About Authors:
Sriharsha Vardhan
SRM College of Pharmacy,
Chennai, Tamil Nadu
sriharshavardhan.51@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
The present study is formulating Rabeprazole modified release beads (Immediate and Time, Pulsatile Release) and to target the release of the drug in intestine and to avoid stability related problems. Preparation of immediate release (IR) Rabeprazole beads has done by drug layering process and barrier coated beads by providing an enteric coating membrane on IR beads. Timed release beads has done by providing a Film coating for IR and lag time coating for TPR (Timed, Pulsatile Release) on enteric coated beads. Encapsulation Process and evaluation of enteric coated IR and TPR beads has done by physical evaluation and chemical evaluation. Stability studies have done for best quality Rabeprazole IR and TPR enteric coated beads formulations. Based on the results Formulation 3 and Formulation 9 were selected as the best formulation developed for Rabeprazole Dual Drug Release Capsules.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1332
INTRODUCTION
Rabeprazole sodium is a weak base and belongs to a class of antisecretory compounds (substituted benzimidazole proton-pump inhibitors) that do not exhibit anticholinergic or histamine H2-receptor antagonist properties, but suppress gastric acid secretion by inhibiting the gastric H+/K+ATPase (hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase) at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. Because this enzyme is regarded as the acid (proton) pump within the parietal cell. Rabeprazole sodium has been characterized as a gastric proton-pump inhibitor which blocks the final step of gastric acid secretion in gastric parietal cells. Rabeprazole sodium is protonated, accumulated, and transformed to an active sulfenamide. When studied invitro Rabeprazole sodium is chemically activated at pH 1.2 with a half-life of 78 seconds (Cassia V. Gargi et al., 2007).
Structure
Fig 1. Rabeprazole sodium
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials Used
Rabeprazole Sodium (Hetero Pharma, Hyderabad), Colloidal Sillicon Dioxide (Colorcon, Mumbai), Ethyl cellulose (Shanghai shenmei Pharma, china), Hypromellose 2910 (Shanghai shenmei Pharma, china), Magnesium Carbonate (Colorcon, Mumbai), Cellulose Acetate Phthalate (Colorcon, Mumbai), PEG 400 (Vasudha Pharma, Hyderabad), Polysorbate 80 (Pee Vee Products Pvt Ltd, Ahmedabad).
Preformulation Studies
The overall objective of preformulation testing is to generate information useful in developing the formulation which is stable and bioavailability. Further the use of preformulation parameters maximizes the chances in formulating an acceptable, safe, efficacious and stable product. For any drug substance to formulate into a dosage form, it is necessary to study the physicochemical properties of the bulk drug like physical appearance, solubility, bulk density, tapped density, compressibility, melting point, molecular weight, sieve analysis (Chein W, 2000).
Drug ExcipientsCompatibility Studies
Compatibility studies were carried out to study the possible interactions between Rabeprazole Sodium and other inactive ingredients in the formulation.The compatibility studies were carried out at 40oC/75% RH for 0,2 and 4 weeks and control samples were to be kept at 2-8oC. With respect to physical and chemical aspects, they were tested (Kearns GL and Winter HS, 2003).
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM analysis)
SEM analysis was used to study the morphology of prepared pellets without any coating by Hitachi (Model: S-3400 N, Japan) (Yun-seok Rhoe et al., 2007).
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
METHODOLGY
Total six formulations F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7, F8 & F9 of rabeprazole sodium modified release capsules have been prepared in which F1, F2, F3 & F4 are by using varying concentration of Drug and Ethyl Cellulose and for F5, F6, F7, F8 & F9 by using varying concentrations of Ethyl Cellulose and Hypro Mellose 2910 by drug layering method (Laila FAA and Chandran S, 2006; Wise Donald L, 2000).
Drug Layering Method
Preparation of Rabeprazole Sodium Modified Release
1st stage:Preparation of Rabeprazole IR beads by drug layering process. 168g of rabrprazole sodium was slowly added to an aqueous solution of 18.6g of Hydroxy propyl cellulose and mixed well. Then charged with 107.4g of 25-30 mesh spheres and seal coated with 2% by weight of opadry and dried.
