{ DOWNLOAD AS PDF }
 ABOUT AUTHORS
ABOUT AUTHORS
G. TARUN KUMAR REDDY *1, G. NAVEEN KUMAR REDDY 2
1 Department of Pharmaceutics and Drug regulatory affairs,
Annamacharya college of Pharmacy,
Rajampet, Kadapa, Andhra Pradesh, India.
2 Department of Pharmaceutical analysis,
Sri Padmavathi school of Pharmacy,
Chittoor, Andhra Pradesh, India.
*gtarunkreddy@gmail.com
ABSTRACT:
The regulatory bodies are being established in various pharmaceutical industries across the globe which plays a vital role to meet the requirements of legal procedures related to drug development process in a country. The pharmaceutical industry is considered as the most highly regulated industries worldwide. The regulatory body ensures compliances in various legal and regulatory aspects of a drug. Countries possess their own regulatory authority, which is responsible for enforcing the rules and regulations and issue the guidelines to regulate drug development process, licensing, registration, manufacturing, marketing, labeling and the product life cycle of pharmaceutical products. In an ever-changing regulatory environment, the role of regulatory affairs personnel is essential to ensure compliance with legislation in all regions in which a company wishes to distribute its drug. This article describes about the development of the drugs as it is a cumbersome process which includes several months of time, volunteers, and a huge finical investment majorly through the funding process, so it is strictly regulated as per the norms and regulations as given by those individual countries to carry out the drug development which were generally governed by the Drug Regulatory Affairs Personals.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-2514
|
PharmaTutor (Print-ISSN: 2394 - 6679; e-ISSN: 2347 - 7881) Volume 5, Issue 8 Received On: 24/04/2017; Accepted On: 02/05/2017; Published On: 01/08/2017 How to cite this article: Reddy GTK, Reddy GNK;Significance of Pharmaceutical Regulatory Bodies - A Review; PharmaTutor; 2017; 5(8); 15-22 |
INTRODUCTION
All substances are poisonous beyond a certain dose. The right dose differentiates whether the substance is poison or remedy. As per Paracelsus no drug product is completely safe or efficacious in all circumstances, but there is a moral as well as legal, expectation that appropriate steps are taken to assure optimal quality, safety and efficacy by the producers concerned. (1) Regulatory affairs serve as a roadmap for prescription drugs, biologics and medical device development. Regulatory affairs focus on harmonization with international regulations, new drug applications, good manufacturing practice, quality system compliance, documentation requirements and facilitate an understanding of compliance and product approval, including clinical trial exemptions, fast track status and advisory committee procedures. (2)
Regulatory authority and organizations are responsible in effective drug regulation required to ensure the safety, efficacy and quality of drugs, as well as the accuracy and appropriateness of the drug information available to the public. Regulatory bodies provide strategic, tactical and operational direction and support for working within regulations to expedite the development and delivery of safe and effective healthcare products to individuals around the world. Every country has its own regulatory agencies which are holding the all the regulatory matters of that country relating to the drug substances.
Regulatory authorities act as a guardian that ensures the safety, efficacy and quality of drugs available to the public, to identify the strengths and weaknesses of drug regulation and to propose strategies to improve drug regulation (2).
They also play a vital role to ensure and increase regulatory implementation in non-regulated parts of the world for safety of people residing there. The international regulatory organizations play essential role in all aspects of pharmaceutical regulations related to drug product registration, manufacturing, distribution, price control, marketing, research, development and intellectual property protection.
The regulatory authorities have a particular need to communicate when incidents occur or when issues are raised, but the communication in these ‘crisis' situations is likely to be much more effective if a relationship has already been established through regular routine communications. Hence proactive communication about safety and regulation when there are no incidents to report can be just as important as communication in response to events.(3)
The major changes in Indian regulatory environment on clinical trials for import and manufacture of new drug were introduced in the Drug and Cosmetics Rules as Schedule Y in 1998. Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical Research on Human subjects was brought by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) in 2000. Good Clinical Practices were adopted by India in 2001 by Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO). The National Institute of Medical Statistics of ICMR also commenced the clinical trials registry in 2009. (4)
Historical background of Regulatory Affairs
In 1950’s, multiple tragedies such as the sulfanilamide elixir, vaccine tragedy and thalidomide tragedy have resulted in substantial increase of the legislations for drug products quality, safety and efficacy. This has also resulted into stricter norms for marketing authorization and good manufacturing practices. In 1937 due to diethylene glycol poisoning, 100 people died and in 1956 a thalidomide disaster which majorly triggered for the development of the modern regulatory controls on the drug development and supply. (7) Hence to ensure the quality, safety and efficacy of drug products and in order to assure the continued protection of public health the regulatory agencies were introduced in the late 1950’s.
