About Authors: 1Arun Kumar Dash*, 2Amitesh Palo,
1. Royal College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Berhampur.
2. College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Mohuda, Berhampur
ABSTRACT
A simple method for the estimation of Olmesartan in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage forms has been developed. Methanol was chosen as the solvent system. The λmax was found to be 257nm and all absorbance values were carried out at 257nm. The responses were linear in the range of 5-35µg/ml. The regression equation of the calibration graph and correlation coefficient were found to be y = 0.049x + 0.007 and 0.999 respectively. The %RSD values for both intraday and interday precision were less than 1%. The recovery of the drug from the sample was ranged between 99.36 and 100.49%. The proposed method was validated for precision, accuracy, intraday, interday assay, robustness and ruggedness. Commercial tablets containing 20mg and 40mg of Olmesartan were analyzed by the proposed method and the results were well within the claimed limits. Furthermore stability studies of Olmesartan were carried out under acidic, alkaline, hydrolytic and photolytic conditions as per SIAM (Stability Indicating Assay Methods).
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
INTRODUCTION
Olmesartan (figure I) is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist used in the treatment of hypertension. It binds to angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptors with high affinity, causing inhibition of the action of angiotensin II on vascular smooth muscle, ultimately leading to a reduction in arterial blood pressure. Chemically Olmesartan is (5-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl, 4-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-propyl-1-({4-[2-(2H-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl}methyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylate. It is used to treat hypertension, heart failure and post-myocardial infarction. A literature survey reveals that there are various methods available for estimation of Olmesartan like, HPLC1,2,3, LC-MS-MS4, UV spectrophotometry5, Capillary Zone Electrophoresis6. However some of these methods are costlier, time consuming and are only for estimation of drugs from the biological fluids. Also the above methods are not validated for its performance under stress conditions thus rendering them unsuitable for stability studies. Thus an attempt was made to develop a new, simple, accurate and validated method for determination of Olmesartan by UV spectrophotometric method along with its stability studies. The method was validated as per the procedures and acceptance criteria of ICH guidelines.

Figure I: Structure of Olmesartan
MATRIALS AND METHOD
Instruments:
All the chemicals and reagents used were of analytical grade (AR) procured from Merck. All absorbance measurements were done with Shimadzu 1700 double beam UV-Spectrophotometer (Japan) with 10mm matched quartz cell and Borosil glass wares were used for the study. All weighing was done on Sartorious BT 2245 electronic balance.
Standard Stock Solution: Standard stock solution was prepared by dissolving 10 mg of drug in 10ml of methanol to get a concentration of 1000 µg/ml. It was further diluted to get a concentration of 100 μg/ml. and was kept as the stock solution.
Determination of λmax: The standard solution of Olmesartan (10 µg /ml) was scanned in the wavelength region of 200-400 nm and the λmax was found to be 257 nm.
Preparation of calibration curve:
The stock solution of Olmesartan was according diluted to obtain concentration in the range of 05-35μg/ml. The absorbances were observed against methanol as blank and the calibration curve was plotted between concentration (x-axis) and absorbance (y-axis).
Assay of tablet dosage form
20 tablets of brand OLSAR (manufactured by Unichem Laboratories Ltd.) containing 20 mg of Olmesartan were weighed, average weight determined and finely crushed to powder. An accurate weight equivalent to 10mg of the drug was transferred to 100ml volumetric flask. The drug was extracted 4 times by adding solvent in potions, 20 ml each time and the volume was made upto the mark by using solvent. It was then diluted (within the linearity range), absorbances of the sample solution were recorded at determined λmax and the concentration of the drug in sample was found out. In a similar manner, the assay of PINOM (manufactured by Lupin Laboratories Ltd.)containing 40mg of Olmesartan was carried out.
VALIDATION
1. Accuracy: The accuracy of the proposed method was tested by recovery studies at 80%, 100%, and 120% by adding a known amount of pure drug to the pre-analyzed formulation of concentration 10µg/ml.
2. Precision: The precision of the proposed method was ascertained by actual determination of 6 replicates of a fixed concentration of the drug (10µg/ml) within the Beer’s range and finding out the absorbance by the proposed method.