2nd stage:Barrier coated beads by providing an enteric coating membrane on IR beads. Those IR beads are coated with a plasticized solution or aqueous dispersion of a water insoluble polymer such as ethylcellulose with water insoluble polymer such as PVP or with a plasticized solution or aqeous dispersion of an enteric polymer such as Hypromellose phthalate.
3rd stage:TR [Timed release] beads by providing a and 4-8% film time coating on entric coated beads for IR lag time coating on enteric coated beads for TPR. Those Enteric coated beads are coated with film polymer solution, which is th mixture of drug and polymer. And another Enteric coated beads are coated with lag time polymer solution, which is the mixture of water insoluble polymer and an enteric polymer at ratio of from about 90:10 t0 50:50 directly on to enteric coated beads for a weight gain of upto 50% by weight. So, lag time of up to 10 hours of pulsatile release.
4th stage:Encapsulation Process consists of filling hard gelatin capsules with 2 types of bead populations using a commercial capsule filling equipment.MG Futura, is the latest automatic capsule filling machine used to fill the capsules with more than one type of bead populations (Wong SM et al., 2006; Youan CB, 2004).
Stability Studies
For all the pharmaceutical dosage forms it is important to determine the stability of the dosage form. This will include storage at both normal and exaggerated temperature conditions, with the necessary extrapolations to ensure the product over its designed shelf life, provide medication for absorption at the same rate as when originally formulated. The design of the formal stability studies for the drug product should be based on the knowledge of the behavior and properties of the drug substance and formal stability studies on the drug substance. Specification which is list of tests, reference to the analytical procedures and proposed acceptance criteria, including the concept of different acceptable criteria for release and shelf life specifications, is addressed in ICH CS L6AS and IS6B (Tang ESK et al., 2005).
Storage Conditions
In general, a drug product should be evaluated under storage condition that tests its stability and if applicable, its sensitivity to moisture or potential for solvent loss. The long term testing should cover a minimum of 12 months study or at least three batches at the time of submission and should be continued for a period of sufficient time till it covers the proposed shelf life.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
PROCEDURE
Specified quantity of non-pareil seeds were accurately weighed and dispensed.
Drug Loading Stage
· 500 ml of purified water was taken in a beaker and kept for stirring under a mechanical stirrer.
· Specified quantities of Starch, Sodium Phosphate, Light Mg. oxide and Colloidal Sillica & Sugar syrups were added slowly was continued for 30 mins.
· Non pareil seed were coated with the prepared drug suspension using Fluidized Bed Coater (FBC).
· Dried pellets were collected and coated efficiency was calculated.
Barrier Coating Stage
· 500 ml of purified water was taken in a beaker and kept for stirring under a mechanical stirrer.
· Specified quantities of HPMC (E5), Polysorbital 80, Titanium oxide and Talcwere added slowly to from a uniform suspension. Stirring was continued for 30 mins.
· Drug loaded pellets were coated with the above suspension using Fluidized Bed Coater (FBC).
· Dried pellets were collected and coating efficiency was calculated.
Enteric Coating Stage
· 300 ML OF Iso propyl alcohol and 900 ml of Acetone were taken in a beaker and kept for stirring under a mechanical stirrer.
· Specified quantities of Cellulose Acetate Phthalate Dispersable AcrylCoat L30D, diethyl Phthalate, Polysorbital 80, Titanium dioxide and Talc (previously passed through 200#) were slowly to from a uniform suspension. Stirring was continued for 30 mins.
· Barrier coated pellets were coated with the above suspension using Fluidized Bed Coater (FBC).
· Dried pellets were collected and coating efficiency was calculated
Time Coating Stage
It includes an additional polymer coating on enteric coating for effective drug release. For IR beads a film coating of drug with a polymer of 0-6% thickness is given for faster drug release in stomach. For TPR beads a Lag time coating of 2 polymer mixture which usually includes water insoluble and enteric polymer for pulsatile n delay release of drug in intestine, thickness of 0-10% (Shaji J et al., 2007; Saptarshi D and Mukul S, 2009).
Formulation F1
Formulation F1 includes 0% of film coating i.e., purely enteric coated beads are used for drug dissolution in acidic pH.
Formulation F2
Formulation F3 includes 2% of film coating on enteric coated beads is used for dissolution for enhanced drug release in gastric pH, stomach. Here Drug and Ethyl Cellulose of (2:8) ratio & Polysorbital 80 in Purified water and coated.