Objectives:-
The main objectives of the regulatory affairs are as given below:-
* Regulatory Affairs specialists coordinate and document internal regulatory processes, such as internal audits, inspections, license renewals or registrations. They may also compile and prepare materials for submission to regulatory agencies.
* The regulatory bodies play a vital role in between the companies and the government agencies.
* Regulatory affairs department plays a vital role to ensure the safety and efficacy of the drugs available to the public in the market.
* Regulatory bodies set guidelines for the manufacturing, importation, distribution of drugs and also monitors adverse drug reactions (ADR’s).
* Regulatory affairs help in the legalization covering all products with a medicinal claim and all relevant pharmaceutical activities, whether carried out by the public or the private sector.
The need of regulatory affairs
Drug development and commercialization is a highly regulated path to drug registration marketing is paved with good intention but can be complicated as things change constantly. Regulatory bodies deal in the areas of administrative law, regulatory law, secondary legislation, and rule making (codifying and enforcing rules and regulations and imposing supervision or oversight for the benefit of the public at large). The existence of independent regulatory agencies is justified by the complexity of certain regulatory and supervisory tasks that require expertise, the need for rapid implementation of public authority in certain sectors, and the drawbacks of political interference. Some independent regulatory agencies perform investigations or audits, and other may fine the relevant parties and order certain measures. (7)

Fig No: 1 Role of regulatory affairs in drug development
Mission of regulating bodies
The Food and Drug Administration is responsible for protecting the public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, and medical devices; and by ensuring the safety of our nation's food supply, cosmetics, and products that emit radiation. FDA also has responsibility for regulating the manufacturing, marketing, and distribution of tobacco products to protect the public health and to reduce tobacco use by minors. FDA is responsible for advancing the public health by helping to speed innovations that make medical products more effective, safer, and more affordable and by helping the public get the accurate, science-based information they need to use medical products and foods to maintain and improve their health. FDA also plays a significant role in the Nation's counterterrorism capability. FDA fulfills this responsibility by ensuring the security of the food supply and by fostering development of medical products to respond to deliberate and naturally emerging public health threats. (8)
Regional Regulatory Bodies
|
S.No.
|
COUNTRIES |
REGULATING BODIES |
|
|
Australia
|
Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) |
|
|
Brazil
|
Agencia Nacional de Vigiloncia Sanitaria (ANVISA ) National Health Surveillance Agency |
|
|
Canada |
Health Canada |
|
|
China |
State Food and Drug Administration |
|
|
Denmark |
Danish Medicines Agency |
|
|
Europe |
European Medicines Agency (EMEA) |
|
|
India
|
Central Drug Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) |
|
|
Italy |
Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA) |
|
|
Ireland |
Irish Medicines Board |
|
|
Japan |
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) |
|
|
Malaysia |
National Pharmaceutical Control Bureau |
|
|
New Zealand
|
Med safe - Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority |
|
|
Netherlands |
Medicines Evaluation Board |
|
|
Nigeria |
National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC) |
|
|
Singapore |
Centre for Pharmaceutical Administration Health Sciences Authority |
|
|
South Africa |
Medicines Control Council (MCC) |
|
|
Switzerland
|
Swissmedic , Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products |
|
|
Thailand |
Thailand Food and Drug Administration |
|
|
USA |
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) |
|
|
United Kingdom
|
Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) |
|
|
Germany |
Federal Institute of health and Medical Devices |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sri Lanka
|
Cosmetics, Devices & Drugs regulatory authority of Sir Lanka |
|
|
Uganda
|
Uganda National Council for Science and Technology (UNCST) |
|
|
Ukraine |
Ministry of Health |
Table: 1 Regional Regulating Bodies (7).
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Many countries include various sub-coordinating bodies in order to achieve the effective functioning of the implemented guidelines.
