- Phrmaceutics{Below}
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
Question Paper of Pharmaceutics for Jharkhand Public Service Commission (JPSC) - 2013
1. Differential scanning calorimetry is used to study ,
(A) identity
(B) purity
(C) polymorphism
(D) All of the above
2. Upper and lower consolute temperatures are noticed in
(A) nicotin-water system
(B) triethylamine-water system
(C) phenol-water system
(D) None of the above
3. One gram-equivalent weight of sodium chloride in 1 litre of solution is equal to
(A) 1 N
(B) 1 M
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
4. Colligative properties of a solution include
(A) osmotic pressure
(B) freezing point
(C) boiling point
(D) All of the above
5. pH is expressed as
(A) -log[H30+ ]
(B) log[ri30+]
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
6. Which of the following is an essential ingredient of orally disintegrating tablets?
(A) Potassium chloride
(B) Sodium bicarbonate
(C) Sodium starch glycolate
(D) All of the above
7. Sodium chloride equivalent method is used to adjust
(A) pH
(B) tonicity
(C) buffer capacity
(D) None of the above
8. Gibbs phase rule is expressed as
(A) F = C-P + 2
(B) F = C + P - 2
(C) F = C + P + 2
(D) None of the above
9. Inclusion complexes are produced by
(A) cyclodextrins
(B) EDTA
(C) iodine
(D) picric acid
10. Protein binding studies are conducted by
(A) filtration
(B) equilibrium dialysis
(C) centrifugation
(D) None of the above
Go to "Next Page" for more questions...
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
11. Drug absorption through biological membrane involves
(A) ultrafiltration
(B) osmosis
(C) diffusion'
(D) diffusion and membrane transporters
12. The amount M of a material flowing through a unit cross- section s of a barrier in unit time t is known as flux and is written as
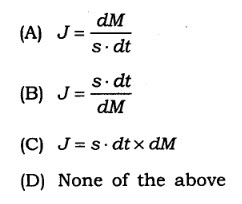
13. pH partition hypothesis explains drug absorption due to
(A) lipophilicity
(B) unionized form
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
14. Drug release from granular matrices involves
(A) penetration of surrounding liquid
(B) dissolution of drug
(C) leaching of drug
(D) All of the above simultaneously
15. Sink condition is essential in the studies of
(A) in vitro dissolution
(B) disintegration
(C) solubility
(D) permeability
16. Osmotic delivery system provides
(A) first-order release
(B) second-order release
(C) zero-order release
(D) None of the above
17. Class II drug as classification hasper BCS
(A)high solubility permeability and high
(B)low solubility permeability and high
(C)high solubility permeability and low
(D)low solubility permeability and low
18. Sink condition implies
(A) dissolved drug than 20% of concentration is less saturation
(B) dissolved drug is more than 20% of saturation concentration
(C) dissolved drug is less than saturation concentration
(D) dissolved drug equals saturation concentration
19. As per USP 26, simulated gastric fluid has a pH of
(A) 1-2
(B) 2-2
(C) 6-8
(D) None of the above
20. Flow through cell is involved in the USP dissolution apparatus
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Go to "Next Page" for more questions...
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
21. Hixson-Crowell cube root law is used to understand dissolution behaviour
(A) when geometric shape of dosage form stays constant during dissolution
(B) when geometric shape of dosage form is altering during dissolution
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
22. The dosage form that is waived off from bioavailability assessment is
(A) intravenous injection
(B) antacid tablet
(C) local analgesic ointment
(D) All of the above
23. The ratio of maximum tolerated dose to minimum effective dose is known as
(A) bioavailability
(B) therapeutic index
(C) therapeutic efficacy
(D) toxicity
24. P-glycoprotein (Pgp) receptors located in the gut rumen are responsible for
(A) enhancing drug absorption
(B) selectively transporting peptides into blood
(C) reducing drug bioavailability
(D) decreasing drug solubility in gut membrane
25. Absolute bioavailability ranges from
(A) 0-1
(B) 0-2
(C) 1-2
(D) None of the above
26. The availability of a drug product as compared to another dosage form or product of same drug given in same dosage’ refers to
(A) absolute bioavailability
(B) relative bioavailability
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
27. ‘Entry of any molecule into a cell is the result of selective solubility in cells’ boundary is related to
(A) DLVO theory
(B) Overton’s rule
(C) Alexander lire’s concept
(D) None of the above
28. Theobroma oil exists in polymorphic forms’ specify
(A) two
(B) three
(C) four
(D) Nil
29. In suspensions, drug degradation follows
(A) first-order kinetics
(B) second-order kinetics
(C) apparent zero order
(D) None of the above
30. Diffusion cell is used to study
(A) dissolution
(B) absorption
(C) permeability
(D) None of the above
Go to "Next Page" for more questions...