Formulation F3
Formulation F3 includes 4% of film coating on enteric coated beads is used for dissolution for enhanced drug release in gastric pH, stomach. Here Drug and Ethyl Cellulose of (4:6) ratio & Polysorbital 80 in Purified water and coated.
Formulation F4
Formulation F4 includes 6% of film coating on enteric coated beads is used for dissolution for enhanced drug release in gastric pH, stomach. Here Drug and Ethyl Cellulose of (6:4) ratio & Polysorbital 80 in Purified water and coated.
Formulation F5
Formulation F5 includes 0% of Lag time coating i.e., purely enteric coated beads are used for drug dissolution in basic pH.
Formulation F6
Formulation F6 includes 2.5% of Lag time coating on enteric coated beads is used for dissolution for pulsatile/delayed drug release in basic pH, intestine. Here HPMCP and Ethyl Cellulose of (1:1) ratio, 2.5mg each with Diethyl Phthalate and PEG 100 in 65% Methylene Chloride & IsoPropyl Alcohol and coated.
Formulation F7
Formulation F6 includes 5% of Lag time coating on enteric coated beads is used for dissolution for pulsatile/delayed drug release in basic pH, intestine. Here HPMCP and Ethyl Cellulose of (1:1) ratio, 5mg each with Diethyl Phthalate and PEG 100 in 65% Methylene Chloride & IsoPropyl Alcohol and coated.
Formulation F8
Formulation F6 includes 7.5% of Lag time coating on enteric coated beads is used for dissolution for pulsatile/delayed drug release in basic pH, intestine. Here HPMCP and Ethyl Cellulose of (1:1) ratio, 7.5mg each with Diethyl Phthalate and PEG 100 in 65% Methylene Chloride & IsoPropyl Alcohol and coated.
Formulation F9
Formulation F6 includes 1o% of Lag time coating on enteric coated beads is used for dissolution for pulsatile/delayed drug release in basic pH, intestine. Here HPMCP and Ethyl Cellulose of (1:1) ratio, 10mg each with Diethyl Phthalate and PEG 100 in 65% Methylene Chloride & IsoPropyl Alcohol and coated (Peter S and Peter K, 1997).
RESULTS
Table 1. Stability studies
|
Study |
Storage condition |
Minimum time period covered by data at submission |
|
Long term |
25ºC ± 2 ºC/ 60% RH ± 5% RH |
12 months |
|
Intermediate |
30ºC ± 2 ºC/ 65% RH ± 5% RH |
6 months |
|
Accelerated |
40ºC ± 2 ºC/ 75% RH ± 5% RH |
6 months |
When significant change occurs at any time during 6 months testing at the accelerated storage condition, additional testing at the intermediate storage condition should be conducted and evaluated against significant change criteria.
Table 2. Comparative studies of Rabeprazole sodium with excipients
|
Diluents |
Drug Excipients Ratio |
40°C ± 2°C / 75% RH ± 5% RH |
|
Rabeprazole Sodium |
1:1 |
4 Weeks |
|
Drug + Magnesium oxide |
1:2 |
4 Weeks |
|
Drug + Sod. Phosphate |
1:1 |
4 Weeks |
|
Drug + HPMCP |
1:1 |
4 Weeks |
|
Drug + EthylCellulose |
1:1 |
4 Weeks |
|
Drug + Talc |
1:0.25 |
4 Weeks |
|
Drug + All excipients |
1:1 |
4 Weeks |
Table 3. Drug excipients Compatibility Study
|
Materials |
Initial Observation |
Drug Excipients Ratio |
Duration in weeks |
||||
|
0 |
I |
II |
III |
IV |
|||
|
Rabeprazole Sodium |
A Yellowish white Powder |
1:1 |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
|
Drug + Magnesium oxide |
A Yellowish white Powder |
1:2 |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
