About Authors:
D.K Jain*, G.N Darwhekar, Vikas Gupta
College of Pharmacy, IPS Academy
Indore (M.P)-452012, India
*jaindkj57@yahoo.com
Abstract
Convenience of administration and patient compliance are gaining significant importance in the design of dosage forms. Metformin hydrochloride and Glimepiride are orally administered antihyperglycemic agent, used in the management of non-insulin-dependent (type-2) diabetes mellitus. Difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia) is common among all age groups, especially in elderly and pediatrics. Unfortunately, a high percentage of patients suffering from type-2 diabetes are elderly people showing dysphagia. Persons suffering from dysphagia may get choked when they consume liquid formulation, thus to alleviate such problem liquid formulation of high viscosity was prepared. Formulation of oral soft jellies was carried out using combination of hydrophilic polymers guar gum and pectin. 3 different concentrations of guar gum (0.3 to 0.5% w/v) and 2 concentration of pectin were used (0.2 to 0.3% w/v) respectively. The prepared batches were evaluated for appearance, viscosity, pH, drug content, syneresis, in vitro drug release, and taste masking. The batch with 0.5% w/v guar gum and 0.2% pectin not only showed 80% drug release at 60 min, but all the desired organoleptic properties. The taste masking was carried out using non nutritive sugar and flavors. The optimized batch showed substantial stability when subjected to short term stability study (0-8°C and Room temperature). The problem of dose measurement by patients was outweighed as oral medicated gels are to be packed in unit dose container.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1279
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive illness and most patients will eventually need more than two oral agents to maintain adequate glucose control. Switching from one drug to another in a patient with poorly controlled glycemia or maximizing the dosage of an existing drug is only rarely hopeful. Adding medications from different groups to the existing regimen often provides more effective glycemic control. Several of the available oral agents have been studied in combination and have been shown to further improve glycemic control when compared with monotherapy(1).
Glimepride is one of the third generation sulfonylurea drug useful for control of diabetes mellitus, type 2. Preclinical investigation of glimepride suggested a number of potential benefits over sulfonylureas currently available including lower dosage, rapid onset possibly due to less stimulation of insulin secretion and more pronounced extra pancreatic effects.
Metformin hydrochloride is an orally administered biguanide, which is widely used in the management of type 2 diabetes. It is a hydrophilic drug and is slowly and incompletely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and the absolute bioavailability of a single 500 mg dose is reported to be 50% to 60%. The compound also has relatively short plasma elimination half-life of 1.5 to 4.5 hours, hence Metformin hydrochloride has to be administered two or three times per day (2).
Unfortunately, a high percentage of patients suffering from type-2 diabetes are elderly people showing dysphagia. The above problem becomes even more severe since the medication has to be taken lifelong everyday and the tablets are quite big due to the high therapeutic dose. A tablet comprising 1000 mg of metformin hydrochloride would need to have a size of 19 mm × 10.5 mm (Glucophage® 1000 mg tablets) or more as functional excipients are needed to modify release of drug from the dosage form and would be very difficult to swallow.
The patients with dysphagia can be choked by water while consuming liquid formulation which can be eliminated by administering liquid formulations with high viscosity. Thus, jelly formulation containing metformin hydrochloride and glimepiride combination was prepared.
The gel dosage form not only overcomes the disadvantages of liquid dosage form, but also of solid dosage forms. The problem of dose measurement by patients is outweighed as oral medicated gels are to be packed in unit dose container (3,4).
The aim of this research was to improve patient compliance by development of jelly preparation of an orally administered oral hyperglycemic agent (metformin hydrochloride/glimepride) used in treatment of non insulin dependent (type-2) diabetes mellitus.
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
Experimental
Materials
Metformin hydrochloride and Glimepiride were received as a gift sample from IPCA Lab Ltd.,Ratlam. All other chemical like guar gum, pectin, mannitol, citric acid, sodiumcitrate, methyl paraben, stevia used were of analytical grade.
Method
Preparation of oral soft jelly
All the required ingredients of the formulation were weighed accurately. Dry guar gum powder and pectin was dispersed in 50 mL of distilled water maintained at 80°C. The dispersion was stirred at 80°C for 20 min using a magnetic stirrer (Remi magnetic stirrer Mumbai, India) to facilitate hydration of guar gum. The required amount of mannitol was added to the gelling agent solution with continuous stirring and the temperature was maintained about 80-85°C. Metformin hydrochloride was added with stirring. Then stevia, citric acid, and preservative (methylparaben) were added with stirring. Finally, required amount of sodium citrate and sodium citrate was disspersed in 10 mL of distilled water and added to the mixture. At last colour and flavor was added. The weight of the gel was monitored continuously during manufacturing and finally it was adjusted to the 50 gm with distilled water. The mixture containing gelling agents, metformin hydrochloride, glimepiride and other additives was packed in polyethylene mould with airtight seal. The mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature to form jelly. The gels were prepared using three different concentrations of guar gum (0.3, 0.4, and 0.5%), each with two different pectin concentrations (0.2 and 0.3%).