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
31. The rate at which a solid dissolves is related to
(A) solubility
(B) diffusion coefficient
(C) surface area
(D) All of the above
32. HLB scale valves of o/w emulsifying agents vary in between
(A) 1-3
(B) 3-8
(C) 8-16
(D) 16-18
33. Sodium lauryl sulfate has an HLB value of
(A) 10
(B) 20
(C) 15
(D) 40
34. The HLB value of a surfactant, when saponification number is 45-5 and acid number is 276, is
(A) 15
(B) 16-7
(C) 20
(D) None of the above
35. Sulfonyl urea’s overdose toxicity can be reduced by
(A) desorption
(B) absorption
(C) dialysis
(D) charcoal adsorption
36. The adsorption isotherm exhibited by activated charcoal- select best fit is
(A) Langmuir type
(B) Freundlich type
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
37. Gegenions have opposite charge to
(A) potential-determining ions
(B) counterions
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
38. Potential located at the shear plane is known as
(A) Nemst potential
(B) zeta potential
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
39. Surfactants form micelles
(A) at CMC
(B) below CMC
(C) below and above CMC
(D) below and at CMC
40. An intramuscular sustained release depot formulation would suit
(A) shear thinning system
(B) shear thickening system
(C) rod-shaped drug crystals in polymer
(D) None of the above
41. Electrokinetic phenomenon is not involved in
(A) electrophoresis
(B) electroosmosis
(C) osmosis
(D) sedimentation potential
42. According to Donnan membrane equilibrium, which of the following statements is correct?
(A) Concentrations of diffusible anion outside and inside the semipermeable membrane are influenced by non- diffusible anion
(B) Nondiffusible anions and diffusible anions behave similarly inside and outside a semipermeable membrane
(C) Nondiffusible anion does not influence the concentration of diffusible anion across a semipermeable membrane
(D) None of the above
43. According to Schultze-Hardy rule, which of the following statements is correct?
(A) Precipitating power
increases rapidly with valency
(B) Precipitating power is nothing to do with valency
(C) Solubilizing power increases rapidly with valency
(D) Solubility parameter
increases rapidly with charge
44. According to Hofmeister series, decreasing order of precipitating power of anions is
(A) citrate < tartarate < sulfate
(B) citrate > tartarate > sulfate
(C) citrate < sulfate < tartarate
(D) tartarate < citrate < sulfate
45. Coacervate is
(A) colloid-rich layer
(B) colloid-poor layer
(C) colloidal solution
(D) crystalloid
Go to "Next Page" for more questions...
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
46. Cloud point is
(A) the temperature above which cloud disappears
(B) the temperature above which cloud appears
(C) the pH above which cloud appears
(D) the pH above which cloud disappears
47. Kraft point is
(A) the temperature at which the solubility of surfactant equals the CMC
(B) the temperature above which cloudiness occurs
(C) not related with solubility
(D) the pH at which solubility is less
48. The surface diameter ‘ds’ is
(A) the diameter of a sphere having the same volume as the particle
(B) the diameter of a sphere having the same observed area as particle when viewed normal to its most stable plane
(C) the diameter of a sphere having the same surface area as the particle in question
