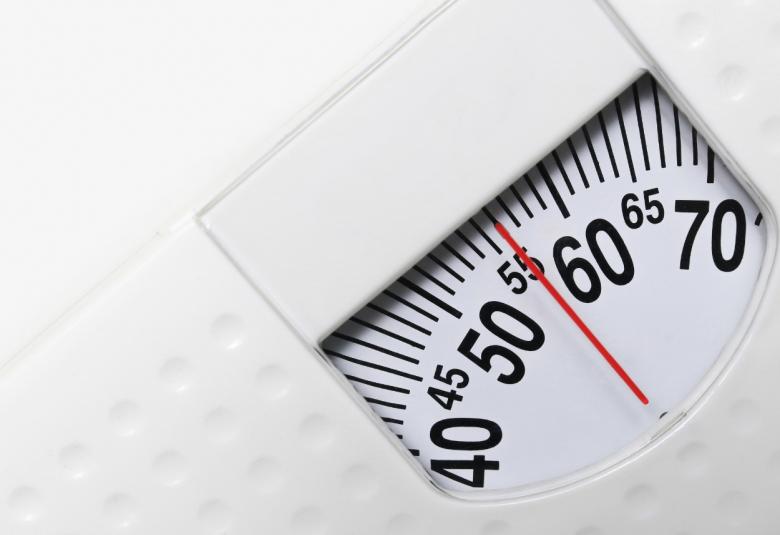
“Game changer” drug for treating obesity cuts body weight by 20%
The findings from the large-scale international trial, published in the New England Journal for Medicine, are being hailed as a “game changer” for improving the health of people with obesity and could play a major part in helping the UK to reduce the impact of diseases, such as COVID-19.




 About Author
About Author