pink colour indicates the presence of proteins.
4) Test for tannins: The extract will be treated with 10% lead acetate solution; appearance of white precipitate indicates the presence of tannins.
5) Test for phenolic compounds:
a) The extract will be treated with neutral ferric chloride solution; appearance of violet colour indicates the presence of phenolic compounds.
b) The extract will be treated with 10% sodium chloride solution; appearance of cream colour indicates the presence of phenolic compounds.
6) Test for flavonoids:
a) 5ml of extract will be hydrolyzed with 10%sulphuric acid and cooled. Then, it will be extracting with diethyl ether and divided in to three portions in three separate test tubes. 1ml of diluted sodium carbonate, 1ml of 0.1N sodium hydroxide, and 1ml of strong ammonia solution will be added to the first, second and third test tubes respectively. In each test tube. Development of yellow colour demonstrated the presence of flavonoids.
b)Shinoda’s test: The extract will be dissolved in alcohol, to which few magnesium turnings will beaded followed by concentrated HCL drop wise and heated, and appearance of magenta colour shows the presence of flavonoids.
7) Test for glycosides : When a pinch the extract was treated with glacial acetic acid and few drops of ferric chloride solution, followed by the addition of conc. Sulphuric acid, formation of ring at the junction of two liquids indicates the presence of glycosides.
8) Test for saponins
Foam test : About 1 ml of the extract was diluted to 20 ml of with distilled water and shaken well in a test tube. The formation of foam in the upper part of test tube indicates the presence of saponins.
PREPARATION OF STOCK SOLUTION:
Stock solution was prepared by dissolving 100mg of extract in 100ml of water.
SELECTION OF DOSE:
Dose was selected according to LD 50 of Bhringraj.LD 50 was found out to be 3000mg/kg.
1st dose was selected as 1/10th of LD 50-300mg/kg.
2nd dose was selected as ½ of LD 50-150mg/kg.
TESTS
Individual tests were performed for
1.Anti microbial,
2.Antianxity &
3.Muscle relaxant activity.
ANTI MICROBIAL ACTIVITY
Two procedures are generally employed in microbial assay
1.CYLINDER PLATE METHOD(CUP): This is based on measurement of the diameter of microbial growth inhibition surrounding the cylinders containing various dilutions of the test compound which are placed on the surface of a solid nutrient medium previously inoculated with a culture of suitable microbe.Inhibition produced by the test compound is compared with that produced by known concentration of a refrence standard.
TURBIDIMETRIC METHOD: Based on inhibition of microbial growth as in indicated by measurement of turbidity(transmittance)of suspension of a suitable micro-organism in a fluid medium,to which have been added graded amounts of the test compounds.Changes in the transmittance produced by the tested compounds are compared with those produced by known concentration of standard.
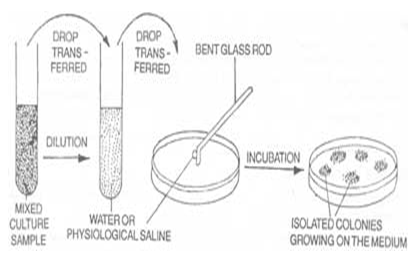
Anti-microbial activity of bhringraj:
Requirements: Aquous as well as ethanolic extract of eclipta alba, B.subtilis, E.coli.nutrient agar medium,cup & plate.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
PROCEDURE:
1. Two bacteria, (gram +ve i.e. B.subtilis, gram-ve i.e E. Coli) were used in the present study to determine the antibacterial activity of the crude extracts by agar diffusion method (cup plate method).
2. In the agar diffusion method, nutrient agar for bacteria used as culture media and cavity were aseptically made over the culture platesusing borer (9mm internal diameter).
3. Thecavities were filled with extracts, standards and control The plates were incubated at 37 0 C for 24 hrs.
4. The activities were determined by measuring the diameter of the zone in mm.
5. The experiment was replicated two times to confirm the reproducible results.
6. Solvent used as negative control in each time. Standard Ciprofloxacin(100mcg/0.1ml), Amoxicillin (100mcg/0.1ml) for bacteria were used as positive control for comparison of the activities.
OBSERVATION TABLE
|
S.No |
Name of drug |
Conc in mcg/disc |
E.coli mm |
B.subtilis |
|
1 |
Ciprofloxacin |
1000 |
41 |
40 |
|
2 |
Amoxicilin |
1000 |
21 |
27 |
|
3 |
Ethanolic extract |
300 |
16 |
17 |
|
4 |
Aquous extract |
300 |
19 |
15 |
RESULT :
Ethanolic and aqueous extracts of Eclipta alba Leaves were evaluated for antibacterial activity against E.coli, B.subtilis with the comparison with positive control (Ciprofloxacin and Amoxicillin) for bacteria.The extract showed good inhibitory activity on the microbes.