(D) None of the above
49. Andreasen’s apparatus (pipette) is used for determination of
(A) particle charge
(B) particle size
(C) particle count
(D) particle shape
50. Which one of the following is used for preparing clear gels?
(A) Carbopol
(B) Starch
(C) Cyclodextrin
(D) Spray-dried lactose
51. Specific surface deals with
(A) surface area per unit volume / weight
(B) surface area of a specified object
(C) surface area of a crystal
(D) surface area of a particle
52. Porosity is defined as the ratio of
(A) void volume to true volume of packing
(B) void volume to bulk volume of packing
(C) true volume to bulk volume of packing
(D) bulk volume to true volume of packing
53. Angle of repose is
(A) maximum angle possible between the surface of pile of powder and vertical plane
(B) maximum angle possible between the surface of pile of powder and horizontal plane
(C) contact angle of powder with surface
(D) refractive angle of a crystal
54. Bingham bodies exhibit
(A) Newtonian flow
(B) simple plastic flow
(C) dilatant flow
(D) simple pseudoplastic flow
55. Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of
(A) absolute viscosity and density of liquid at a definite temperature
(B) absolute viscosity and volume of liquid at a definite temperature
(C) absolute viscosity and density of water at a definite temperature
(D) absolute viscosity and density of liquid at any temperature
56. Dilatant materials exhibit
(A) shear thinning
(B) shear thickening
(C) both shear thinning and shear thickening
(D) None of the above
57. Thixotropy is desirable in case of
(A) suspensions
(B) solutions
(C) ointments
(D) tablets
58. Brookfield viscometer (Searle type) is a
(A) cup and bob type
(B) cone and plate type
(C) falling sphere type
(D) capillaiy type
59. Plug flow is a disadvantage in
(A) cone and plate viscometer
(B) cup and bob viscometer
(C) capillary viscometer
(D) falling sphere-type viscometer
60. Deflocculated particles
(A) settle slowly, eventually form sediment, aggregate and result in hard cake
(B) settle rapidly, do not form a cake and resuspend easily
(C) do not settle and sediment
(D) remain in a state of Brownian motion
Go to "Next Page" for more questions...
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
61. Structured vehicles
(A) provide stability to suspensions by reducing sedimentation
(B) provide instability to suspensions and hasten sedimentation
(C) improve the solubility in suspensions
(D) decrease the solubility in suspensions
62. Ostwald ripening is observed in
(A) solutions
(B) suspensions
(C) tablets
(D) capsules
63. When a gel stands for sometime, it shrinks and some of its liquid is pressed out. This phenomenon is known as
(A) syneresis
(B) imbibition
(C) bleeding
(D) drying
64. Bentonite gel belongs to
(A) organic hydrogel
(B) absorption base
(C) inorganic gel
(D) emulsion base
65. OROS is also known as
(A) oral rehydration powder
(B) oral solution
(C) elementary osmotic pump
(D) oral solid dosage form
66. Partial or complete separation of the top or bottom crowns of a tablet from the main body of tablet is known as
(A) breaking
(B) picking
(C) mottling
(D) capping
67. The use of colourants may solve
(A) picking problem
(B) lamination problem
(C) mottling problem
(D) capillary problem
68. In tablet weight variation test as per USP 20, the tolerance allowed for tablets above 324 mg is
(A) 5%
(B) 7-5%
(C) 10%
(D) 2%
69. In weight variation test, the number of tablets tested as per USP is
(A) 10
(B) 15
(C) 20
(D) 5
70. A roller compacter is used in
(A) wet granulation
(B) compression granulation
(C) direct compression
(D) None of the above
71. Microcrystalline cellulose belongs to the category of
(A) lubricant
(B) diluent
(C) binder
(D) glidant
72. Cellulose acetate phthalate is used in
(A) sugarcoating
(B) film coating
(C) enteric coating
(D) None of the above
73. Capsule shells are prepared by
(A) type-A gelatin
(B) type-B gelatin
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
74. The capsule size which holds maximum volume comparatively is
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 4
(D) 5
75. Bloom strength is related to
(A) cohesive strength of cross- linking that occurs between gelatin molecules
(B) the higher the bloom strength, the more is the capsule stability
(C) cost of gelatin is directly proportional to bloom strength
(D) All of the above
Go to "Next Page" for more questions...
