About Author:
Mr. Piyush Tripathi
Kota College of Pharmacy
Kota, Rajasthan.
piyushtripathi1992@rediffmail.com
Introduction:
The term Clinical Research refers to the entire bibliography of a drug from its inception in the lab to its introduction to the consumer market & beyond. Not every compound that is tested in the lab is marketed. Before a drug is marketed, it has to undergo several stages of development.
Hence Clinical research may define as a “branch of medical science that determines the safety & effectiveness of medications, devices, diagnostic procedures & treatment regimens intended for human use.”
A clinical trial targets specific health issues in human volunteers. Performing clinical trials is one of the best methods in clinical research field for finding new treatments & practices for combating illness.
Clinical trials are studies performed with human subjects to test new drugs or combinations of drugs, new approaches to surgery or radiotherapy or procedures to improve the diagnosis of disease and the quality of life of the patient.
Reference Id: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1857
Types of Clinical trials:
Clinical trials can be classified based on the purpose as under-
- Treatment Trials- test new medical, surgical, and/or radiation treatments for combating illness.
- Prevention trials: test methods for preventing first time occurrences or recurrences of diseases. Methods could include medical treatment, diet and lifestyle changes, dietary supplements, exercise, and vaccines
- Diagnostic trials: look for new or improved methods for diagnosing a particular disease or condition.
- Screening trials: look for new or improved ways to detect a particular disease or condition.
- Quality of Life or Supportive Care trials: look for ways to improve the quality of life for individuals with a chronic illness.
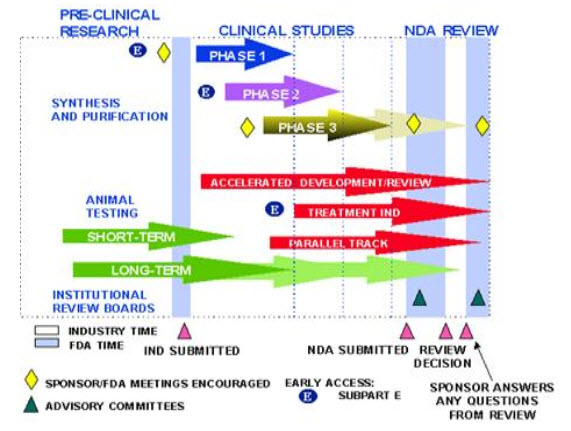
Clinical trials involving new drugs are commonly classified into 4 phases. Each phase of drug approval process is treated as a separate clinical trial. The drug-development process will normally proceed through all four phases over many years. If the drug successfully passes through Phases I, II, and III, it will usually be approved by the national regulatory authority for use in the general population. Phase IV are 'post-approval' studies.
Phase 1– Is the treatment safe?
After an experimental drug or treatment has been tested in the lab and/or on animals, it enters a phase 1 trial. This is the first testing of a new drug. Phase 1 trials are generally carried out in healthy volunteers who are small in number, usually 20- 80.The purpose of Phase 1 studies is to identify metabolic and pharmacological effects of drug in human and to determine the side effects associated with increasing doses and to gain early evidence on effectiveness. During Phase 1 sufficient information about the drugs pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects is required. The purpose of this phase is to mainly determine the safety profile.
Phase 2– Does the treatment work?
After determining that a treatment is reasonably safe in people, it enters Phase 2 trials. These are done to test for effectiveness – does the treatment work? Since a larger number of people are studied, further information is gained on safety during phase 2 trials. Phase 2 studies are typically well controlled, closely monitored and conducted in large number of people (100-300)
Phase II studies are sometimes divided into Phase IIA and Phase IIB.
- Phase IIA is specifically designed to assess dosing requirements (how much drug should be given).
- Phase IIB is specifically designed to study efficacy (how well the drug works at the prescribed dose(s)
Phase 3– Does the new treatment work better than the standard treatment?
Phase 3 trials test the new drug or treatment on hundreds or thousands of individuals (1000-3000) these studies are often “double blind” trials, which mean that neither the patient nor the investigator knows which treatment is being used. They are performed after preliminary evidence suggesting effectiveness of the drug has been obtained in Phase 2 and are intended to gather the additional information about effectiveness and safety that is needed to evaluate the overall benefit-risk relationship of the drug. They are designed to answer the question of whether or not the new treatment works better, or has fewer side effects, than the standard treatment.
Phase 4– Is the treatment safe over time?
Phase 4 known as Post Marketing Surveillance is carried out once the drug is approved and marketed. The aim of Phase 4 is to further characterize the safety of the drug through the identification of unknown adverse reactions and potentially researching new therapeutic indications. Companies often use this phase to gain exposure to different physicians and clinics, which aids in the marketing of their product.
