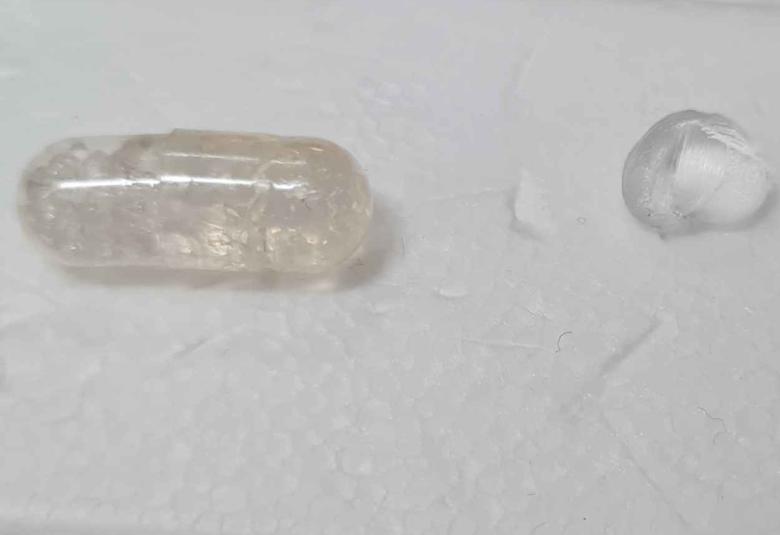
Wonder drug-capsule may one day replace insulin injection for diabetics
Scientists in Melbourne have designed a new type of oral capsule that could mean pain-free delivery of insulin and other protein drugs. Co-lead researcher Professor Charlotte Conn, a biophysical chemist from RMIT University, said protein drugs had proven challenging to deliver orally as the drugs degrade very quickly in the stomach – until now.