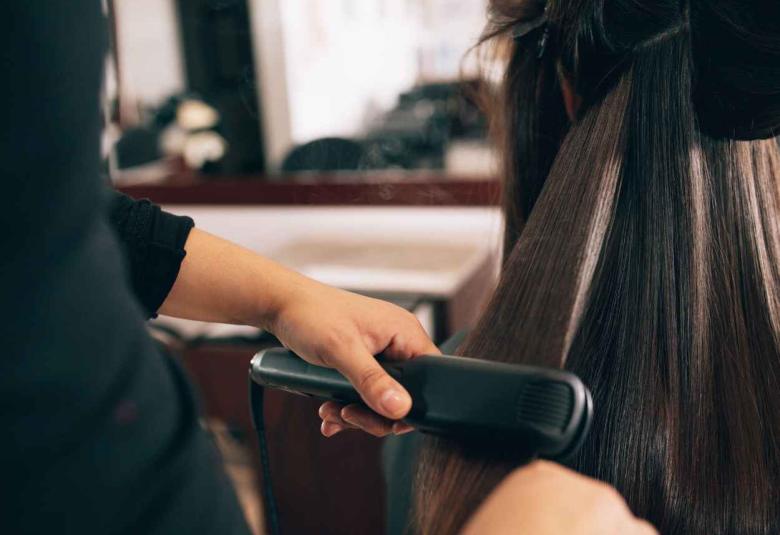
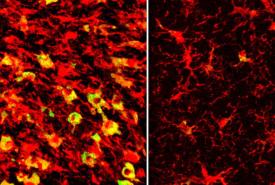
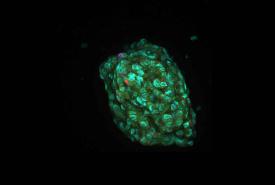
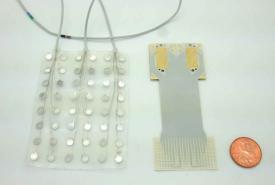
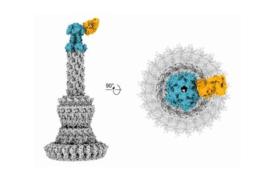
Mixing heat with hair styling products may be bad for your health
Hair products often contain ingredients that easily evaporate, so users may inhale some of these chemicals, potentially posing health repercussions. Now, researchers have studied emissions of these volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including siloxanes, which shine and smooth hair. The scientists report in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology that using these hair care products can change indoor air composition quickly, and common heat styling techniques straightening and curling increase VOC levels even more.