3. Sensitivity: The sensitivity of the method was determined with respect to LOD and LOQ. The LOD and LOQ were separately determined based on the standard calibration curve using the formula LOD = (3.3 x S.D /S) and LOQ = 10 x S.D/S, where, S.D is the standard deviation of the y- intercept of regression line and S is the average slope of the calibration curve.
4. Intraday Assay: The intraday assay of the proposed method was ascertained by actual determination of 6 replicates of a fixed concentration of the drug (10µg/ml) within the Beer’s range and finding out the absorbance by the proposed method at 3 different time period of the same day.
5. Interday Assay: The interday assay of the proposed method was ascertained by actual determination of 6 replicates of a fixed concentration of the drug (10µg/ml) within the Beer’s range and finding out the absorbance by the proposed method on 3 different days.
DEGRADATION STUDIES:
Acid degradation: Accurately weighed 10 mg of the drug was taken in a 10 ml volumetric flask. To this minimum amount of methanol was added to dissolve the drug and the volume was made up with freshly prepared 0.1N HCl. Then this solution was kept inside a water bath maintained at a temperature of 70°C. Samples were withdrawn in regular interval of 1 hour and the absorbance was measured at the determined λmax and recorded.
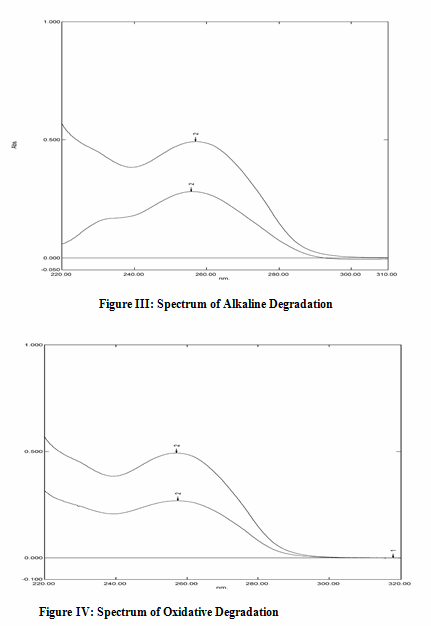
Alkali Degradation: Accurately weighed 10 mg of the drug was taken in a 10 ml volumetric flask and minimum amount of methanol was added to dissolve the drug. The volume was made up freshly prepared 0.1N NaOH. This solution was kept inside a water bath maintained at a temperature of 70°C. The samples were withdrawn in regular interval of 1 hour and the absorbance was measured at the determined λmax and recorded.
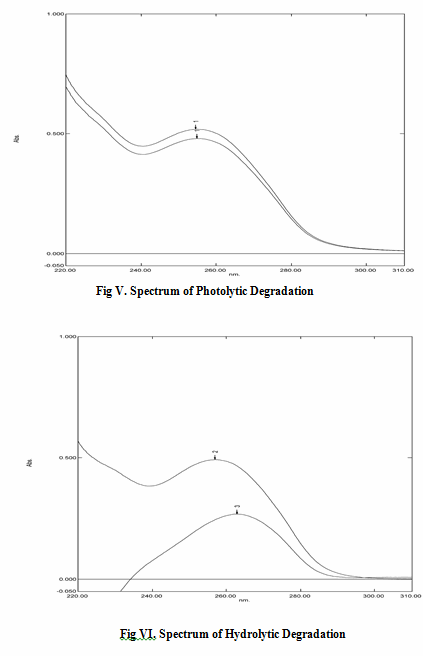
Hydrolytic Degradation: Similarly 10 mg of the drug was taken in a 10 ml volumetric flask and minimum amount of methanol was added to dissolve the drug. Distilled water was added to make up the volume. This solution was kept inside a water bath maintained at a temperature of 70°C. The samples were withdrawn in regular interval of 1 hour and absorbance was measured and recorded.
Oxidation Degradation: Accurately weighed 10 mg of the drug was taken in a 10 ml volumetric flask and minimum amount of methanol was added to dissolve the drug. Freshly prepared 3% H2O2 was added till the mark. This solution was kept inside dark condition for 36 hours. The samples were withdrawn in regular interval of 6 hour and absorbance were measured at the determined λmax and recorded.
