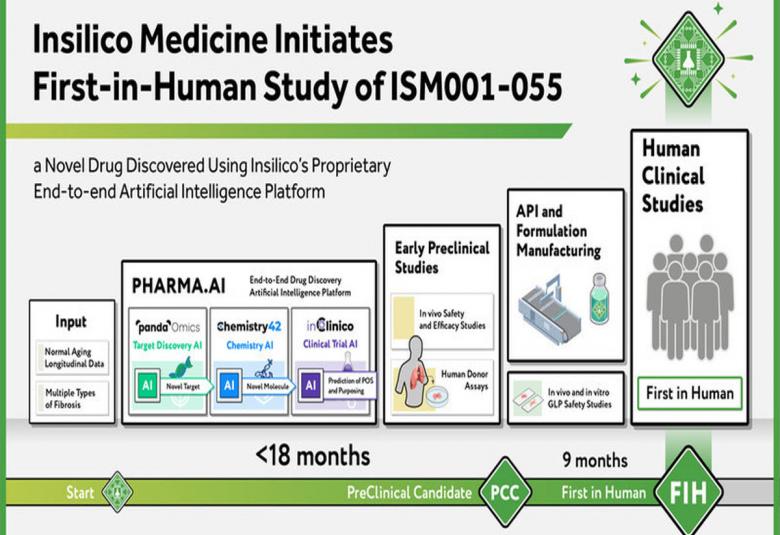
Insilico medicines initiates human trial for AI discovered drug
Insilico Medicine, an end-to-end artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company announced that the first healthy volunteer has been dosed in a first-in-human microdose trial of ISM001-055.