 About Author:
About Author:
Mridula Jayaraman,
Amity Institute of Pharmacy,
Amity University, India
mridulajayaraman1990@gmail.com
Abstract
The word ‘cancer’ itself sends chills down our spines as its prognosis and treatment, even if detected at an early stage is cumbersome and tortuous. With the advent of modern medicines, even though it is claimed that cancer is curable, there exists virtually no chemotherapeutic agent for cancer without side effect(s), not to mention the cost of these medicines which are skyrocketing.
Hence, we are left with little choice but to go for new fronts in research on the therapeutic agents present in plants (Phytotherapy), which are not only cost effective but also relatively side effects free. These plants are available in plenty in the Himalayan and Aravali Region of India.
University of Wisconsin lists 150 plants which they have established as having potential value in the treatment of cancer. However, the real issue here is that not many drugs derived from plants have been standardized and standardization of these plants for therapeutic purpose is still in the nascent stage.
[adsense:336x280:8701650588]
REFERENCE ID: PHARMATUTOR-ART-1896
1. Introduction – Understanding Malignancy and Oncogenesis
Tumor- Tumor is a neoplastic growth with an uncontrolled multiplication of cells.
The main types of tumors are:-
1. Benign tumors
2. Malignant tumors
Benign tumours:- A benign tumor is a tumour that lacks the ability to metastasize, i.e. these tumours do not spread from one organ or part to another organ or part of an organ. Eg. Moles, uterine fibroids etc.
Malignant tumors: - These tumors tend to invade and metastasis, i.e. they can spread from one part of the body to another and these cells divide uncontrollably within a short span of time. Malignant tumors are generally termed as cancer.
Whereas treatment and prognosis for benign tumors is quite easy and generally successful, treating the malignant tumors is not only arduous but also not always successful and in many cases fatal.
Oncogenesis - Mechanism by which the cancer cells multiply
Oncogenes are genes present in the normal healthy cells that have been altered by mutation to make the cells grow and divide faster. This alteration results in the process of oncogenesis leading to division of cells in an unpredictable fashion and uncontrollably.

Fig no.1- illustration of metastasis.
2. Phytotherapy and Phytotoxins
Phytotherapy is the study of the use of extracts from natural origin as medicines or health-promoting agents.
Phytotoxin are substance produced by a plant that is toxic or a substance that is toxic to the plant. These toxins are not only toxic to the normal cells but also to the malignant cell. This concept is used in the therapy using these agents. Some examples of phytotoxins are alkaloids, terpenes, phenolics, herbicides and substances produced by bacteria.
Brief discussion on some popular plants having known therapeutic/preventive effect on cancer
1. Allium sativum (Garlic, lehsun) - Scientists have isolated two active ingredients in garlic, allicin and allyl sulfur, and demonstrated that they prevent and fight cancer in both animals and humans. So, adding garlic to our diet can act as a preventive measure.
2. Aloe vera (grith kumari):- Lectins and emodines are two anti-cancer agents in Aloe vera which are effective against blood cancer (leukaemia)
3. Zingiber officinalis(Ginger, Adrak)- Dietary ginger constituents, galanals A and B, are potent apoptosis inducers in Human T lymphoma Jurkat cells.
4. Artemisia capillaries- It is a Korean medicine. The oil extracted from this plant has anti tumour activity and is effective against colon cancer
5. Viscum album (Mistletoe)- It is a traditional European remedies either as extract or homoeopathic doses and stimulates cell metabolism. It is effective against breast and cervical/uterine cancer.