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
76. Microencapsulation technique is used for getting
(A) taste masking
(B) sustained release
(C) reduction in gastric irritation
(D) All of the above
77. The half-life of a drug that is most suitable for development of peroral sustained release is
(A) >12 hours
(B) 3 hours
(C) < 1 hour
(D) None of the above
78. The material that is not used as release retardant in matrix tablet is
(A) hydroxypropyl methyl-cellulose 4000 cps
(B) methylcellulose
(C) ethylcellulose
(D) starch
79. The useful concentration of phenol for preservative action is
(A) 02%-05%
(B) 1%
(C) 0-1%
(D) 2%
80. Aspartame is used as
(A) sweetener
(B) colourant
(C) binder
(D) lubricant
81. Crystal habit of a drug is important for suspensions due to
(A) redispersibility
(B) sedimentation
(C) physical stability
(D) All of the above
82. Anhydrous hydrophilic petrolatum (USP XX) is made of
(A) cholesterol, steaiyl alcohol, white wax and white petrolatum
(B) stearyl alcohol, white wax and white petrolatum
(C) cholesterol, white wax and white petrolatum
(D) cholesterol, stearyl alcohol and white wax
83. Borax and beeswax combination is used in
(A) hydrophilic petrolatum USP XX
(B) lanolin absorption base
(C) cold cream
(D) None of the above
84. Cocoa butter is most widely used in the manufacture of
(A) ointments
(B) suppositories
(C) gels
(D) None of the above
85. Quality control tests of suppositories include
(A) melting range test
(B) breaking test
(C) dissolution test
(D) All of the above
Go to "Next Page" for more questions...
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Job Alerts by Email
86. Aerosol product consists of
(A) propellant, container,product concentrate, valve and actuator
(B) product concentrate,container,valve actuator and
(C) propellant,actuator valve and
(D) None of the above
87. Propellant II is known as
(A) Trichloromonofluoromethane
(B) Dichlorodifluoromethane
(C) Trichloromonofluoroethane
(D) None of the above
88. Containers of aerosols should withstand the following pressure as high as
(A) 140-180 psig at 130° F
(B) 100-140 psig at 130° F
(C) 50-100 psig at 130° F
(D) None of the above
89. Formulation systems of pharmaceutical aerosol may include
(A) solution system
(B) water-based system
(C) dispersion systems, quick-breaking foam system
(D) All of the above
90. Disposable syringes are sterilized by
(A) ethylene oxide
(B) moist heat
(C) UV radiation
(D) boiling with bacteriocide
91. USP type I glass is
(A) highly resistant borosilicate glass
(B) treated soda lime glass
(C) soda lime glass
(D) None of the above
92. For sterile products, preferred type of glass is
(A) type III
(B) type II
(C) type I
(D) NP
93. Water for injection is prepared by
(A) reverse osmosis
(B) filtration
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above
94. Water for injection is stored in industries by holding at
(A) 80 °C
(B) 50 °C
(C) 37 °C
(D) 4 °C
95. Quality control tests of parenteral injection include
(A) leaker test and clarity test
(B) pyrogen, sterility, leaker and clarity tests
(C) pyrogen, leaker and clarity tests
(D) pyrogen, sterility and clarity tests
96. LAL test is based on
(A) formation of gel within 60 min at 37 °C
(B) formation of gel within 15 min at 37 °C
(C) no gel formation at all
(D) None of the above
97. Class 100 area deals with
(A) a clean room in which particle count in the air is not more than 100 per cubic foot of 0-5 pm and larger size
(B) a clean room in which particle count in the air is not more than 100 per cubic inch of 0 5 pm and larger size
(C) a clean room in which particle count in the air is not more than 100 per cubic meter of 0-5 pm and larger size
(D) None of the above
98. The .area suitable for critical operations is
(A) class 100
(B) class 1000
(C) class 10000
(D) None of the above
99. Depyrogenation of glassware and equipment is done by
(A) heating to 650 °C for 1 min
(B) heating to 250 °C for 45 min
(C) None of the above
(D) Both of the above
100. Filled glass ampoules are sealed by
(A) tip seals
(B) pull seals
(C) Either of the above
(D) None of the above









