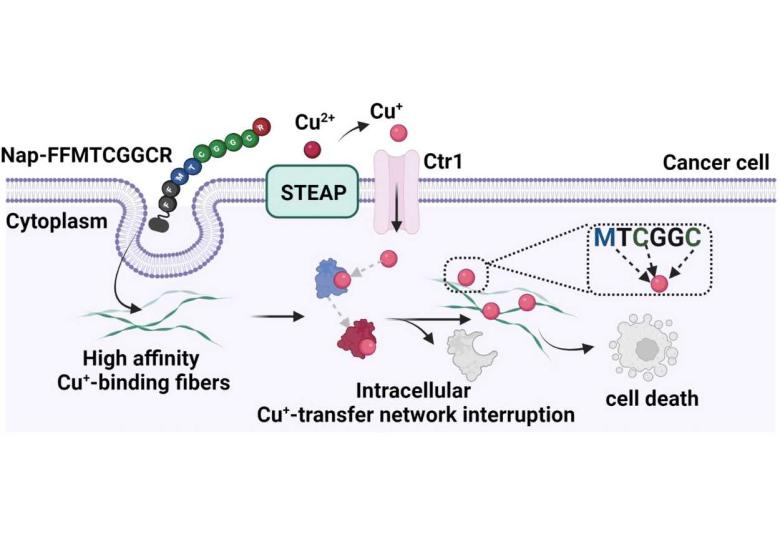
Tumor Cells Suffer Copper Withdrawal Nanofibers made of copper-binding peptides disrupt copper homeostasis in cancer cells
While toxic in high concentrations, copper is essential to life as a trace element. Many tumors require significantly more copper than healthy cells for growth a possible new point of attack for cancer treatment. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a research team from the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research has now introduced a novel method by which copper is effectively removed from tumor cells, killing them.