Fig No.2 Mistletoe Tree
3.Some FDA approved plants with their Phytotheraphic activity
3.1Catharanthus roseus (Periwinkle,Sadhabahar) (Family Apocynaceae)
Biological source-
It is the dried whole plant of Catharanthus roseus

Fig no.3 – Catharantus roseus and the cancers against which it is effective
[adsense:468x15:2204050025]
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia:- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia is basically the cancer of WBC’s specially lymphocytes characterized by increase of lymphoblast cells.
Lymphomas: - Lymphoma shortly defined is a type of cancer involving cells of the immune system, called lymphocytes. It affects the cells that play a role in the immune system and primarily represents cells involved in the lymphatic system of the body.
Hodgkin's lymphoma: - Hodgkin's lymphoma previously known as Hodgkin's disease is a type of lymphoma, which is a cancer originating from white blood cells called lymphocytes. It was named after Thomas Hodgkin, who first described abnormalities in the lymph system in 1832. Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by the orderly spread of disease from one lymph node group to another and by the development of systemic symptoms with advanced disease.
Nephroblastoma: - Nephroblastoma is cancer of the kidneys that typically occurs in children, rarely in adults.
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
Chemical constituents (Kokate et al, 2005)of periwrinkle exhibiting anti cancer activity are
-
Vincristine
- Vinblastine
They are administered intravenously in their sulphate form. These solutions are fatal if they're administered any other way and can cause a lot of tissue irritation if they leak out of the vein. Although these compounds are very similar in structure and have the same basic action, they have distinctly different effects on the body.
Vincristine
Vincristine binds to tubulin dimmers (structural protein that polymerizes to microtubules), inhibiting assembly of microtubule structures (Bauely. C. Bruce et al 2002)

Fig no. 4 Structure of Vincristine
Disruption of the microtubules arrests mitosis in metaphase. Therefore, the vinca alkaloids affect all rapidly dividing cell types not only the cancer cells, but also those of intestinal epithelium and bone marrow. Hence these should be administered quite carefully.It is highly effective against non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, leukemia, nephroblastoma.
Vinblastine
Microtubule disruptive drug like vinblastine have been reported to act by two mechanisms. At very low concentrations they suppress microtubule dynamics and at higher concentrations they reduce microtubule polymer mass(Bauely. C. Bruce et al 2002). Recent findings indicate that they also produce microtubule fragments by stimulating microtubule(1)minus-end detachment from their organizing centers. Dose-response studies further indicate that enhanced microtubule detachment from spindle poles correlate best with cytotoxicity. Vinblastine is highly effective against Hodgkin's lymphoma.
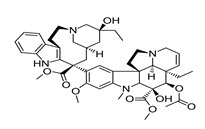
Fig no. 5 Structure of Vinblastine