|
Drug + Sod. Phosphate |
A Yellowish white Powder |
1:1 |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
|
Drug + HPMCP |
A Yellowish white Powder |
1:1 |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
|
Drug + EthylCellulose |
A Yellowish white Powder |
1:1 |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
|
Drug + Talc |
A Yellowish white Powder |
1:0.25 |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
|
Drug + All excipients |
A Yellowish white Powder |
1:1 |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Compiles |
Table 4. Drug coating on to Non Pareil seeds (neutral pellets)
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (%w/w) |
|
1 |
Rabeprazole sodium |
10 |
|
2 |
Starch |
55 |
|
3 |
Sodium phosphate |
2.5 |
|
4 |
Light magnesium oxide |
1.5 |
|
5 |
Colloidal silica |
1 |
|
6 |
HPMC (E5) |
5 |
|
7 |
Sodium methyl paraben |
2.5 |
|
8 |
Sodium propyl paraben |
2.5 |
|
9 |
PG Sugar Regular |
20 |
|
10 |
P.Water |
QS |
Table 5. Barrier coating
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (%w/w) |
|
1 |
HPMC (E5) |
5% |
|
2 |
Polysorbital 80 |
5% |
|
3 |
Titanium Dioxide |
2.5% |
|
4 |
Talc |
2.5% |
|
5 |
P.Water |
QS |
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Table 6. Enteric coating
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (%w/w) |
|
1 |
Cellulose Acetate Pthalate |
5.5 |
|
2 |
Dispersable Acrylcoat L30D |
5.5 |
|
3 |
Diethyl Pthalate |
3 |
|
4 |
Polysorbital 80 |
5 |
|
5 |
Titanium Dioxide |
2.5 |
|
6 |
Talc |
2.5 |
|
7 |
P.Water |
QS |
Table 7. Film coating
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (%w/w) |
|||
|
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
||
|
1 |
Rabeprazole Sodium |
- |
2 |
4 |
6 |
|
2 |
Ethyl Cellulose |
- |
8 |
6 |
4 |
|
3 |
Polysorbital 80 |
- |
0.8 |
0.6 |
0.4 |
|
4 |
P.Water |
- |
QS |
QS |
QS |
Table 8. Lag Time Coating
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
|
Contents (%w/w) |
|||
|
F5 |
F6 |
F7 |
F8 |
F9 |
||
|
1 |
Ethyl Cellulose |
- |
2.5 |
5 |
7.5 |
10 |
|
2 |
HPMCP |
- |
2.5 |
5 |
7.5 |
10 |
|
3 |
Diethyl Pthalate |
- |
0.25 |
0.5 |
0.75 |
1 |
|
4 |
PEG 100 |
- |
0.25 |
0.5 |
0.75 |
1 |
|
5 |
Methylene Chloride |
- |
QS |
QS |
QS |
QS |
|
6 |
IsoPropyl Alcohol |
- |
QS |
QS |
QS |
QS |
Table 9. Coating Parameters
|
S. No |
PARAMETER |
COATING |
DRYING |
|
1 |
Inlet air pressure |
2 kg/cm2 |
1kg/cm2 |
|
2 |
Inlet temperature |
54°C |
54°C |
|
3 |
Bed temperature |
43°C |
50°C |
|
4 |
Spray rpm |
6-8 |
- |
|
5 |
Blower rpm |
300 |
200 |
Table 10. Label Claim: Each Dual Drug Release capsules contain Rabeprazole USP 40 mg
|
Test |
Results |
||||||||
|
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
F6 |
F7 |
F8 |
F9 |
|
|
Description |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
White To Off White Colored Pellets Filled In size ‘1’ capsule |
|
Assay |
- |
99.5% |
99.3% |
100.0% |
99.9% |
100.1% |
99.9% |
100.5% |
100.1% |
|
Content uniformity |
- |
99.56% |
100.4% |
100.5% |
100.0% |
99.8% |
100.4% |
100.4% |
100.4% |
|
Moisture content (%w/w) |
- |
2.3 |
2.0 |
1.96 |
1.99 |
1.92 |
1.94 |
1.96 |
1.86 |
Dissolution Studies
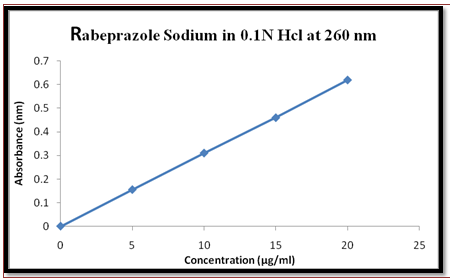
Fig 2. Graph of std calibration curve of Rabeprazole Sodium in 0.1N Hcl at 260nm.
