Body Posture Affects How Oral Drugs Absorbed by Stomach
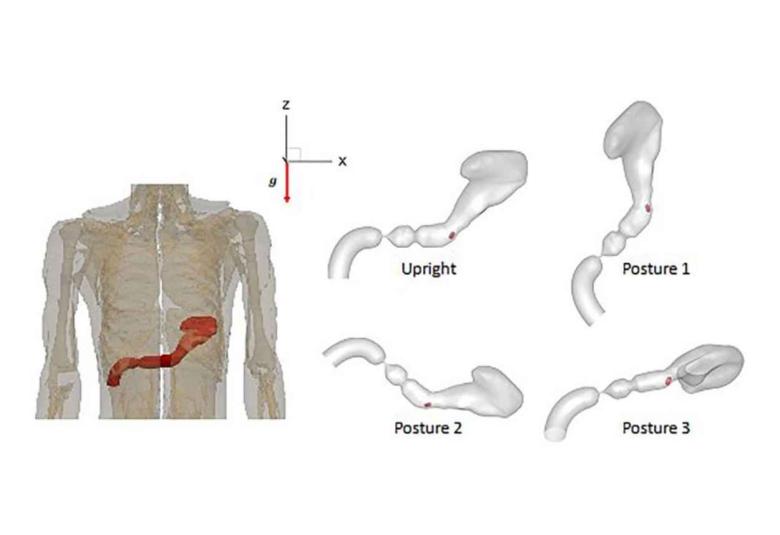
A common, economic, and easy method of administering drugs is orally, by swallowing a pill or capsule. But oral administration is the most complex way for the human body to absorb an active pharmaceutical ingredient, because the bioavailability of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract depends on the medication’s ingredients and the stomach’s dynamic physiological environment.