Fig no. 6 Mechanism of Destabilization of microtubules by Vinca alkaloids
Marketed preparations using the vincristine/vinblastine from Periwrinkleused in treatment of Cancer
· Oncovin, Eli Lilly-Vincristine, injection IV-hodkings lymphoma
· Velban, Eli Lilly–Vinblastine, injection IV-lymphoma
· Vincasar PFS- Vincristine, injection IV- rhabdomyosarcoma(2)
3.2 Podophyllum peltatum, Podophyllum emodi (Indian podophyllum, Himalayan May apple)
Family- Berberidaceae
Biological Source-
Podophyllum consists of dried rhizomes and roots of Podophyllum emodi, Podophyllum hexandrum Royle. Americam podophyllum consists of dried rhizomes and roots of Podophyllum peltatum.
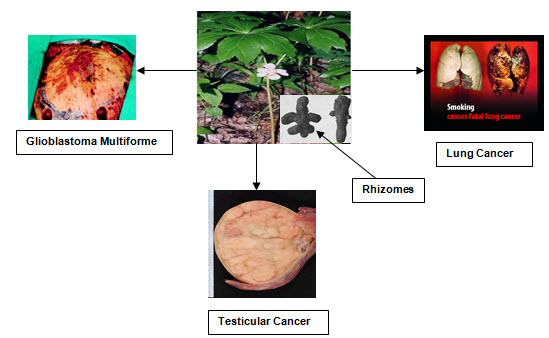
Fig no.7– Podophyllum spp. plant and the cancers against which it is effective
Lung cancer: - Lung canceris a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If it is left untreated the growth would spread beyond the lung resulting in metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. The main types of lung cancer are small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), also called oat cell cancer & non small-cell lung cancer.
Testicular Cancer:-Most testicular germ cell tumors have too many chromosomes, and most often they are triploid to tetraploid. The short arm of chromosome 12 on both sides of the same centromere, is present in about 80 % of the testicular cancers, and the other cancers usually have extra material from this chromosome arm through other mechanisms of genomic amplification (3)is prevalent in 1-2% of Indian men.
Glioblastoma Multiforme: - Glioblastoma multiforme(GBM) is the most common and most aggressive malignant primary brain tumor in humans, involving glial cells and accounting for 52% of all functional tissue brain tumor cases and 20% of all intracranial tumors.Glioblastoma multiforme tumors are characterized by the presence of small areas of necrotizing tissue that is surrounded by anaplastic cells.
Chemical constituents (Kokate et al, 2005) of podophyllum exhibiting anticancer activity-
- Podophyllum peltatum- Podophyllotoxin
-
Podophyllum emodi
1. Etopside
2.Teniposide
Mechanism of Action
1- Podophyllotoxin
Podophyllotoxin has antineoplastic activity but it is highly toxic. This lignan inhibits mitosis by destroying the structural organization of the mitotic apparatus. Podophyllotoxin's anticancer property can be attributed to the inhibition of tubulin polymerization. As podophyllotoxin binds to the tubulin, microtubule formation is prevented. Consequently, podophyllotoxin arrests the cell cycle in the metaphase.
Podophyllotoxin derivatives display binding activity to the enzyme topoisomerase II during the late S and early G2 stage. For instance, etoposide binds and stabilizes the temporary break caused by the enzyme, disrupts the reparation of the break through which the double-stranded DNA passes, and consequently stops DNA unwinding and replication.
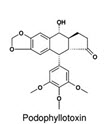
Fig no.8 –Structure of Podophyllotoxin
2-Etopside
Etoposide inhibits the enzyme topoisomerase II, which aids in DNA unwinding and by doing so causes DNA strands to break. Cancer cells rely on this enzyme more than healthy cells, since they divide more rapidly. It is used as a form of chemotherapy for cancers such as Ewing's sarcoma, lung cancer, testicular cancer, lymphoma, non lymphocytic leukemia, and glioblastoma multiforme. It is often given in combination with other drugs. It is also sometimes used in a conditioning regimen prior to a bone marrow or blood stem cell transplant. Its chemical make-up derives from podophyllotoxin, a toxin found in the Podophyllum peltatum

Fig no.9 –Structure of Etoposide
Mechanism of Action
Etoposide forms a ternary complex(4)with DNA and the topoisomerase II enzyme, preventing re-ligation of the DNA strands. This causes errors in DNA synthesis and promotes apoptosis of the cancer cell.

Fig no. 10 Mechanism of action of Etoposide against cancer cell cycle.
3-Tenoposide
Teniposide is a chemotherapeutic medication mainly used in the treatment of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is in a class of drugs known as podophyllotoxin derivatives and slows the growth of cancer cells in the body.
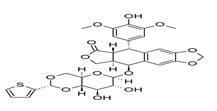
Fig no.11 Structure of Tenoposide
Mechanism of Action
Teniposide causes dose-dependent single- and double-stranded breaks in DNA and DNA-protein cross-links. The mechanism of action appears to be related to the inhibition of type II topoisomerase activity since teniposide does not intercalate into DNA or bind strongly to DNA(Bauely. C. Bruce et al 2002). The cytotoxic effects of teniposide are related to the relative number of double-stranded DNA breaks produced in cells, which are a reflection of the stabilization of a topoisomerase II-DNA intermediate.