Evaluation of oral soft gel
Following studies were carried out for evaluation of oral guar gum soft jelly of metformin hydrochloride and glimepiride.
General appearance
Texture and clearity of the soft gel was evaluated in terms of stickiness and grittiness by mildly rubbing the gel between two fingers. Consistency and odour were also evaluated by physical observation
Rheological measurement
Viscosity of the all the batches of soft gels was measured using Brookfield DV-II+Pro viscometer. The metformin hydrochloride and glimepiride containing soft jelly was squeezed out from the polyethylene plastic mould by making a cut of uniform size on the mould and viscosity was measured using spindle number LV4 at the rotation of 50 rpm at room temperature. The viscosity measurements were made in triplicate using fresh samples each time (4).
pH of the soft jelly
The pH of the final gel has got influence not only on stability, but also on the taste. The pH of metformin hydrochloride and glimepiride containing soft jelly was measured using Electroquip Digital pH meter at room temperature (6).
Syneresis
Syneresis is one of the major problems associated with low acylated guar gum gels. Syneresis means contraction of gel upon standing and separation of water from the gel. Syneresis is more pronounced in the gels where lower concentration of gelling agent is used. Gels were kept under scrutiny for signs of syneresis. The gels showing signs of syneresis were rejected and not considered for further studies (7).
Drug content
10 jellies were taken from jelly mould in a beaker and there average weight was determined They were breaked to gel consistency. Then gel equivalent 500mg of metformin hydrochloride and 2mg of glimepiride was taken in 100 mL volumetric flask and dissolved in 70 ml of methanol with vigrous shaking for 5-10 minutes. Finally the volume was made up to mark with methanol. Then it was analyzed in HPLC after proper dilution and filtration (4).
In vitro drug release
In vitro drug release studies was carried out using USP dissolution apparatus 2 using paddle at a speed of 100 rpm using 900 mL of 0.1N HCl as dissolution media containing 0.1% sodium lauryl sulphate at 37±2°C. The ready to use soft jelly (2.5 gm) containing 500 mg of metformin hydrochloride and 2mg glimepiride was used in the dissolution test. Five milliliters of sample was withdrawn at the interval of every five minutes and the drug solution was replaced with the same volume of 0.1N HCl (pH 1.2) maintained at 37±2°C. One milliliter of the filtered sample was diluted up to 50 mL with methanol and absorbance was measured at 251 nm using HPLC (8,9).
Evaluation of taste masking
5 mL of pH 6.8 phosphate buffer (to simulate salivary pH and volume) was used to study the taste masking efficiency of jelly preparation. One jelly equivalent to 500mg of metformin hydrochloride hydrochloride and 2mg glimepiride selected from batch F5 was placed in 50 mL beaker. 5 mL of the buffer solution was then added and the bottles were allowed to stand for 60 sec and 120 sec, respectively. After the specified time, the suspensions were filtered using 0.45 μ nylon filters. The filtrates were analyzed for drug content. The test was performed in triplicate (10,11).
Stability studies of soft gel
A physically stable oral jelly retains its viscosity, color, clarity, taste, and odor throughout its shelf-life. Gels were checked for syneresis during storage. A freshly made sample should serve as a reference standard for subjective evaluations.
The samples were kept at different temperatures (0-8°C and room temperature) for four weeks. The samples of soft gel were observed for pH, viscosity, and appearance at the interval of one week. All the measurements were performed after allowing the samples to be equilibrated at 25°C for two hours (4).
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
HPLC Method
Chromatographic condition:
Column:C8 coloumn (phenominex) (250×4.6mm, 5µm particle size)
Mobile Phase: Phosphate buffer of pH 6.8: methanol (75:25)
Detector:UV detection at 251nm
Loop size:20 µl
Stock standard solutions of Metformin hydrochloride, Glimepiride were freshly prepared in Methanol as 1g/mL. Calibration curve for each of analytes after appropriate dilution of stock solution to obtain final concentrations of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 µg/mL for Glimepiride and 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 µg/mL for Metformin hydrochloride. The calibration curve was prepared taking the peak area of the analytes (Glimepride/ Metformin hydrochloride) versus the concentration (μg/mL) using a linear least squares regression as the mathematical model. The regression equation of the calibration curve was then used to calculate the drug conten, in vitro taste evaluationt and in vitro drug release (12).