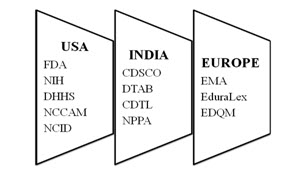
Fig: 2 Coordinating bodies in various countries
International Regulating Bodies
Many of the countries don’t have their own regulating bodies or the improper regulated agencies so they follow the global guidelines. Majority of the Gulf countries don’t have their own regulatory bodies, some of the countries such as Iran, Israel, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria etc., so they adopt the most suitable guidelines according to their region. (9)
|
Regulating body |
Headquarters |
|---|---|
|
World Health Organization (WHO) |
Geneva, Switzerland |
|
World Trade Organization (WTO) |
Geneva, Switzerland |
|
International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) |
Belgium, Europe |
|
Pan American health organization (PAHO) |
Washington D.C. USA |
|
World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) |
Geneva, Switzerland |
Table: 2 International Regulating Bodies (7).
Role of regulatory bodies in drug development process
This department is responsible for knowing the regulatory requirements for getting new products approved. They know what commitments the company has made to the regulatory agencies where the product has been approved. They also submit annual reports and supplements to the agencies. Regulatory Affairs is a comparatively new profession which has developed from the desire of governments to protect public health, by controlling the safety and efficacy of products in areas including pharmaceuticals, veterinary medicines, medical devices, pesticides, agrochemicals, cosmetics and complementary medicines(4). The companies responsible for the discovery, testing, manufacture and marketing of these products also want to ensure that they supply products that are safe and make a worthwhile contribution to public health and welfare. Regulatory Affairs professionals, with their detailed knowledge of the regulations and guidelines, are frequently called in to advice on such matters. The drug approval process is not same for every country as it changes from country to country.
In some countries, only a single body regulates the drugs and responsible for all regulatory tasks such as approval of new drugs, providing license for manufacturing and inspection of manufacturing plants e.g. in USA, FDA performs all the functions. However in some counties all tasks are not performed by a single regulatory authority, such as in India, this responsibility is divided on Centralized and State authorities.
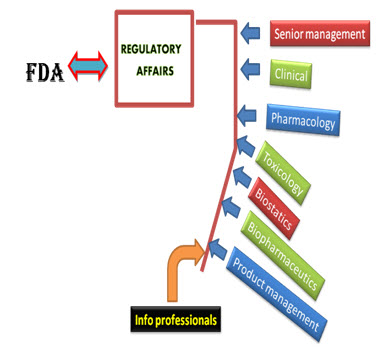
Fig: 3 Approval processes of drug substances (10).
The major responsibilities of the regulatory bodies
• To promote public health and protect the public from harmful and dubious drugs.
• To establish proper legalization covering all products with a medicinal claim and all relevant pharmaceutical activities, whether carried out by the public or the private sector.
• To increase worldwide regulatory growth to ensure safety of people.
• The regulatory affairs cumulatively collect the data from all the bodies which involves in the drug development.
• Regulatory bodies deals from the earliest non-clinical studies, through development and the product manufacturing and the post marketing surveillances.
• The regulatory affairs department also handles the drug pricing, prescribing, and also the special control if any (narcotics).
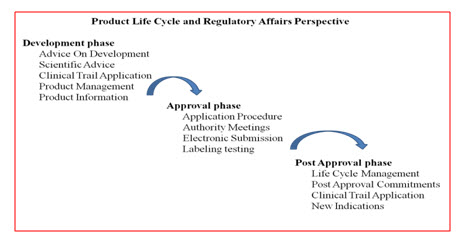
Fig: 4 Product Life Cycles and Regulatory Affairs Perspective (6).
Regulatory affairs in R&D
The affairs personals work in collaborative with the R&D and FR&D to develop, innovative products that meets the new technological and the regulatory developments to accelerate time to market. The new products are expected to increase the revenues of the organization; losses due to delayed marketing will eventually get nullified with the large materials gains in revenue and profit over time. Employing adaptive clinical trial strategies to obtain the quick approval from regulatory authorities and avoiding the pitfalls in processes can accelerate development of new products and helps to reduce the expensive errors and time lags.
Regulatory affairs in Clinical Trails
Regulatory affairs professionals are the primary link between the company and worldwide regulatory agencies such as official bodies (US FDA, CDSCO, MCCA, TGA etc.). These professional’s work is to furnish timely reports of the new data which is obtained in the trails and help in the approval process of the new products as according to the local regulating bodies in their respective states.