Fig no.12 Mechanism of action of Teniposide on cancer cells
Marketed Preparation
Etoposide
- Vepesid- soft capsules- Bristol Myer Pharmaceuticals
- Toposar- Injection,IV- Pfizer
- Etopophos -100mg powder solution for IV injection- Bristol Myer Pharmaceuticals
Teniposide
- Vumon-IV- Bristol Myer Pharmaceuticals
Podophyllotoxins
- Podofilox- Banned drug, Topical agent, Real food Company
- Podoxin- Topical agent, Pablo Cassara Laboratory
- Podocon-25- Topical agent, Paddock Laboratory
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
3.3 Taxus brevifolia (Pacific yew) (Family- Taxaceae)
Biological source-
It consists of stem bark of Taxus brevifolia

Fig no.13 Taxus brevifolia plant, and the cancers against which it is effective
Breast Cancer:-Breast cancer(malignant breast neoplasm) is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas.
Ovarian cancer: - Ovarian canceris a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and urinary frequency, and are easily confused with other illnesses. Most (more than 90%) ovarian cancers are classified as "epithelial" and are believed to arise from the surface (epithelium) of the ovary. However, some evidence suggests that the fallopian tube could also be the source of some ovarian cancers.
Kaposi sarcoma:-Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a tumor caused by Human herpes virus 8 (HHV8), also known as Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV).
Head and neck cancer:-Head and neck cancer refers to a group of biologically similar cancers originating from the upper aero digestive tract, including the lip, oral cavity (mouth), nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, and larynx. 90% of head and neck cancers are squamous cell carcinomas (SCCHN), originating from the mucosal lining (epithelium) of these regions.
Chemical Constituents
· The active principle which exhibits anti cancerous activity is Taxol (Palcitaxel)

Fig no.14 Structure of Taxol
Taxol is the most potent mitotic inhibitor used in chemotherapy discovered in NCI(National Cancer Institute, USA) by Monroe E. Wall and Mansukh C. Wani . They isolated it from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia and named it taxol.
Mechanism of Action
Paclitaxel-treated cells have defects in mitotic spindle assembly, chromosome segregation, and cell division. Unlike other tubulin targeted drugs such as colchicine that inhibit microtubule assembly, however, paclitaxel stabilizes the microtubule polymer and protects it from disassembly. The inability of the chromosomes to achieve a metaphase spindle configuration leads to a mitotic block in which there is prolonged activation of the mitotic checkpoint with the subsequent triggering of apoptosis or slippage back into the G1-phase of the cell cycle without cell division,. The ability of paclitaxel to inhibit spindle function is generally attributed to its suppression of microtubule dynamics; but recent studies have demonstrated that suppression of dynamics occurs at concentrations lower than those needed to block mitosis. At the higher antimitotic concentrations, paclitaxel appears to act by suppressing microtubule detachment from centrosomes, a process normally activated during mitosis. The binding site for paclitaxel has been shown to reside on the beta-tubulin subunit.

Fig no.15 -Tubulin hetero dimmer structure of palcitaxel

Fig no.16- Mechanism of action of palcitaxel on cancer cells (Paclitaxel binding to Tubulins hetero-dimer - a- Tubulin and B-Tubulin are the basic units of Microtubule. the Paclitaxel molecule binding Tubulin and make it stagged together. The Microtubules cannot disassemble, the cell cannot divide.)
Marketed Preparation
Onxol – Teva Parentral Med. Inc., IVAX Research.
3.4 Camptotheca acuminate (Family –Nyssaceae) (Cancer tree)
Biological Source-
It consists of dried stem wood of Camptotheca acuminate (Spiridon E. Kintzios et al 2003)