Photolytic degradation: Around 150mg of bulk drug was put it into the petridish and were placed under direct sun light for three day. Samples were taken with an interval of 6 hours. From the samples accurately weighed 10mg of the drug was dissolved in 10 ml of methanol and then the required concentration of the drug was prepared. The absorbances were measured at the specified λmax and recorded.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
a. Calibration Curve: The absorbance for the different concentrations (05-35μg/ml) was recorded at 257nm. The calibration curve (figure II) data is shown in table 1. The assay results of the marketed formulations are shown in table 2.
Table 1: Optical Characters of the Proposed
|
Concentration |
Absorbance |
|
05 |
0.268 |
|
10 |
0.493 |
|
15 |
0.755 |
|
20 |
0.973 |
|
25 |
1.237 |
|
30 |
1.504 |
|
35 |
1.739 |
Table 2: Assay result of the marketed formulation by the proposed method
|
Formulation Label claimed Observed Amount % Recovery |
|
OLSAR 20mg 19.69 98.47 PINOM 40mg 39.14 97.87 |
b. Accuracy:The % recovery was found to be in the range of 99.36 and 100.49%.
c. Precision:The %RSD for precision was found to be 0.498255.
d. Sensitivity: Low values for SD indicates the method was precise. The limit of detection was found to be 0.23µg/ml and the limit of quantification was found to be 0.70µg/ml at 257nm. respectively.
e. Intraday and Interday Assay: The %RSD for Intraday and Interday Assay were found to be 0.003488and 0.17528respectively. Low values of %RSD indicate that the proposed method is accurate.
f. Stability Results: The results obtained in alkaline degradation, oxidative degradation, photolytic degradation, hydrolytic degradation and acidic degradation are depicted as spectrums and given in figure III, IV, V and VI. respectively and data is represented in table no. 3
Table 3:Stability Study Results:
|
Stress conditions |
Time (in hours) |
Absorbance after degradation |
Conc.(µg/ml) |
% Degradation |
|
|
Initial |
Final |
||||
|
Acidic degradation |
05 |
0.389 |
10 |
07.795 |
22.05 |
|
Alkali degradation |
05 |
0.275 |
10 |
05.649 |
40.08 |
|
Hydrolytic Degradation |
05 |
0.261 |
10 |
05.183 |
48.17 |
|
Oxidative Degradation |
48 |
0.309 |
10 |
06.163 |
33.87 |
|
Photolytic degradation |
48 |
0.135 |
10 |
08.743 |
12.57 |
CONCLUSION:
The proposed method was found to be simple, precise and rapid for the determination of Olmesartan from pure and its dosage forms. The sample recoveries in all formulations were in good agreement with their respective label claims. Thus the proposed method can be used as an alternative method to the reported ones for the routine analysis of the drug in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage forms and can also be used for dissolution or similar studies.

REFERENCES:
1. M Tomonori, K Hidetoshi, F Naoto, O Michinobu, K Takao. Identification of a degradation product in stressed tablets of Olmesartan medoxomil by HPLC hyphenated techniques. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008, 47, 553–559.
2. BG Raveendra, AL Ramprasad, P Srinivasu, R Jayachandra, M Mustafa. New RP-HPLC method for the determination of Olmesartan medoxomil in tablet dosage form. Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 2, 58-61.
3. K. Raghunathan, JM Reddy. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method development and validation of Olmesartan medoxomil. AJPBR. 2011, 33-37.
4. V Vikas, M Shikha, N. Roy, M Santosh, S Santosh, SA Parekh. LC–MS–MS determination of Olmesartan in human plasma. Chromatographia.2011, 67(1-2), 147-150.
5. A. R. Rote, P D Bari. Spectrophotometric estimation of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Hydrochlorothiazide in tablet. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2010, 72(1), 111–113.
6. Ç Mustafa, A Sacide. Development of a CZE method for the determination of Olmesartan medoxomil in tablets. Chromatographia. 2007, 66(11-12), 929-933.
Reference ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1020
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









