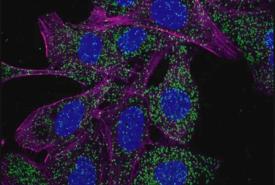
Protein found in brain linked to frontotemporal dementia
An international team of researchers including experts at the Indiana University School of Medicine has identified a protein found in the brains of people with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), discovering a new target for potential treatments for the disease.


















.png)