Fig no.17 Camptotheca acuminate plant, and the cancers against which it is effective
Coloncancer: - Coloncancer, less formally known as bowel cancer, is a cancer characterized by neoplasia in the colon, rectum, or appendix. Coloncancer is clinically distinct from anal cancer, which affects the anus.
Cervical cancer:-Cervical cancer is malignant neoplasm of the cervix uteri or cervical area. One of the most common symptoms is abnormal vaginal bleeding, but in some cases there may be no obvious symptoms until the cancer is in its advanced stages.
Chemical constituents
Main chemical constituents (Kokate et al, 2005)of campotheca acuminata used as anti cancer agents are
- Irinotecan
- Topotecan
- Camptothecin
They are active against colorectal, ovarian, cervical and lung cancer
Irinotecan
Irinotecan is a topoisomerase 1 inhibitor, which prevents DNA from unwinding. In chemical terms, it is a semisynthetic analogue of the natural alkaloid camptothecin.
Its main use is in colon cancer, in particular, in combination with other chemotherapy agents. This includes the regimen FOLFIRI, which consists of infusional 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan.
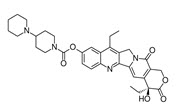
Fig. no.18- Structure of irinotecan
Mechanism of Action
Irinotecan is activated by hydrolysis to SN-38, an inhibitor of topoisomerase I. This is then inactivated by glucuronidation by uridine diphosphate glucoronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1). The inhibition of topoisomerase I by the active metabolite SN-38 eventually leads to inhibition of both DNA replication and transcription.

Fig no.19 Inhibition of topoisomeraseI by irinotecan
Topotecan
Topotecan hydrochloride is a chemotherapy agent that is a topoisomerase I inhibitor. It is the water-soluble derivative of camptothecin. It is used to treat ovarian cancer and lung cancer, as well as other cancer types.

Fig. no. 20- Structure of Topotecan
Mechanism of Action
Hycamtin or topotecan is a semi-synthetic derivative of camptothecin. Camptothecin is a natural product extracted from the bark of the tree Camptotheca acuminata. Topoisomerase-I is a nuclear enzyme that relieves torsional strain in DNA by opening single strand breaks. Once topoisomerase-I creates a single strand break, the DNA can rotate in front of the advancing replication fork. Topotecan intercalates between DNA bases. This intercalation disrupts the DNA deplication machinery when it reaches a site where topotecan is intercalated. This disruption prevents DNA replication, and ultimately leads to cell death. Mammalian cells cannot efficiently repair these double strand breaks. This process leads to breaks in the DNA strand resulting in apoptosis.

Fig. no.21-Prevention of DNA replication by Topotecan
Camptothecin
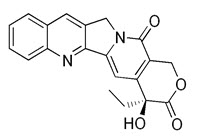
Fig no.22 Structure of Camptothecin
Mechanism of Action
In a brief description, cancer occurs due to errors in DNA and RNA replications. It is the fundamental causes of most cancers known today. If DNA does not funtion are normal rates, cells will be dividing or multiplying without limits. The human system then needs help from outside sources.
All DNA are wrapped around by topoisomerase I enzyme. Topoisomerase functions collaterally with DNA replication, by winding and unwinding chromosomes. Once entered cells, camptothecin inhibits topoisomerase I.Consequently, topoisomerase hold chromosomes tightly. It interrupts DNA replication and transcription. Proteins canot be synthesized, cell growth halts, and eventually die. Camptothecin cannot differentiate tumor and normal cells. Both cells will be killed. However, normal cells grow back.
Market preparation
- Hycamtin- Glaxo Smith Kline- IV,Capsules (Topotecan)
- Camptosar- Pfizer- IV (Irinotecan)
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE
3.5 Colchicum autumnale (Family- Liliaceae) (Autumn crocus)
Biological source-
It consists of dried ripe seeds of Colchicum autumnale Linn. (Spiridon E. Kintzios et al 2003)