Results and Discussion
General appearance
The results of evaluation of metformin hydrochloride soft gel batches are shown in Table 1. All the batches of soft gels were transparent in appearance. The gel of batches F3, F4, and F5were non-sticky and non-gritty while the gel of batch F6 was slightly sticky. The non-gritty nature of the batches F3 to F5 may be due to the suitable concentration of guar gum and pectin but F6 was sticky due to higher concentration of both guar gum and pectin.
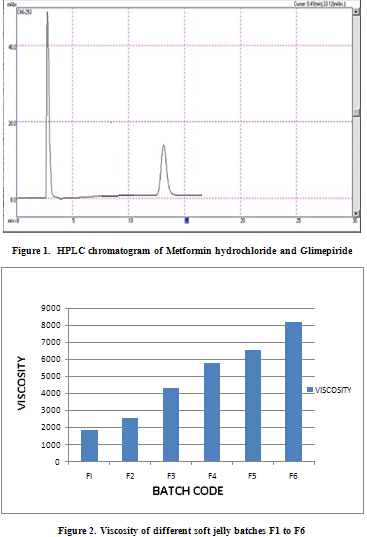
Viscosity
Viscosity is the one important parameter which provides vital information during the optimization of the soft gel. The results of evaluation of me soft jelly batches F1-F6 are shown in Table 2. The viscosity of the batches (as shown in figure 2.) F1 and F2 were low because of its fluid like consistency while the viscosity of the batches F5 and F6 were high because they were very thick in consistency. But, viscosity of batch F5 was near to in house specification. Thus, it was considered for evaluation along with F3 and F4. As the jellies of batch F6 were thick in consistency, sticky and gritty, they may failed to give good mouth feel. The viscosity of the batches F4 and F5 were acceptable supported by their acceptable consistency. The consistency and viscosity of the soft gels are related to each other because both are dependent on concentration of guar gum, pectin sodium citrate, and co-solute.
pH
The pH of the jelly preparation in the form of solution just before gelation is adjusted preferably to 4.0 or more upto 7. This is because when pH is below 4 jelly preparation liable to cause syneresis and stability of the preparation deteriorates in some cases. When the pH is 6 or more close to neutrality, the jelly preparation is far more excellent in stability. Therefore, the pH of the formulated gels was adjusted and maintained in between 5 and 7 with help of buffering agents such as citric acid and sodium citrate.
Syneresis
Syneresis is more pronounced in the gels where lower concentration of gelling agent is used. Syneresis was not noticed at room temperature probably due to binding of free water by co-solute. The batch F3 showed slight syneresis on standing, thus it was not considered for further studies.F5 and F6 showed very less degree of syneresis at room temperature and in refrigerator also (2-8°C). Syneresis was observed after 24 hrs of jelly preparation.
Drug content
The drug content of all the batches were in between 97.6±1.5 for metformin hydrochloride hydrochloride and 96.8 ±1.5 for glimepiride which is well within acceptable limits.
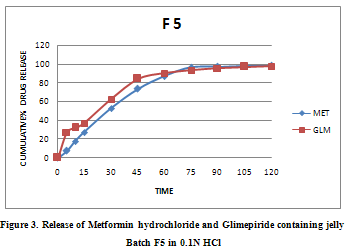
In vitro dissolution studies
The results shown in reveal that jelly of the batches F5 exhibited acceptable consistency and viscosity. Thus, it was subjected to dissolution study to draw any conclusion and their percentage drug release at different time intervals has been shown in Figure 3.
In vitro Taste Evaluation
There was no significant drug release observed during in vitro taste evaluation hence it can be correlated to taste feel. As insignificant drug was released, it is insufficient to impart bitterness.
Stability studies
The results of short-term stability studies, shown in Table 3. indicated insignificant changes in pH, viscosity, and appearance in the optimized formulation with time. Precipitation of drugs in the soft gels was not observed in any of the gels. Also, insignificant syneresis was not observed in any of the samples at both temperatures. Therefore, it is recommended that soft gel should be stored at about 25°C.
Conclusion
From Table No. 2 and Table No.3 it was found that the optimized soft jelly batch F5 was substantially stable at both room temperature and also at low temperature, thus storage at room temperature is possible. Also,fig.2 showed F5 was able to release 85% of drug before 2 H, thus meets in house specification. Finally, it was concluded out that batch F5 meets all laid in house specifications thus is the optimized batch.
REFERENCES
1. Ingle PV, Talelle GS. Rationale behind the combination of sulfonylurea and metformin hydrochloride in diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res.2010;1(7):1-5
2. Tripathi KD. Essentials of pharmacology 5th Ed..New Delhi, Jaypee brothers medical publisher;2005
3. Danish M, Kottke MK. Pediatric and Geriatric aspect of Pharmaceutics In: Banker G and Rhodes CT. Modern pharmaceutics. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc; 2007.