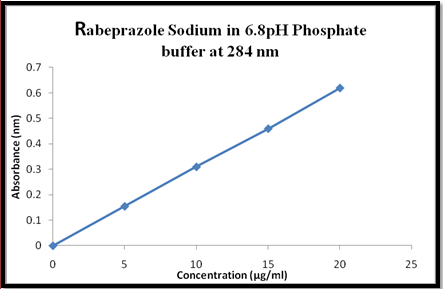
Fig 3. Graph of std calibration curve of Rabeprazole Sodium in 6.8pH phosphate buffer at 284nm.
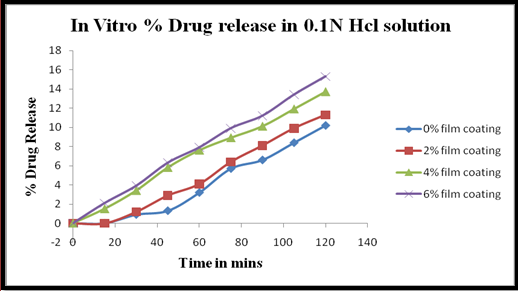
Fig 4. Graph of In Vitro % drug release of Rabeprazole Sodium in 0.1N Hcl at 260nm.
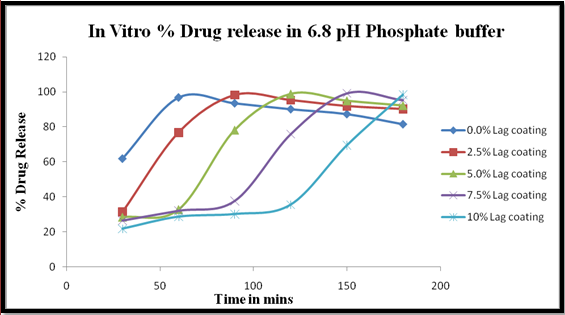
Fig 5. Graph of In Vitro % drug release of Rabeprazole Sodium in 6.8pH Phosphate Buffer at 284nm.
Stability Studies of Rabeprazole Sodium Modified Release Capsules
Table 11. 6 month stability profile of Rabeprazole sodium (20mg) Immediate release
|
Condition period |
Assay of Rabeprazole (%) |
% dissolution of Rabeprazole |
|
|
GF (2 Hrs) |
IF (30 Mins) |
||
|
Initial |
102.5 |
14.2 |
92.1 |
|
40°C 75%RH 1M |
97.2 |
11 |
91.1 |
|
40°C 75%RH 3M |
97.7 |
12.6 |
93.4 |
|
40°C 75%RH 6M |
94.32 |
16.8 |
91.3 |
|
30°C 65%RH 1M |
99.1 |
5.4 |
97.6 |
|
30°C 65%RH 6M |
95.91 |
9.9 |
93.1 |
Table 12. 6 month stability profile of Rabeprazole sodium (20mg) Pulsatile release
|
Condition period |
Assay of Rabeprazole (%) |
% dissolution of Rabeprazole |
|
|
GF (2 Hrs) |
IF (3 Hrs) |
||
|
Initial |
102.5 |
3.4 |
97.6 |
|
40°C 75%RH 1M |
97.2 |
2.5 |
96.3 |
|
40°C 75%RH 3M |
97.7 |
2.9 |
98.1 |
|
40°C 75%RH 6M |
94.32 |
4.2 |
96.8 |
|
30°C 65%RH 1M |
99.1 |
1.3 |
100.2 |
|
30°C 65%RH 6M |
95.91 |
2.4 |
96.1 |
Optimized Formulation
Table 13. Drug coating on to Non Pareil seeds (neutral pellets)
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (%w/w) |
|
1 |
Rabeprazole sodium |
10 |
|
2 |
Starch |
55 |
|
3 |
Sodium phosphate |
2.5 |
|
4 |
Light magnesium oxide |
1.5 |
|
5 |
Colloidal silica |
1 |
|
6 |
HPMC (E5) |
5 |
|
7 |
Sodium methyl paraben |
2.5 |
|
8 |
Sodium propyl paraben |
2.5 |
|
9 |
PG Sugar Regular |
20 |
|
10 |
P.Water |
QS |
Table 14. Barrier coating
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (%w/w) |
|
1 |
HPMC (E5) |
5% |
|
2 |
Polysorbital 80 |
5% |
|
3 |
Titanium Dioxide |
2.5% |
|
4 |
Talc |
2.5% |
|
5 |
P.Water |
QS |
Table 15. Enteric coating
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (%w/w) |
|
1 |
Cellulose Acetate Pthalate |
5.5 |
|
2 |
Dispersable Acrylcoat L30D |
5.5 |
|
3 |
Diethyl Pthalate |
3 |
|
4 |
Polysorbital 80 |
5 |
|
5 |
Titanium Dioxide |
2.5 |
|
6 |
Talc |
2.5 |
|
7 |
P.Water |
QS |
Table 16. Film coating
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (4%w/w) |
|
1 |
Rabeprazole Sodium |
4 |
|
2 |
Ethyl Cellulose |
6 |
|
3 |
Polysorbital 80 |
0.6 |
|
4 |
P.Water |
QS |
Table 17. Lag Time Coating
|
S.NO |
Excipients |
Contents (10%w/w) |
|
1 |
Ethyl Cellulose |
10 |
|
2 |
HPMCP |
10 |
|
3 |
Diethyl Pthalate |
1 |
|
4 |
PEG 400 |
1 |
|
5 |
Methylene Chloride |
65 |
|
6 |
IsoPropyl Alcohol |
35 |