Fig no.23 Colchicum autumnale plant and the cancer against which it is effective
Liver cancer: - Liver canceror hepatic cancer is properly considered to be a cancer which starts in the liver, as opposed to a cancer which originates in another organ and migrates to the liver, known as a liver metastasis.
Chemical Constituents
Colchicine present in the seed. The seed contain 0.2-1% of amino alkaloids
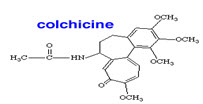
Fig no.24 Structure of Colchicine
Mechanism of Action
Colchicine inhibits microtubule polymerization by binding to tubulin, one of the main constituents of microtubules. Availability of tubulin is essential to mitosis, and therefore colchicine effectively functions as a "mitotic poison" or spindle poison. Since one of the defining characteristics of cancer cells is a significantly increased rate of mitosis, this means that cancer cells are significantly more vulnerable to colchicine poisoning than are normal cells(Bauely. C. Bruce et al 2002). The mitosis inhibiting function of colchicine has been of great use in the study of cellular genetics. To see the chromosomes of a cell under a light microscope, it is important that they be viewed near the point in the cell cycle in which they are most dense. This occurs near the middle of mitosis, so mitosis must be stopped before it completes. Adding colchicine to a culture during mitosis is part of the standard procedure for doing karyotype (8) studies.
Apart from inhibiting mitosis (a process heavily dependent on cytoskeletal changes), colchicine also inhibits neutrophil motility and activity, leading to a net anti-inflammatory effect.

Fig no.25-Mechanism action of colchicines on microtubules
Market Preparation
- Colchicine- Colcrys, this drug is basically used in treating gout; Use of this drug for cancer is still under trial.
4- Recent Developments of Phytotherapy
4.1 Papaver somniferum (raw opium) (afeem) (Family-Papaveraceae)
Biological source-
It is the dried latex obtained by the incision from the unripe capsules of Papaver somniferum, Linn (Spiridon E. Kintzios et al 2003)
Fig no.26 Papaver somniferum plant, and the cancers against which it is effective
Prostrate cancer: - Prostate canceris a form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, there are cases of aggressive prostate cancers. The cancer cells may metastasize (spread) from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly the bones and lymph nodes.

Fig no.27 Structure of noscapine
Mechanism of Action
In cancer treatment, noscapine appears to interfere with microtubule function, and thus the division of cancer cells in a way similar to the taxanes. Early studies in treatment of prostate cancer are very promising.
Studies are currently underway to assess the effectiveness of this drug in cancer and stroke treatment. Noscapine is non-addictive, widely available, has a low side-effect incidence, and is easily administered orally, thus it has great potential for use, especially in developing countries.
Market Preparation
The drugs from this plant basically used as cough suppressants, and in treating heart diseases.
· Niaspan-extended release tablets, Abott Laboratory
For treatment of cancer the drugs are still under trials.
4.2 Betula alba (Family-Betulaceae) (White Birch, Silver birch vriksh, Monoecia triandria)
Biological Source-
It consists of dried leaves and barks of Betula alba (Spiridon E. Kintzios et al 2003)

Fig no.28 Betula alba plant, and the cancers against which it is effective
Skin Cancer:-Skin neoplasmsare skin growths with differing causes and varying degrees of malignancy. The three most common malignant skin cancers are basal cell cancer, squamous cell cancer, and melanoma.
Squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant epithelial tumor which originates in epidermis, squamous mucosa or areas of squamous metaplasia (5).
Brain and CNS Tumour:- A brain tumour is an intracranial solid neoplasm, a tumor (defined as an abnormal growth of cells) within the brain or the central spinal canal.
Chemical Constituents-
The betula bark mainly consists of betullinic acid which is a naturally occurring.
Betulinic acid- Potent anti cancerous agent whose nucleus is pentacyclic triterpenoid and has anti-retroviral, anti-malarial, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a more recently discovered potential as an anticancer agent, by inhibition of topoisomerase. They are mainly active against skin cancer, brain cancer and lung cancer.
Betulinic acid

