Advanced Brain Circuit-Mapping Technique Reveals New Anxiety Drug Target
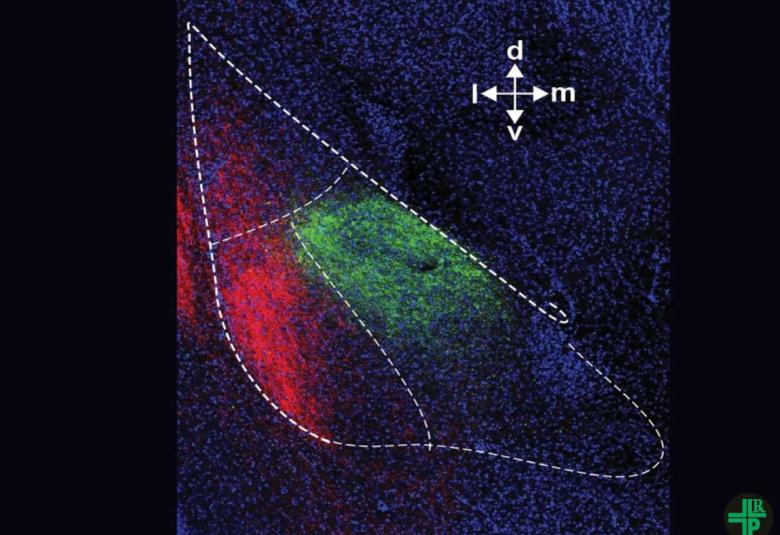
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have identified in a preclinical model a specific brain circuit whose inhibition appears to reduce anxiety without side effects. Their work suggests a new target for treating anxiety disorders and related conditions and demonstrates a general strategy, based on a method called photopharmacology, for mapping drug effects on the brain.