Role of Regulatory affairs in Product Development The drug products are highly regulated channels compared to the others. These regulations are generally maintained and handled by the regulatory bodies, these bodies generally gives advice on the product development based on the IND/NDA guidelines once after the approval process completes these bodies generally focus on the drug post market properties and also on the Pharmacovigilance aspects of the drug product, and it also reminds the drug Renewal period.
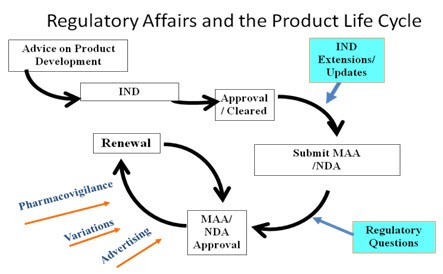
Fig: 5 Product Life Cycles (11).
Regulatory affairs in Product Management
The general role of the Regulatory Affairs is broader than the registration of products, they advise companies both strategically and technically at the highest level. Their role begins right from development of a product, marketing, and post marketing strategies. Their advice at all stages both in terms of legal and technical requirements help companies to save a lot of time and money in the developing the new products.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
CONCLUSION
The regulatory affairs profession believes the new approach to regulation will eventually be adopted for all healthcare products as it represents the best model for delivering new healthcare advances to market in a reasonable time with acceptable safety. The regulatory bodies will deal with the growing and is the one which is least impacted during the acquisition and merger, and also during recession. Regulatory Affairs departments are growing within companies. Due to the changing resources which are necessary to fulfill the regulatory requirements, some companies also choose to outsource or task regulatory affairs to external service providers. In today’s competitive environment the reduction of the time taken to reach the market is critical to product’s and hence the company’s success. The proper conduct of its Regulatory Affairs activities is considerable for the economic growth of the company.
REFERENCES
1. D.K Sanghi & Rakesh Tiwal; Role of Regulatory affairs in a Pharmaceutical Industry; International journal of pharmacy review and research.
2. Regulatory Affairs from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia [online] 7th April. Available from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regulatory_Affairs.
3. International Atomic Energy Agency; iaea.org/ ns/tutorials/regcontrol/ commun/com811.htm. ; As on 20-4-2017.
4. Subash Philip and Ansa Philip; The Scope of Regulatory Affairs in the Pharmaceutical Industry HYGEIA - Journal For Drugs And Medicines.
5. Regulatory Agency; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regulatory_agency; as on 20-4-2017.
6. Sumit Kumar, Rishabh Panwar, Upendra Singh; Regulatory Affairs In The Pharmacy Curriculum; International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences.
7. Charlotte Enochsson; Biomedicine the Profession – 2 December 2014; Regulatory Affairs, the role in pharma – BMC.
8. USFDA; fda.gov/aboutfda/whatwedo/; as on 20-4-2017.
9. Regulatory Affairs Professional Society; raps.org/Regulatory-Focus/ News/ Databases/2015/04/06/21908/The-Essential-List-of-Regulatory-Authorities-in-Asia/; as on 20-4-2017.
10.Geetanjali Sengar, Pranab Tripathy; Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agencies and Organizations around the World.
11. E.Gopinath , R.S. Bhadauria, Jodan Gunjan, zaidi Insha; pharmaceutical regulatory affairs – review.
12.Mahesh Shinde; Drug regulatory affairs; slideshare.net/Mahesh
shinde 25/regulatory-affairsintroduction-to-ctd.
13. International regulatory affair updates available at iraup. com/ about .php.
14.Topra brought by dimension associates available at topra.org /TOPRA/ TOPRA_Member/What_is_regulatory_affairs.aspx.
15Ayushi Srivastava, veena Gupta; Regulatory Canvas of Indian Pharmaceutical Industry; Challenges and Future; pharmatutor.org; as on 27-03-2017.
16. indianpharmaceuticalassociation.org .
17.Carlos Langezaal; The importance of developing the regulatory strategy towards the goal of registration; slideshare.in; as on 26-03-2017.
18.Central Drugs Standard Control Organization; cdsco.nic.inas on 25-3-2017.
19. Eva Kopecna; Role and Strategic Importance of Regulatory Affairs; topra.org; as on 25-3-2017.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT editor-in-chief@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