Fig no.29 Structure of Betulinic acid
Mechanism of Action
Regarding the action of betulinic acid, little is known about its antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing mechanisms.
In neuroectodermal tumour cells betulinic acid–induced apoptosis is accompanied by caspase activation, mitochondrial membrane alterations and DNA fragmentation. Caspases are produced as inactive proenzymes(6) which are proteolytically processed to their active forms.
These proteases can cooperate in proteolytic cascades, in which caspases activate themselves and each other. The initiation of the caspases cascade may lead to the activation of endonucleases like caspase-activated DNAase (7)(CAD).
After activation CAD contributes to DNA degradation. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis by direct effects on mitochondria, leading to cytochrome-c release, which in turn regulates the "downstream" caspase activation. Betulinic acid bypasses resistance to CD95 and doxorubicin-mediated apoptosis, due to different molecular mechanism of betulinic acid-induced apoptosis. The ability of betulinic acid to induce two different effects (cytotoxic and cytostatic) on two clones derived from the same human melanoma metastasis suggests that the development of clones resistant to this agent will be more unlikely, than that to conventional cytotoxic drugs. Moreover in spite of the lower potency compared with doxorubicin, betulinic acid seems to be selective for tumor cells with minimal toxicity against normal cells. The effect of betulinic acid on melanoma cell lines is stronger than its growth-inhibitory effect on primary melanocytes.
Marketed preparation-
For treatment of cancer the drugs are still under trials.
5-Conclusion
The conventional cancer therapy, viz., radiotherapy and chemotherapy are not only painful but also have lots of side effects like hair loss, constipation, muscular pain, bone pain etc. They are also extremely costly and in a poor country like India not affordable to the people under the poverty line.
The cancer drugs derived from the plants have a distinct advantage over the conventional therapy in as much that tolerance by patients and acceptance of these drugs is better. These plants are renewable sources and our only hope for sustainable supplies of cheaper medicines for the world’s growing population. The cultivation and processing of these plant based medicines is environmental friendly.
Availability of these plants is not a problem especially in developing countries like India having rich agro-climatic, cultural and ethnic biodiversity. For example, Catharanthus roseus grows in dry climate with well drained soil and podophyllum spp. requires hot and humid climate with well drained and textured soil which is available in plenty in India.
Even though the potential plants are available in plenty, most of the drugs extracted from these plants are still under trials and standardized form of the drugs is not available as yet except for a few which I have already discussed. Many of them have some toxic components which are to be removed. I fervently hope that more people will undertake research on this useful and relatively unexplored area and more firms undertake commercial production of these relatively cheap drugs for gifting us with more phytotherapic agents for cancinoma treatment.
6- References
1. Bauely. C. Bruce, Kerr J David, ,(2002),Anti Cancer Drug Development, Cell Death Pathways as Target for Anti Cancer Drugs, pg no. (56-70)
2. Spiridon E. Kintzios, Maria G. Barberaki-(2003), Plants That Fight Cancer, alkaloids& terpenes pg.no.(200-208)
3. Kokate C.K., Gokhale S.B., 2005 Chemical Constituents A Text Book of Pharmacognosy, Nirali Prakashan pg.no(9.90-9.97)
4. Shankar PS Oxford New Medical Dictionary(2001),(485,802)
5. Website references-
a. Browsed a lot of information and images in Wikipedia (for basics)
b. WHO official site - who.int/en/ accessed on 20th May 2011
c. Pharmainfo.net accessed on 20th May 2011
d. Phytotherapy Plants Used In the Treatment of Cancer - freelancecommentaries.com/phytotherapy-%E2%80%93-plants-used-in-the-treatment-of-cancer – accessed on 5th June 2011
e. NCI (National Cancer Institute)- cancer.gov - accessed on 12th June 2011
f. US FDA- fda.gov accessed on 23rd June 2011
g. For marketed preparation of drugs- drugs.com - accessed on 12th July 2011
NOW YOU CAN ALSO PUBLISH YOUR ARTICLE ONLINE.
SUBMIT YOUR ARTICLE/PROJECT AT articles@pharmatutor.org
Subscribe to Pharmatutor Alerts by Email
FIND OUT MORE ARTICLES AT OUR DATABASE