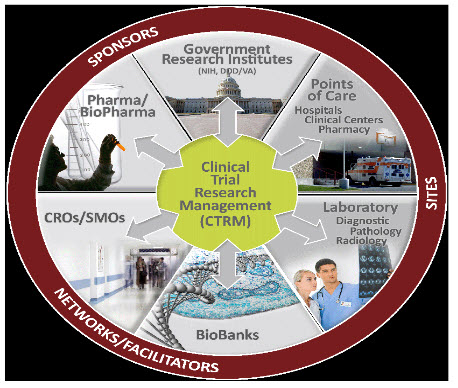
Stakeholders in Clinical Research-
The clinical research industry is an ever-evolving and ever-changing enterprise. It is continuously achieving advancements that would not be possible without the many key players and stakeholders within the industry. These stakeholders range from a broad spectrum that includes -
SPONSORS- are the primary stakeholders who initiate the research process. They are typically pharmaceutical or biotechnology companies in the business of making drugs, biologics, or medical devices. They may also be academic institutions or even government agencies such as the National Institutes of Health. Either way, before they can conduct their studies or introduce any drugs, biologics, or medical devices into the market, they must first gain approval by verification of their safety and efficacy. This is done by going through the clinical investigation process.
RESEARCH TEAM- The investigative site in any trial generally consists of Principal Investigator, Sub-investigators, Clinical Research Coordinators, Site managers, Laboratory personnel, Technicians, Analysts, Pharmacists, Research assistants, Recruiters, and many others.
PARTICIPANTS
REGULATORS
MONITORS
GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
Contract Research Organizations (CROs)- A CRO is a service organization that provides support to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries in the form of research services out sourced (often domestically) on a contract basis. A C.R.O. can provide such services as biopharmaceutical development, preclinical research, clinical research, and clinical trials management.
List of Major CROs :
* Quintiles
* Synchron
* Lambda
* Siro ClinpharmI-
* Gate
* Reliance Clinical
* Services
* PPD
* Onmnicare
* ICONClin
* TracPharmaNet
* Pharm-Olam
* Lotus Labs
* Vimta
* GVK
* BioServe Clinical Research
* Apothecaries
* Kendle
* Bioassay
* Clinworld
* Perinclinical
* Quest Life Sciences
Site Management Organizations (SMOs)- A Site Management
Organization (SMO) is an organization that provides clinical trial related services to a contract research organization(CRO), a pharmaceutical company, a biotechnology company, a medical device company or a clinical site. The site is usually a hospital or a similar health care institution that has adequate infrastructure and staff to meet the requirements of the clinical trial protocol. The scope of an SMO's responsibility is limited to the SITE.
Academic institutions
Ethics Committee or Institutional Review Boards (IRBs)- The Institutional Review Board, or IRB is the stakeholder that holds the role of protecting human subjects as detailed in the regulations. Before a research team can begin on a study, this specially constituted review body must conduct an initial review to see if the study can be done ethically and safely. The IRB carefully analyzes the study protocol and assesses the risks and benefits, which ultimately decide whether or not the investigator can go on with conducting the study.
SCOPE OF CLINICAL RESEARCH IN INDIA-
Clinical Research is multinational, multibillion & multidisciplinary industry. Indian pharmaceutical industry is one of the fastest growing sectors of the Indian economy and has made rapid strides over the years. From being import dependent in the 1950s, the industry has achieved self-sufficiency and gained global recognition as a producer of low cost, high quality bulk drugs and formulations. Having proved itself in the international market, India is ready to face the challenges of proving its efficiency as the preferred destination for global clinical trials.
A number of factors favor India as a clinical research hub.
- Firstly, there are numerous government-funded medical and pharmaceutical institutions with state-of-the-art facilities, which can serve as ideal centers for multi-centered clinical trials.
- Well-trained and qualified manpower, well versed in English
- Resources- There is vast clinical material which can be utilized.
- In terms of the cost efficiency, India is a better bet as the cost to conduct a trial here is lower by 50 to 75 percent than in United States or European Union. New drug development costs in India are substantially less than those in the developed world and it is possible to conduct both new drug discovery research and novel drug delivery system programmes at competitive rates.
- There is a good communication link, which favors fast recruitments and approvals. Thus, studies can be completed quickly, providing an edge over competitors.
JOB OPPURTUNITIES IN CLINICAL RESEARCH-
Clinical Research has emerged as a popular career choice in India and abroad. Holding a strong growth potential, a clinical research profile has become a calling for many. With operational players including some of the top Indian Pharmaceutical companies, such as Ranbaxy, Dr. Reddy’s Labs, Biocon, Dabur, Wockhard, Merck, Astra Zeneca, a clinical research profile offers a plenty of job opportunities.
Career opportunities for a Clinical Research Professional:
1. Clinical operations
- Clinical Research Coordinator
- Clinical Trial Assistant
- Clinical Research Associate
- Project Manager
- Clinical Team Leader
2. Clinical Data Management
- Clinical Data Analyst
- Clinical Data Coordinator
- Clinical Data Associate
- Data Manager
3. PHARMACOVIGILANCE
- Drug Safety Associate
- Drug Safety Physician
- Pharmacovigilance Officer
4. Regulatory Affairs
5. Medical writing
6. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
CLINICAL TRIAL QUOTATIONS:
“India is an emerging market with growing number of entrepreneurs foraying into research and healthcare. Indian government is creating an effective regulatory framework. Protection of patents and IPR is now improving. India has a better place than countries like China in the clinical trials field”, Dr Charles Pierce, president Global Clinical Partners, Inc. USA, said
“Indian contract research Organizations will have good chance to shine, Indian CROs are competitive compared to western companies. There are several advantages to global companies to outsource research service from us” Dr. Goutam Das , CEO, Syngene International Pvt. Ltd.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