ANTI ANXIETY ACTIVITY:
Keeping this in mind, this study was under taken Assesment of antianxity activity by: Elevated plus maze apparatus: It is the most simple apparatus to study anxiolytic activity of almoxt all type of anti anxiety drugs. Exposure of the animals to novel maze alley evokes an approach- avoidance conflict which is stonger in open arm as compared to enclosed arm. Rodents(rats and mice) have aversion for high open space and prefer enclosed arm & therefore spend greater amount of time in enclosed arm. When animals enter open arm, they freeze, become immobile, deficate and show fear like movements. The plasma cortisol level is also reported to be increased, as a true reflection of anxiety. Major advantages of this test procedure are:
1. It is simple, fast and less time consuming.
2. No prior training or noxious stimuli is needed. & it is predictable and reliable method.
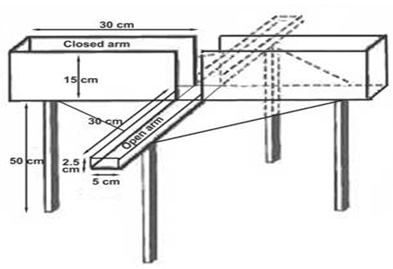
REQUIRMENTS:
Animal- Mice(20-25 gram)
Drugs- Ethanolic and aquous extract of bhringraj dose 300 and 150 mg/kg
Equipments: Plus maze apparatus consisted of 2 open arm and two enclosed arm with an open roof and is elevated to aheight of 25 cm,stop watch.
PROCEDURE:
1. All the animals were weighed and numbering was done Divided them into 3 groups each consisting of 2 mice each.One group was used as control and other 2 for drug treatment.
2. Placed the animals individually in the centre of the maze apparatus, head facing towards open arm and started the stop watch and the following parameters were noted -
a. First preference of mouse to open or closed arm.
b. Number of entries in open and closed arm.
c. Average time each animal spends in open and closed arm
d. 300mg/kg and 150mg/kg dose of extract of bhringraj was given to them orally..After 30 min the animals were placed individually in the centre of the maze and all parameters described in step 2 were repeated.
e. The preference of the animal to open /enclosed arm ,average time spent time in open arm and number of entries in open arm in each group were compared.
OBSERVATION TABLE
|
S.No. |
Drug |
Dose 1 |
Dose 2 |
n |
%prefrence to open arm |
Average time spent in open arm |
|
1 |
Control |
- |
|
2 |
11 |
7.5 |
|
2 |
Ethanolic extract |
300mg/kg |
150mg/kg |
2 |
35 |
16 |
|
3 |
Aquous extract |
300mg/kg |
150mg/kg |
2 |
32 |
14 |
RESULT: Extract of bhringraj increases % preference of the animals to open arm and increases the number of entries and average time spent by the mouse in open arm.As the dose increases the anti anxiety activity also increases.

MUSCLE RELAXANT ACTIVITY:
REQUIRMENTS: ANIMAL:mice (20-25 gm)
DRUG: Ethanolic and aquous extract of bhringraj dose 300 and 150 mg/kg.
EQUIPMENT: Rota rod apparatus

PROCEDURE:
1. All the animals were weighed and numbering was done .
2. The rota rod was turned on .An approx speed (20-25 rpm) was selected.
3. The animas were placed one by one on the rotating rod.(the rod was divided into several compartments and one mouse was placed at each compartment.The fall off time was noted when the mouse falls from the rotating rod.Anormal untreated mouse falled within 3-5 min.
4. The ethanolic extract (150mg/kg) was given orally to all the mouse. After 30 min the 3rd step was repeated. The fall off time was noted.
5. The 3rd and 4th step was repeated with ethanolic extract(300mg/kg)
6. The reading was taken.
7. The entire procedure was repeated with aquous extract(150 and 300 mg/kg)
8. The comparision was done of the fall off time of the animals before and after drug treatment.
OBSERVATION TABLE
|
S.no |
Body wt.(gm) |
treatment |
Dose1 |
Dose2 |
Fall off time before drug |
Fall of time after drug |
% decrease in time |
|
1 |
25 |
Ethanolic extract |
150mg/kg |
300mg/kg |
32 |
12 |
62.5 |
|
2 |
25 |
Aqouous extract |
150mg/kg |
300mg/kg |
32 |
15 |
53.125 |
RESULT: Both the alcoholic and aquous extract showed good muscle relaxant activity.As the conc. of the extract increased the activity as also found to be increased.
