Neuroscientists roll out first comprehensive atlas of brain cells
When you clicked to read this story, a band of cells across the top of your brain sent signals down your spine and out to your hand to tell the muscles in your index finger to press down with just the right amount of pressure to activate your mouse or track pad.
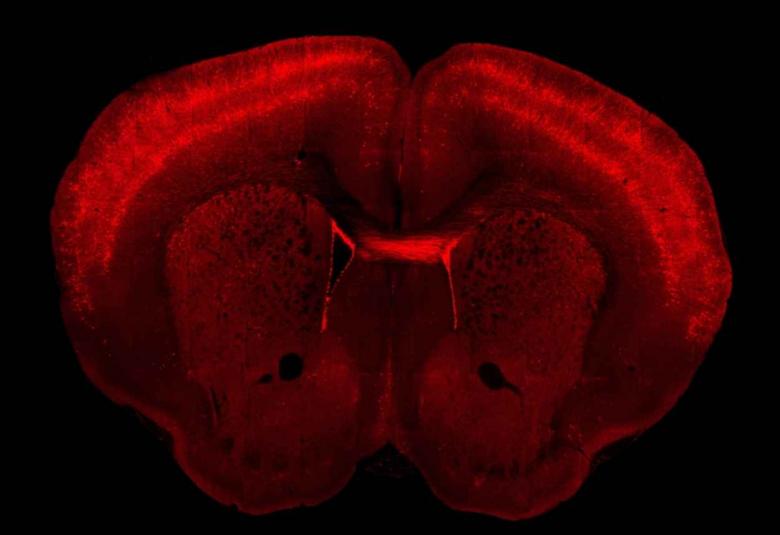
A slew of new studies now shows that the area of the brain responsible for initiating this action — the primary motor cortex, which controls movement — has as many as 116 different types of cells that work together to make this happen.