4. Mohapatra A, Parikh RK, Gohel MC. Formulation development and Evaluation of Patient Friendly Dosage Form of Metformin hydrochloride, part II: Oral soft gel. Asian J. Pharm. 2008;(2): 172-176
5. Gohel M C, Parikh RK, Nagori SA, Dabhi MR. Preparation and Evaluation of Soft Gellan Gum Gel Containing Paracetamol. Indian J. Pharm. Science. 2009;71(2):120-124
6. Ishibashi M, Endo M, Miwa Y,inventors; Gel preparation for oral administration. US Patent No. US2008/0160087 A1.2008 July25
7. Yokoyama H, Hirata A, Hamamoto H. Inventor. Biguanide drug containing jelly preparation US Patent No. US2007/0053939A1.2007 March 13
8. Aitha S, Ayappan T, Sundarmoorthy K and Vetrichevlan T. Optimization, Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Tablets of Levocetrizine Hydrochloride for the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis. J. Pharm. Sci. & Res. 2010; 2 (9): 555-561
9. Rao M, Sunil R, Kumar P and Rajanarayana K. Formulation and Release Characteristic of a Bilayer Matrix Tablet Containing Glimepride Immediate Release Component and Metformin Hydrochloride as Sustained Release Component I. J. Pharm. Sci. and Nanotechnology,2010; 3(1):851-859
10. Jogia H, Mehta T, Patel M. Evaluation of Dissolution Media Containing a Novel Synthetic Surfactant by In Vitro Testing of BCS Class II Drugs. J. Dissolution Technologies. 2009:14-19
11. Mishra B, Shukla D, Chakraborthy S and Singh S Mouth dissolving tablets II: an overview of evaluation techniques. Sci.Pharm.2009; 77: 327-341
12. Jain D, Jain S, Jain D and Amin M. Simultaneous Estimation of Metformin hydrochloride. Pioglitazone hydrochloride, and Glimepiride by RP-HPLC in Tablet Formulation. J Chromatographic Science.2008;(46):501-504
Table 1.Composition of various jelly formulation
|
S.NO.
|
INGREDIENTS
|
||||||
|
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
F6 |
||
|
1. |
Metformin hydrochloride % |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
|
2. |
Glimepiride% |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
|
3. |
Citric Acid % |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
|
4. |
Sodium citrate % |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
|
5. |
Guar gum % |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.4 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
|
6. |
Pectin % |
0.2 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
|
7. |
Stevia % |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
|
8. |
Mannitol % |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
|
9. |
Methyl paraben % |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
|
10. |
Colour |
q.s |
q.s |
q.s |
q.s |
q.s |
q.s |
|
11. |
Flavour |
q.s |
q.s |
q.s |
q.s |
q.s |
q.s |
|
12. |
Distilled water upto % |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
Table 2. Physio-chemical properties of oral soft jelly
|
Test parameter |
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
F6 |
|
|
Clearity |
T |
T |
T |
T |
T |
T |
|
|
Consistency |
L |
L L |
L L |
A |
A |
A |
|
|
Texture |
NS &NG |
NS & NG |
NS & NG |
NS & NG |
NS & NG |
S & NG |
|
|
Odour |
P & F |
P & F |
P & F |
P & F |
P & F |
P & F |
|
|
pH( n=3) |
6.63±0.37 |
6.78 ±0.05 |
6.74 ±0.08 |
6.94 ± 0.08 |
6.98 ± 0.04 |
6.10 ± 0.06 |
|
|
Viscosity (n=3) |
1868 ± 30 |
2578 ± 52 |
4325 ± 32 |
5790 ± 35 |
6548 ± 20 |
8161 ± 20 |
|
|
Syneresis at R.T |
+++ |
++ |
++ |
+ |
- |
- |
|
|
Drug Content (n=3) |
MET |
98.23 ± 0.15 |
98.26 ± 0.09 |
98.22±0.15 |
98.23±0.16 |
98.58±0.05 |
98.22±0.12 |
|
GLM |
97.24 ± 0.15 |
97.20 ± 0.02 |
97.36±0.08 |
97.02±0.17 |
97.36±0.09 |
97.22±0.12 |
|
Table 3. Stability study of oral soft jelly batch F3
|
S.No. |
Storage condition |
Week |
Genral appearance |
Syneresis |
pH |
Viscosity
|
Drug content
|
|
|
MET |
GLM |
|||||||
|
1. |
2-8°C |
2 |
No change |
+ |
6.68±0.03 |
6554 |
98.26 |
97.54 |
|
|
4 |
No change |
++ |
6.62±0.03 |
6592 |
98.06 |
97.12 |
|
|
2. |
25 ± 5 °C |
2 |
No change |
- |
6.64±0.04 |
6549 |
98.38 |
97.66 |
|
|
4 |
No change |
+ |
6.02±0.05 |
6511 |
98.26 |
97.54 |
|
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