CONCLUSION:
Eclipta alba offers a remarkable activities for curing of many diseases.It has wide range of chemical constituents.Clinical investigations have been done on pharmacological activities like hepatotoxicity,proliferative,diabitic,hypolipedemic etc.It has a greater potential to inhibit the growth of the bacteria and fungus.Furtheer nvestigation of the plant can increase the isolation of the newer molecules which will be helpful for the study of the pharmacological activitiesand to discover from the plant thus preventing the human and economic losses in the environment.
REFERENCES:
1. H. Zhang., Xing, W.W., LI, Y.S., Zhu, Z.Wu,J.Z., Zhang,O.Y.,Zhang,W., Qin,L.P, Maturitas, 2008, 61,334-339.
2. D. Chamundeeswari., Vasantha, J., Gopalakrishnan, S., Sukumar, E, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2003, 88: 51-56.
3. O.A. Olajide., Echianu, C.A., Adedapo, A.D., Makinde, J. M , Inflammo pharmacology, 2004, 12: 196-202.
4. V. Cardile, Russo, A, Formisano, C. Rigano, D, Senatore, F, Arnold, N.A, Piozzi, F, J. Ethnopharmacol, 2009, 126: 265–272.
5. A. Mathur,R. Purohit, D. Mathur, G.B.K.S. Prasad, V.K. Dua, Der Chemica Sinicia, 2011, 2, 1, 174-181.
6. A. Mathur,R. Purohit, D. Mathur, G.B.K.S. Prasad, V.K. Dua, Der Pharmacia Sinicia, 2011, 2, 1, 208-216.
7. G. E. Trease and Evans WC, Text book of Pharmacognosy. 14 th Edition, London, 1996, pp 545.
8. S. P. Shri, Ambasta, Useful Plants of India, CSIR Publications, 1986, pp 189.
9. K.R .Kirtikar, B. D. Basu, Indian Medicinal Plants, Allahabad, 3: 1935,1361 Pocket Handbook of Chinese Herbal Medicine, Miami: Waclion International, 2000, pp.106.
11. M. McGuffin, Hobbs C, R. Upton, American Herbal Products Association’s Botanical Safety Handbook. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1997, pp. 44.
12. A.K. Saxena, Singh B, K. K.Anand, J Ethnopharmacol, 1993, 40 (3):155-61.
13. H. Wagner, Geyer B, Yoshinobu K, S.R. Govind, Planta Medica., 1986,5: 370-4
14. H. Wagner H, Planta Medica., 1986, 5:370-4.
15. S.C. Gupta, Bajaj UK,V.N. Sharma, J Res Ind Med Yoga & Homeop, 1976, 11:3, 91-93.
16. K.R. Brain, T. D. Turner, The Practical Evaluation of Phytopharmaceuticals. Wright- Science Technical, Bristol,1975, pp 57.
17. R. Parvataneni, P. Rajeswara Rao, J.Archana, N. K.Rao, Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2005, 28(7): 1311- 1315.
18. Bauer, Kirby, Sherris, Turck, Am. J. Clin. Path. 1966, 45: 493 -499.
19. Upadhyaya rk,Pandey MB,Jha R.N. ,Pandey V B.Eclipta alba a triterpine saponin from ECLIPTA ALBA
20. Scott Treadway. An ayurvedic herbal approach to a Healthy Liver. Clinical nutrition insights. 1998; 6(16): 01-03.
21. Baig MI, Bhagwat VG. Study the efficacy of Galactin Vet Bolus on milk yield in dairy cows. Veterinary world. 2009; 2 (4):140-42.
23. Rolf teschke, Ruediger bahre. Severe hepatotoxicity by Indian herbal products: A structured causality assessment. 2009; 8(3): 258-66.
24. Sagar B.P, Sangwan A, Panwar A, Sangwan A. In-vitro Production of Anti-hepatotoxic Compounds in Cultures of Eclipta alba Linn. and Silybum marianum gaertn. 2006; 6: 88.
25. Samudram P, Rajeshwari Hari, Vasuki R, Geetha, Sathiya moorthi P. Hepatoprotective activity of Bi-herbal ethanolic extract on CCl4 induced hepatic damage in rats. AJBR. 2008; 2(2): 61-65.
26. Lal V.K, Amit Kumar, Prashant Kumar, Kuldeep Singh Yadav. Screening of Leaves and Roots of Eclipta alba for Hepatoprotective Activity. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res.2010; 2(1): 86-94.
27. Dhandapani R. Hypolipidemic activity of Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. leaf extract in atherogenic diet induced hyperlipidemic rats. 2007; 45: 617-19.
28. Dae-Ik Kima, Sung-Hyen Lee, Jin-Ho Choia, Hyun Soon Lillehoj, Mi-Hee Yu, Gun-Soon Lee. The butanol fraction of Eclipta prostrata (Linn) effectively reduces serum lipid levels and improves antioxidant activities in CD rats. Nutrition Research. 2008; 28: 550-54.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









