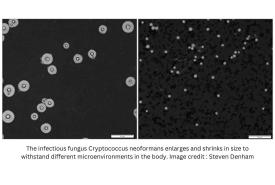
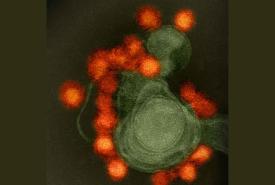
Drug Turns Cancer Gene Into Eat Me Flag for Immune System
Tumor cells are notoriously good at evading the human immune system; they put up physical walls, wear disguises and handcuff the immune system with molecular tricks. Now, UC San Francisco researchers have developed a drug that overcomes some of these barriers, marking cancer cells for destruction by the immune system.