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The formulations of Rabeprazole Sodium Dual Drug Release Capsules were developed by Time release coating process varying the compositions of drug & polymer mixture in Film coating, water insoluble and enteric coating polymer mixture in lag time coating. Cellulose Acetate Phthalate and Acryl coat L30D were used as enteric polymers. The enteric coated beads were prepared in a Fluidized bed coater. Drug and Ethyl Cellulose were used as Film coating polymers. The Film coated beads were prepared in a Fluidized bed coater. HPMC Phthalate and Ethyl Cellulose were used as Lag time polymers. The lag time coated beads were prepared in a Fluidized bed coater.
The present study concluded that the process variables were standardized and the different batches prepared were evaluated for assay/drug content, content uniformity, water content, acid resistance and dissolution rate. Based on the results Formulation 3 and Formulation 9 were selected as the best formulation developed for Rabeprazole Dual Drug Release Capsules.
REFERENCES
- Cassia V. Gargi et al. Development and validation of dissolution test for Rabeprazole sodium in coated tablets. International journal of Pharmaceutics. 2007: 120-125.
- Chein W. Novel drug delivery systems, 2nd Edition., Marcel Dekker, Newyork, 2000: 43-135.
- Kearns GL, Winter HS. Proton pump inhibitors in pediatrics: relevant pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition. 2003; 7(1): S52-9.
- Laila FAA, Chandran S. Multiparticulate Formulation approach to colon specific drug delivery current perspectives. Journal of Pharm Sci. 2006; 9(3): 327-338.
- Peter S, Peter K. New multiparticulate delayed release system. Journal of Controlled Release. 1997; 147(2): 181-189.
- Saptarshi D, Mukul S. Modified release dosage form and drug delivery. Journal Pharm Research. 2009; 2(11): 1728-29.
- Shaji J, Chadawar V, Talwalkar P. Multiparticulate Drug Delivery System. The Indian Pharmacist. 2007; 6(60): 21-28.
- Tang ESK, Chan LW, Heng PWS. Coating of Multiparticulates for Sustained Release. American Journal of Drug Delivery. 2005; 3(1): 17-28.
- Wise Donald L. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Controlled Release Technology. 2000: 473.
- Wong SM et al. Enhancement of the dissolution rate and oral absorption of a poorly water soluble drug by formation of surfactant containing microparticles. International Journal Pharmaceutics. 2006; 317: 61-68.
- Youan CB. Chronopharmaceutics: gimmick or clinically relevant approach to drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release. 2004; 98: 337-353.
- Yun-seok Rhoe et al. Application of instrumental evaluation of color for the pre-formulation and formulation of Rabeprazole. International journal of Pharmaceutics. 2007; 65(3): 131-136.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to PharmaTutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









